基本
二叉搜索树(BST)
- 二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点。
- 二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值, 在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值。 前中后序其实就是二叉树根节点在遍历过程中的位置,固定的顺序是先左后右,只是根节点位置不一样。比如后序指根节点在最后
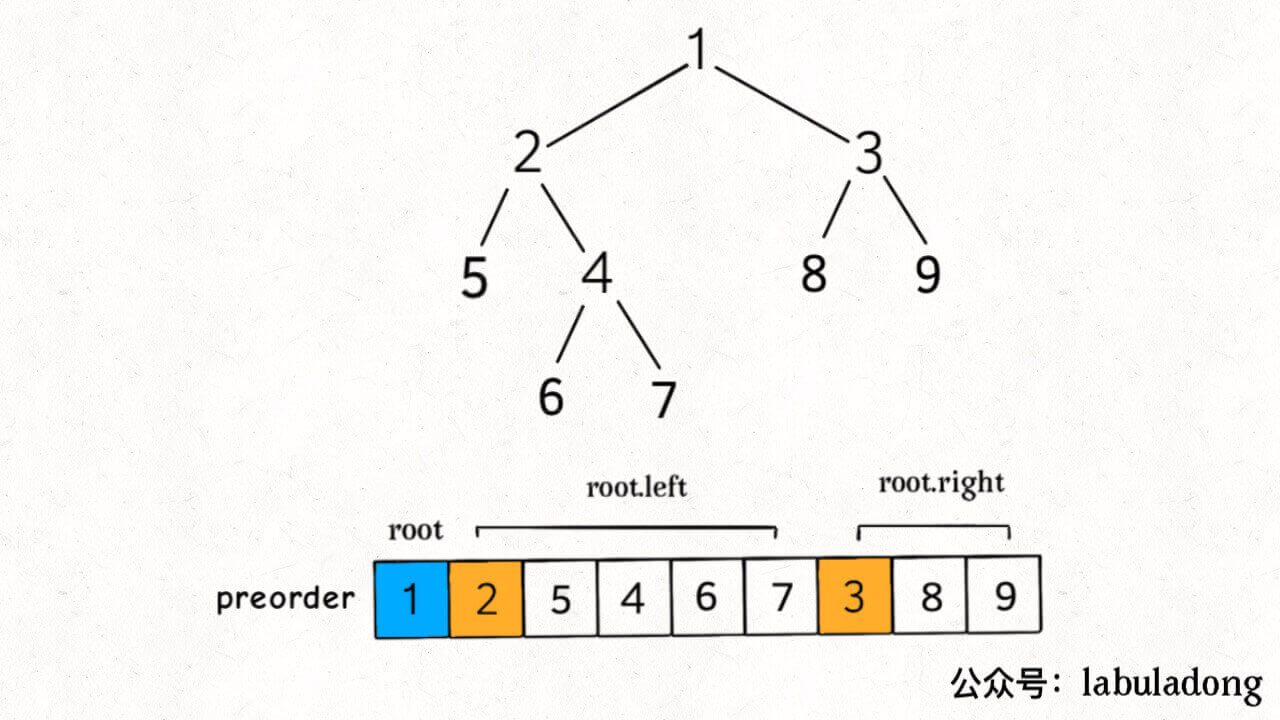
先序(前序)遍历(根节点-左子树-右子树)先访问本身,再访问左侧节点,再访问右侧节点;先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档。
中序遍历(左子树-根节点-右子树) 从小到大, 即先访问左侧节点,访问节点本身,再访问右侧节点;中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作。
后序遍历(右子树-根节点-左子树) 从大到小,即先访问右侧节点,访问节点本身,再访问左侧侧节点;后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目录及其子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小。

class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
// 插入节点
insert(key) {
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = new Node(key)
} else this.insertNode(this.root, key)
}
insertNode(node, key) {
if (key < node.key) {
if (node.left) {
this.insertNode(node.left, key)
} else node.left = new Node(key)
} else {
if (node.right) {
this.insertNode(node.right, key)
} else node.right = new Node(key)
}
}
// 中序遍历 从小到大, 即先访问左侧节点,访问节点本身,再访问右侧节点
inOrderTraverse(cb) {
if (this.root) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, cb)
}
}
inOrderTraverseNode(node, cb) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, cb)
cb(node.key)
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, cb)
}
}
// 先序遍历 先访问本身,在访问左侧节点,再访问右侧节点
preOrderTraverse(cb) {
if (this.root) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, cb)
}
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node, cb) {
if (node) {
cb(node.key)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, cb)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, cb)
}
}
// 后续遍历,从大到小,即先访问右侧节点,访问节点本身,再访问左侧侧节点
postOrderTraverse(cb) {
if (this.root) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, cb)
}
}
postOrderTraverseNode(node, cb) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, cb)
cb(node.key)
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, cb)
}
}
// 层次遍历
levelTraverse (cb) {
if (this.root) {
this.levelTraverseNode(this.root, cb)
}
}
levelTraverseNode (root, cb) {
const queue = []
queue.push(root)
while(queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift()
// result.push(node.key)
cb(node)
if(node.left) queue.push(node.left)
if(node.right) queue.push(node.right)
}
// return result
}
// 最小值节点
min() {
return this.minNode(this.root)
}
minNode(node) {
let current = node
while (current.left) {
current = current.left
}
return current
}
// 最大值节点
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root)
}
maxNode(node) {
let current = node
while (current.right) {
current = current.right
}
return current
}
// 搜索节点
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key)
}
searchNode(node, key) {
if (!node) return false
if (node.key > key) return this.searchNode(node.left, key)
else if (node.key < key) return this.searchNode(node.right, key)
else return node
}
// 移除节点
remove(key) {
this.root = this.removeNode (this.root, key)
}
removeNode (node, key) {
if (!node) return null
if (node.key > key) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key)
return node
} else if (node.key < key) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key)
return node
} else {
// 开始移除
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
node = null
} else if (node.left === null) {
node = node.right
} else if (node.right === null) {
node = node.left
} else {
// 移除左右节点都有的
/*
1、找出移除节点右侧节点的最小节点
2、改变移除节点的key
3、移除找到的那个右侧最小节点
*/
const rightMinNode = this.minNode(node.right)
node.key = rightMinNode.key
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, rightMinNode.key)
return node
}
}
}
}
const tree = new BinarySearchTree()
tree.insert(11)
tree.insert(7)
tree.insert(15)
tree.insert(5)
tree.insert(3)
tree.insert(9)
tree.insert(8)
tree.insert(10)
tree.insert(13)
tree.insert(12)
tree.insert(14)
tree.insert(20)
tree.insert(18)
tree.insert(25)
console.dir(tree.root)
tree.inOrderTraverse((key) => console.log(key))
// tree.preOrderTraverse((key) => console.log(key))
// tree.postOrderTraverse((key) => console.log(key))
// console.log(tree.min())
// console.log(tree.max())
// console.log(tree.search(3))
tree.remove(20)
console.log('-----')
// console.dir(tree.root)
console.log(tree.inOrderTraverse((key) => console.log(key)))Adelson-Velskii-Landi 树( AVL 树)及平衡二叉树
AVL树是一种自平衡树。添加或移除节点时, AVL树会尝试保持自平衡。任意一个节点(不论 深度)的左子树和右子树高度最多相差 1。添加或移除节点时, AVL树会尽可能尝试转换为完全树。
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
const BalanceFactor = {
UNBALANCED_RIGHT: 1,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT: 2,
BALANCED: 3,
SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT: 4,
UNBALANCED_LEFT: 5
};
class AVLTree extends BinarySearchTree {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(compareFn);
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.root = null;
}
getNodeHeight(node) {
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(this.getNodeHeight(node.left), this.getNodeHeight(node.right)) + 1;
}
/**
* Left left case: rotate right
*
* b a
* / \ / \
* a e -> rotationLL(b) -> c b
* / \ / \
* c d d e
*
* @param node Node<T>
*/
rotationLL(node) {
const tmp = node.left;
node.left = tmp.right;
tmp.right = node;
return tmp;
}
/**
* Right right case: rotate left
*
* a b
* / \ / \
* c b -> rotationRR(a) -> a e
* / \ / \
* d e c d
*
* @param node Node<T>
*/
rotationRR(node) {
const tmp = node.right;
node.right = tmp.left;
tmp.left = node;
return tmp;
}
/**
* Left right case: rotate left then right
* @param node Node<T>
*/
rotationLR(node) {
node.left = this.rotationRR(node.left);
return this.rotationLL(node);
}
/**
* Right left case: rotate right then left
* @param node Node<T>
*/
rotationRL(node) {
node.right = this.rotationLL(node.right);
return this.rotationRR(node);
}
getBalanceFactor(node) {
const heightDifference = this.getNodeHeight(node.left) - this.getNodeHeight(node.right);
switch (heightDifference) {
case -2:
return BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT;
case -1:
return BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT;
case 1:
return BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT;
case 2:
return BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT;
default:
return BalanceFactor.BALANCED;
}
}
insert(key) {
this.root = this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
insertNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return new Node(key);
} if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
node.left = this.insertNode(node.left, key);
} else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
node.right = this.insertNode(node.right, key);
} else {
return node; // duplicated key
}
// verify if tree is balanced
const balanceFactor = this.getBalanceFactor(node);
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.left.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
// Left left case
node = this.rotationLL(node);
} else {
// Left right case
return this.rotationLR(node);
}
}
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.right.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
// Right right case
node = this.rotationRR(node);
} else {
// Right left case
return this.rotationRL(node);
}
}
return node;
}
removeNode(node, key) {
node = super.removeNode(node, key); // {1}
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
// verify if tree is balanced
const balanceFactor = this.getBalanceFactor(node);
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
// Left left case
if (
this.getBalanceFactor(node.left) === BalanceFactor.BALANCED
|| this.getBalanceFactor(node.left) === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT
) {
return this.rotationLL(node);
}
// Left right case
if (this.getBalanceFactor(node.left) === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
return this.rotationLR(node.left);
}
}
if (balanceFactor === BalanceFactor.UNBALANCED_RIGHT) {
// Right right case
if (
this.getBalanceFactor(node.right) === BalanceFactor.BALANCED
|| this.getBalanceFactor(node.right) === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_RIGHT
) {
return this.rotationRR(node);
}
// Right left case
if (this.getBalanceFactor(node.right) === BalanceFactor.SLIGHTLY_UNBALANCED_LEFT) {
return this.rotationRL(node.right);
}
}
return node;
}
}红黑树
红黑树特点:
红黑树是一种近似平衡的二叉搜索树,它可以确保任何一个节点的左右子树的高度差小于两倍。
每个节点要么红,要么黑
根节点是黑色
每个子叶节点(NIL节点)是黑色的
不能有相邻接的两个红色节点
从任一节点到其每个子叶的所有路径都包含数量相同的黑色节点
最关键的性质是:从根到叶子的最长可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长
AVL & 红黑树比较 AVL查询更快,因为更加严格平衡
红黑树增加删除更快,因为相比AVL,红黑树需要的旋转操作更少
AVL要存储平衡因子或子树高度,所以会消耗更多空间,而红黑树每个节点只需要1位信息(红 or 黑)
所以读操作非常多写操作不多时,AVL更好;写操作较多或读写参半时红黑树更好;
比如主流语言的库函数如map等是用红黑树实现的,而数据库用AVL实现较多
二叉堆
- 它是一棵完全二叉树,表示树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点), 并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点,这叫作结构特性。
- 二叉堆不是最小堆就是最大堆。最小堆允许你快速导出树的最小值,最大堆允许你快速 导出树的最大值。所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)每个它的子 节点。这叫作堆特性。
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0
};
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
function swap(array, a, b) {
/* const temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp; */
[array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
}
export class MinHeap {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.heap = [];
}
getLeftIndex(index) {
return (2 * index) + 1;
}
getRightIndex(index) {
return (2 * index) + 2;
}
getParentIndex(index) {
if (index === 0) {
return undefined;
}
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() <= 0;
}
clear() {
this.heap = [];
}
findMinimum() {
return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.heap[0];
}
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
const index = this.heap.length;
this.heap.push(value);
this.siftUp(index);
return true;
}
return false;
}
siftDown(index) {
let element = index;
const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const right = this.getRightIndex(index);
const size = this.size();
if (
left < size
&& this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[left]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
element = left;
}
if (
right < size
&& this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[right]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
element = right;
}
if (index !== element) {
swap(this.heap, index, element);
this.siftDown(element);
}
}
siftUp(index) {
let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0
&& this.compareFn(this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
swap(this.heap, parent, index);
index = parent;
parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
}
}
extract() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removedValue = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.siftDown(0);
return removedValue;
}
heapify(array) {
if (array) {
this.heap = array;
}
const maxIndex = Math.floor(this.size() / 2) - 1;
for (let i = 0; i <= maxIndex; i++) {
this.siftDown(i);
}
return this.heap;
}
getAsArray() {
return this.heap;
}
}
export class MaxHeap extends MinHeap {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(compareFn);
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.compareFn = reverseCompare(compareFn);
}
}图Graph
「图」 的两种表⽰⽅法, 邻接表就是链表, 邻接矩阵就是⼆维数组。 邻接矩 阵判断连通性迅速, 并可以进⾏矩阵运算解决⼀些问题, 但是如果图⽐较稀 疏的话很耗费空间。 邻接表⽐较节省空间, 但是很多操作的效率上肯定⽐不 过邻接矩阵。
- 图是由边连接的节点, G=(V, E), V是一组顶点, E是一组边,连接V中的顶点
- 图的实现用邻接矩阵或邻接表或关联矩阵
- 遍历分为 广度优先搜索(breadth-first search, BFS)和深度优先搜索(depth-first search, DFS) 广度优先搜索算法和深度优先搜索算法基本上是相同的,只有一点不同,那就是待访问顶点列表的数据结构,如下表所示。
| 算 法 | 数据结构 | 描 述 |
|---|---|---|
| 深度优先搜索 | 栈 | 将顶点存入栈,顶点是沿着路径被探索的,存在新的相邻顶点就去访问 |
| 广度优先搜索 | 队列 | 将顶点存入队列,最先入队列的顶点先被探索 |
export default class Graph {
constructor(isDirected = false) {
this.isDirected = isDirected;
this.vertices = [];
this.adjList = new Map();
}
addVertex(v) {
if (!this.vertices.includes(v)) {
this.vertices.push(v);
this.adjList.set(v, []); // initialize adjacency list with array as well;
}
}
addEdge(a, b) {
if (!this.adjList.get(a)) {
this.addVertex(a);
}
if (!this.adjList.get(b)) {
this.addVertex(b);
}
this.adjList.get(a).push(b);
if (this.isDirected !== true) {
this.adjList.get(b).push(a);
}
}
getVertices() {
return this.vertices;
}
getAdjList() {
return this.adjList;
}
toString() {
let s = '';
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices.length; i++) {
s += `${this.vertices[i]} -> `;
const neighbors = this.adjList.get(this.vertices[i]);
for (let j = 0; j < neighbors.length; j++) {
s += `${neighbors[j]} `;
}
s += '\n';
}
return s;
}
}广度优先搜索BFS
- (1) 创建一个队列 Q。
- (2) 标注 v 为被发现的(灰色),并将 v 入队列 Q。
- (3) 如果 Q 非空,则运行以下步骤:
- (a) 将 u 从 Q 中出队列;
- (b) 标注 u 为被发现的(灰色);
- (c) 将 u 所有未被访问过的邻点(白色)入队列;
- (d) 标注 u 为已被探索的(黑色)。
const Colors = {
WHITE: 0,
GRAY: 1,
BLACK: 2
}
const initializeColor = vertices => {
const color = {}
vertices.forEach(v => {
color[v] = Colors.WHITE
})
return color
}
const breadthFirstSearch = (graph, startVertex, callback) => {
const vertices = graph.getVertices()
const adjList = graph.getAdjList()
const color = initializeColor(vertices)
const queue = new Queue()
queue.enqueue(startVertex)
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
const u = queue.dequeue();
const neighbors = adjList.get(u);
color[u] = Colors.GREY;
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const w = neighbors[i];
if (color[w] === Colors.WHITE) {
color[w] = Colors.GREY;
queue.enqueue(w);
}
}
color[u] = Colors.BLACK;
if (callback) {
callback(u);
}
}
}
const printVertex = (value) => console.log('Visited vertex: ' + value)
breadthFirstSearch(graph, myVertices[0], printVertex)
// 最短路径
const BFS = (graph, startVertex) => {
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
const color = initializeColor(vertices);
const queue = new Queue();
const distances = {}; // 从 v 到 u 的距离
const predecessors = {}; // 前溯点 predecessors[u],用来推导出从 v 到其他每个顶点 u 的最短路径。
queue.enqueue(startVertex);
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
distances[vertices[i]] = 0;
predecessors[vertices[i]] = null;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
const u = queue.dequeue();
const neighbors = adjList.get(u);
color[u] = Colors.GREY;
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const w = neighbors[i];
if (color[w] === Colors.WHITE) {
color[w] = Colors.GREY;
distances[w] = distances[u] + 1;
predecessors[w] = u;
queue.enqueue(w);
}
}
color[u] = Colors.BLACK;
}
return {
distances,
predecessors
};
};深度优先搜索DFS
const Colors = {
WHITE: 0,
GREY: 1,
BLACK: 2
};
const initializeColor = vertices => {
const color = {};
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
color[vertices[i]] = Colors.WHITE;
}
return color;
};
const depthFirstSearchVisit = (u, color, adjList, callback) => {
color[u] = Colors.GREY;
if (callback) {
callback(u);
}
// console.log('Discovered ' + u);
const neighbors = adjList.get(u);
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const w = neighbors[i];
if (color[w] === Colors.WHITE) {
depthFirstSearchVisit(w, color, adjList, callback);
}
}
color[u] = Colors.BLACK;
// console.log('explored ' + u);
};
export const depthFirstSearch = (graph, callback) => {
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
const color = initializeColor(vertices);
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
if (color[vertices[i]] === Colors.WHITE) {
depthFirstSearchVisit(vertices[i], color, adjList, callback);
}
}
};
const DFSVisit = (u, color, d, f, p, time, adjList) => {
// console.log('discovered ' + u);
color[u] = Colors.GREY;
d[u] = ++time.count;
const neighbors = adjList.get(u);
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const w = neighbors[i];
if (color[w] === Colors.WHITE) {
p[w] = u;
DFSVisit(w, color, d, f, p, time, adjList);
}
}
color[u] = Colors.BLACK;
f[u] = ++time.count;
// console.log('explored ' + u);
};
export const DFS = graph => {
const vertices = graph.getVertices();
const adjList = graph.getAdjList();
const color = initializeColor(vertices);
const d = {};
const f = {};
const p = {};
const time = { count: 0 };
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
f[vertices[i]] = 0;
d[vertices[i]] = 0;
p[vertices[i]] = null;
}
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
if (color[vertices[i]] === Colors.WHITE) {
DFSVisit(vertices[i], color, d, f, p, time, adjList);
}
}
return {
discovery: d,
finished: f,
predecessors: p
};
};