目录
- 核心响应式原理
- v-model
- template是如何编译成render function的
- this.$set() 与this.$del
- 数组响应式变化原理
- Vue中$nextTick源码解析
- 生命周期
- 抽象组件及函数式组件
- 插槽和作用域插槽
- computed和watch
- Vue中组件生命周期调用顺序
- 视图渲染过程
- vue Diff
- Vue中key属性的作用
- updateChildren
- vue3 diff
- 虚拟dom
- 数据改变到页面渲染的过程是怎么样的
- vue模板渲染-compile
- spa路由
- 打包懒加载
- vue-loader原理分析
- Vue CLI是如何实现的
面试题
Vue.js 技术揭秘
渲染器
Vue源码全解
核心响应式原理

vue采用数据劫持结合观察者模式的方式,通过
Object.defineProperty()来劫持各个属性的setter,getter,在数据变动时通知订阅者(watcher),触发相应的监听回调。 每个组件实例都对应一个 watcher 实例,它会在组件渲染的过程中把“接触”过的数据 property 记录为依赖。之后当依赖项的 setter 触发时,会通知 watcher,从而使它关联的组件重新渲染。 Dep 对象用于依赖收集,它实现了一个观察者模式,完成了数据 Data 和渲染视图 Watcher 的订阅
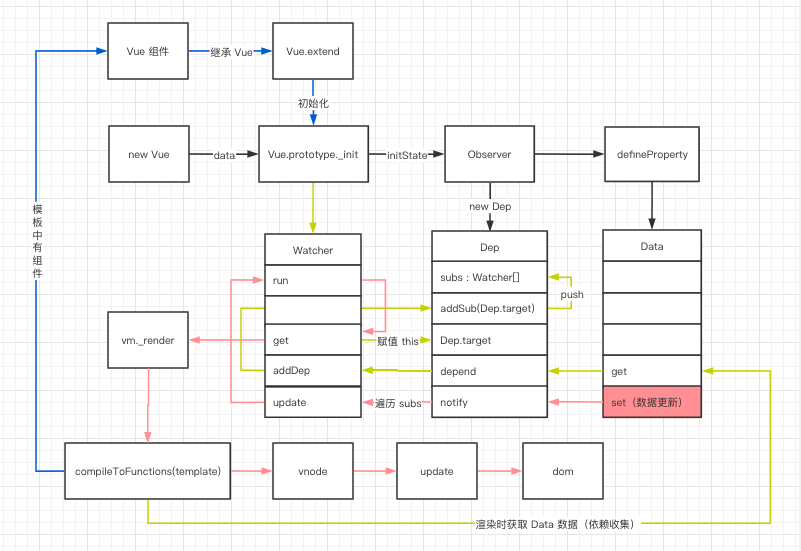

总结
- 1、在
beforeCreate和created之间调用initState(vm)方法, 获取data并遍历,调用observe方法,ob = new Observer(value)进行依赖收集和派发更新; - 2、在
Observer中调用defineReactive使用defineProperty进行get和set操作,defineReactive中var dep = new Dep();Object.defineProperty在getter时if (Dep.target)则执行dep.depend()即Dep.target.addDep(this);setter的时候dep.notify()派发更新。 - 3、在
beforeMount和mounted之间new Watcher(),watcher实例化的时候,会执行this.get()方法,把Dep.target赋值为当前渲染watcher并压入栈(为了恢复用),具体是new的时候执行this.get(),然后这个get先执行pushTarget(this);然后执行this.getter.call(vm, vm), 这个getter是new的时候赋值的updateComponent函数,里面执行了render组件的方法。 接着执行vm._render()方法,生成渲染VNode,并且在这个过程中对vm上的数据访问,这个时候就触发了数据对象的getter(执行了Dep.target.addDep(this)方法, 将watcher订阅到这个数据持有的dep的subs中,为后续数据变化时通知到拉下subs做准备)。然后递归遍历添加所有子项的getter。
data中的数据是对象或者基本类型,对比多做了一些工作,会给这个对象属性添加
__ob__的属性,即new Observer中创建了依赖收集dep,在Object.defineReactive中判断有这个 属性,则添加依赖,方便后续的$set,$deleteapi的处理
观察者模式实现自动更新:
- 创建主题对象
- 添加观察者
- 通知观察者

点击查看代码
function initState (vm) {
vm._watchers = [];
var opts = vm.$options;
if (opts.props) { initProps(vm, opts.props); }
if (opts.methods) { initMethods(vm, opts.methods); }
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm);
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */);
}
if (opts.computed) { initComputed(vm, opts.computed); }
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}
function initData (vm) {
var data = vm.$options.data;
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {};
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {};
warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
);
}
// proxy data on instance
var keys = Object.keys(data);
var props = vm.$options.props;
var methods = vm.$options.methods;
var i = keys.length;
while (i--) {
var key = keys[i];
{
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
("Method \"" + key + "\" has already been defined as a data property."),
vm
);
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
warn(
"The data property \"" + key + "\" is already declared as a prop. " +
"Use prop default value instead.",
vm
);
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
proxy(vm, "_data", key);
}
}
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */);
}
/* 依赖dep */
var uid = 0;
/**
* A dep is an observable that can have multiple
* directives subscribing to it.
*/
var Dep = function Dep () {
this.id = uid++;
this.subs = [];
};
Dep.prototype.addSub = function addSub (sub) {
this.subs.push(sub);
};
Dep.prototype.removeSub = function removeSub (sub) {
remove(this.subs, sub);
};
Dep.prototype.depend = function depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this);
}
};
Dep.prototype.notify = function notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
var subs = this.subs.slice();
if (!config.async) {
// subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async
// we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct
// order
subs.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; });
}
for (var i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update();
}
};
// The current target watcher being evaluated.
// This is globally unique because only one watcher
// can be evaluated at a time.
Dep.target = null;
var targetStack = [];
function pushTarget (target) {
targetStack.push(target);
Dep.target = target;
}
function popTarget () {
targetStack.pop();
Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1];
}
/**
* Observer class that is attached to each observed
* object. Once attached, the observer converts the target
* object's property keys into getter/setters that
* collect dependencies and dispatch updates.
*/
var Observer = function Observer (value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods);
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys);
}
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
this.walk(value);
}
};
/**
* Walk through all properties and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
Observer.prototype.walk = function walk (obj) {
var keys = Object.keys(obj);
for (var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive$$1(obj, keys[i]);
}
};
/**
* Observe a list of Array items.
*/
Observer.prototype.observeArray = function observeArray (items) {
for (var i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i]);
}
};
// helpers
/**
* Augment a target Object or Array by intercepting
* the prototype chain using __proto__
*/
function protoAugment (target, src) {
/* eslint-disable no-proto */
target.__proto__ = src;
/* eslint-enable no-proto */
}
/**
* Augment a target Object or Array by defining
* hidden properties.
*/
/* istanbul ignore next */
function copyAugment (target, src, keys) {
for (var i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) {
var key = keys[i];
def(target, key, src[key]);
}
}
/**
* Attempt to create an observer instance for a value,
* returns the new observer if successfully observed,
* or the existing observer if the value already has one.
*/
function observe (value, asRootData) {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
var ob;
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__;
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value);
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++;
}
return ob
}
/**
* Define a reactive property on an Object.
*/
function defineReactive$$1 (
obj,
key,
val,
customSetter,
shallow
) {
var dep = new Dep();
var property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
var getter = property && property.get;
var setter = property && property.set;
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key];
}
var childOb = !shallow && observe(val);
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend();
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend();
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) { return }
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
dep.notify();
}
});
}
/* */
// watcher调用
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before: function before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate');
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */);
var uid$2 = 0;
/**
* A watcher parses an expression, collects dependencies,
* and fires callback when the expression value changes.
* This is used for both the $watch() api and directives.
*/
var Watcher = function Watcher (
vm,
expOrFn,
cb,
options,
isRenderWatcher
) {
this.vm = vm;
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this;
}
vm._watchers.push(this);
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep;
this.user = !!options.user;
this.lazy = !!options.lazy;
this.sync = !!options.sync;
this.before = options.before;
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false;
}
this.cb = cb;
this.id = ++uid$2; // uid for batching
this.active = true;
this.dirty = this.lazy; // for lazy watchers
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = [];
this.depIds = new _Set();
this.newDepIds = new _Set();
this.expression = expOrFn.toString();
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn;
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop;
warn(
"Failed watching path: \"" + expOrFn + "\" " +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
);
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get();
};
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
Watcher.prototype.get = function get () {
pushTarget(this);
var value;
var vm = this.vm;
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, ("getter for watcher \"" + (this.expression) + "\""));
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value);
}
popTarget();
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value
};
/**
* Add a dependency to this directive.
*/
Watcher.prototype.addDep = function addDep (dep) {
var id = dep.id;
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id);
this.newDeps.push(dep);
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this);
}
}
};
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
*/
Watcher.prototype.cleanupDeps = function cleanupDeps () {
var i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
var dep = this.deps[i];
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this);
}
}
var tmp = this.depIds;
this.depIds = this.newDepIds;
this.newDepIds = tmp;
this.newDepIds.clear();
tmp = this.deps;
this.deps = this.newDeps;
this.newDeps = tmp;
this.newDeps.length = 0;
};
/**
* Subscriber interface.
* Will be called when a dependency changes.
*/
Watcher.prototype.update = function update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true;
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run();
} else {
queueWatcher(this);
}
};
/**
* Scheduler job interface.
* Will be called by the scheduler.
*/
Watcher.prototype.run = function run () {
if (this.active) {
var value = this.get();
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
var oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, ("callback for watcher \"" + (this.expression) + "\""));
}
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
}
}
}
};
/**
* Evaluate the value of the watcher.
* This only gets called for lazy watchers.
*/
Watcher.prototype.evaluate = function evaluate () {
this.value = this.get();
this.dirty = false;
};
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
Watcher.prototype.depend = function depend () {
var i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend();
}
};
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
*/
Watcher.prototype.teardown = function teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this);
}
var i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this);
}
this.active = false;
}
};
/**
* Push a watcher into the watcher queue.
* Jobs with duplicate IDs will be skipped unless it's
* pushed when the queue is being flushed.
*/
function queueWatcher (watcher) {
var id = watcher.id;
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true;
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher);
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
var i = queue.length - 1;
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--;
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher);
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true;
if (!config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue();
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue);
}
}
}
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow();
flushing = true;
var watcher, id;
// Sort queue before flush.
// This ensures that:
// 1. Components are updated from parent to child. (because parent is always
// created before the child)
// 2. A component's user watchers are run before its render watcher (because
// user watchers are created before the render watcher)
// 3. If a component is destroyed during a parent component's watcher run,
// its watchers can be skipped.
queue.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; });
// do not cache length because more watchers might be pushed
// as we run existing watchers
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index];
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before();
}
id = watcher.id;
has[id] = null;
watcher.run();
// in dev build, check and stop circular updates.
if (has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1;
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
'You may have an infinite update loop ' + (
watcher.user
? ("in watcher with expression \"" + (watcher.expression) + "\"")
: "in a component render function."
),
watcher.vm
);
break
}
}
}
// keep copies of post queues before resetting state
var activatedQueue = activatedChildren.slice();
var updatedQueue = queue.slice();
resetSchedulerState();
// call component updated and activated hooks
callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue);
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue);
// devtool hook
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (devtools && config.devtools) {
devtools.emit('flush');
}
}如何实现this.key 访问到vm._data.key的
initData初始化data函数中调用proxy(vm, "_data", key);
function noop (a, b, c) {}
var sharedPropertyDefinition = {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: noop,
set: noop
};
function proxy (target, sourceKey, key) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () {
return this[sourceKey][key]
};
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val;
};
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition);
}v-model
就是<input type="text" v-model="message">变成了
<input type="text" :value="message" @input="if($event.target.composing)return;message = $event.target.value">event.target.composing用于判断此次input事件是否是IME构成触发的,如果是IME构成,直接return。IME 是输入法编辑器(Input Method Editor) 的英文缩写,IME构成指我们在输入文字时,处于未确认状态的文字。
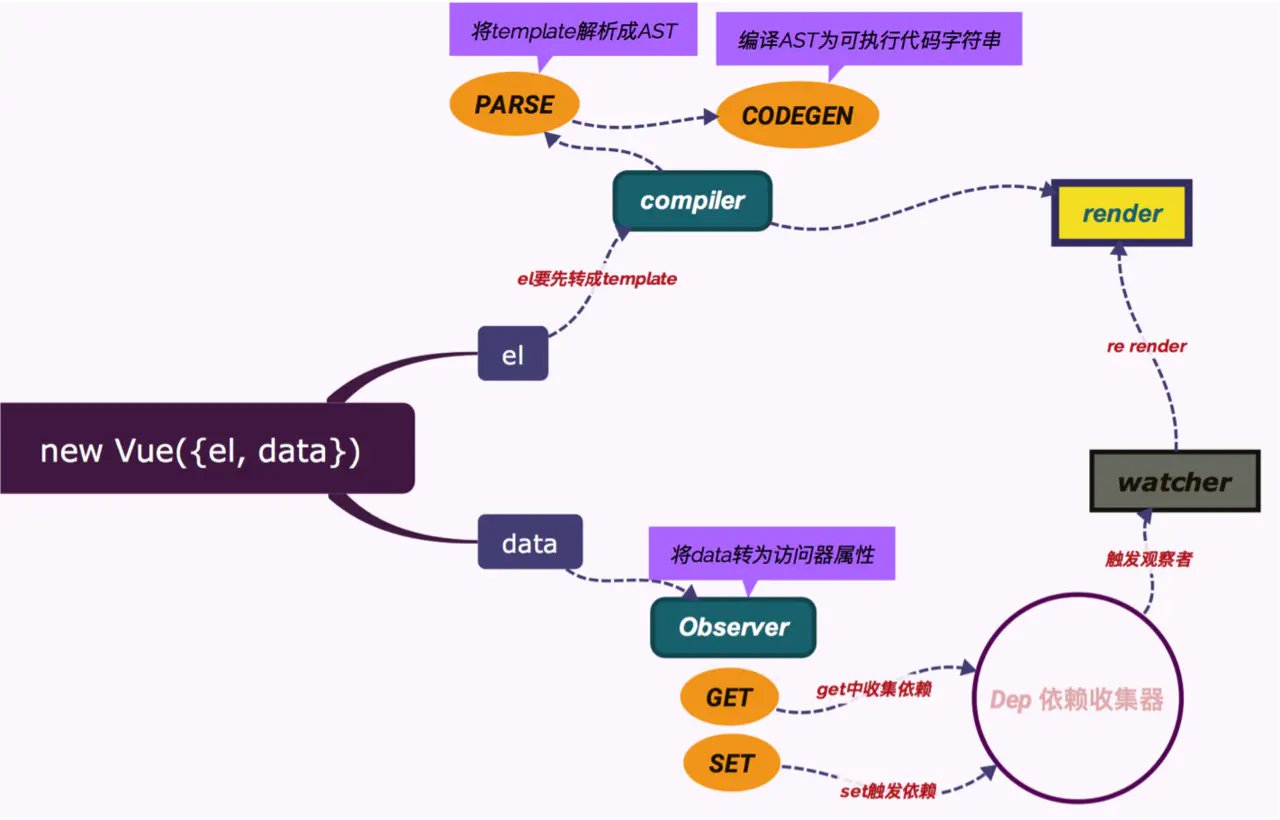
template是如何编译成render function的?
Vue提供了两个版本,一个是Runtime+Compiler版本的,一个是Runtime only版本的。Runtime+Compiler是包含编译代码的,可以把编译过程放在运行时来做。而Runtime only是不包含编译代码的,所以需要借助webpack的vue-loader来把模版编译成render函数。
编译主要有三个过程:
- 1.解析模版字符串生成AST
AST(在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree或者缩写为AST),或者语法树(syntax tree),是源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表现形式,这里特指编程语言的源代码。)
var ast = parse(template.trim(), options);parse 会用正则等方式解析 template模板中的指令、class、style等数据,形成AST树。AST是一种用Javascript对象的形式来描述整个模版,整个parse的过程就是利用正则表达式来顺序地解析模版,当解析到开始标签,闭合标签,文本的时候会分别对应执行响应的回调函数,从而达到构造AST树的目的。
举个例子:
<div :class="c" class="demo" v-if="isShow">
<span v-for="item in sz">{{item}}</span>
</div>经过一系列的正则解析,会得到的AST如下:
点击查看代码
{
/* 标签属性的map,记录了标签上属性 */
'attrsMap': {
':class': 'c',
'class': 'demo',
'v-if': 'isShow'
},
/* 解析得到的:class */
'classBinding': 'c',
/* 标签属性v-if */
'if': 'isShow',
/* v-if的条件 */
'ifConditions': [
{
'exp': 'isShow'
}
],
/* 标签属性class */
'staticClass': 'demo',
/* 标签的tag */
'tag': 'div',
/* 子标签数组 */
'children': [
{
'attrsMap': {
'v-for': "item in sz"
},
/* for循环的参数 */
'alias': "item",
/* for循环的对象 */
'for': 'sz',
/* for循环是否已经被处理的标记位 */
'forProcessed': true,
'tag': 'span',
'children': [
{
/* 表达式,_s是一个转字符串的函数 */
'expression': '_s(item)',
'text': '{{item}}'
}
]
}
]
}当构造完AST之后,下面就是优化这颗AST树。
- 2.optimize:优化AST语法树
optimize(ast, options)为什么此处会有优化过程?Vue是数据驱动,是响应式的,但是template模版中并不是所有的数据都是响应式的,也有许多数据是初始化渲染之后就不会有变化的,那么这部分数据对应的DOM也不会发生变化。后面有一个 update 更新界面的过程,在这当中会有一个 patch 的过程, diff 算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了 patch 的性能。
/**
* Goal of the optimizer: walk the generated template AST tree
* and detect sub-trees that are purely static, i.e. parts of
* the DOM that never needs to change.
*
* Once we detect these sub-trees, we can:
*
* 1. Hoist them into constants, so that we no longer need to
* create fresh nodes for them on each re-render;
* 2. Completely skip them in the patching process.
*/
function optimize (root, options) {
if (!root) { return }
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || '');
isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no;
// first pass: mark all non-static nodes.
markStatic$1(root);
// second pass: mark static roots.
markStaticRoots(root, false);
}可以看到,optimize实际上就做了2件事情,一个是调用markStatic()来标记静态节点,另一个是调用markStaticRoots()来标记静态根节点。
- 3.code generate:将优化后的AST树转换成可执行的代码(主要功能就是根据 AST 结构拼接生成 render 函数的字符串。通过
new Function生成可运行的render function)。generate就是将AST转化成render funtion字符串的过程,得到结果是render的字符串以及staticRenderFns字符串。最后render函数在执行时就会把_c和_l等替换成真正的函数,从而返回一个vnode,再继续完成patch,插入真实dom树完成渲染。
render function中有with的原因
function render () {
with (this) {
return _c('div',{on:{"click":change}},[_c('span',[_v(_s(number))]),_v(" "),_c('span', [_v(_s(name))])])
}
}vue并没有对模板中的javascript表达式进行ast语法分析,如果要移除with,就需要对javascript表达式进行ast语法分析,并且还需要一个专门的解释器对ast语法树进行解释,这样就会导致存在两个并行的解析器,这样维护成本高,还可能会有潜在的bug风险。所以呢,作者并没有想做这个事情,麻烦费力不讨好
var code = generate(ast, options);template模版经历过parse->optimize->code generate三个过程之后,就可以得到render function函数了。
Vue.js源码角度:剖析模版和数据渲染成最终的DOM的过程
点击查看代码
// `createCompilerCreator` allows creating compilers that use alternative
// parser/optimizer/codegen, e.g the SSR optimizing compiler.
// Here we just export a default compiler using the default parts.
var createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template,
options
) {
var ast = parse(template.trim(), options);
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options);
}
var code = generate(ast, options);
return {
ast: ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
});
function createCompilerCreator (baseCompile) {
return function createCompiler (baseOptions) {
function compile (
template,
options
) {
var finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions);
var errors = [];
var tips = [];
var warn = function (msg, range, tip) {
(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg);
};
if (options) {
if (options.outputSourceRange) {
// $flow-disable-line
var leadingSpaceLength = template.match(/^\s*/)[0].length;
warn = function (msg, range, tip) {
var data = { msg: msg };
if (range) {
if (range.start != null) {
data.start = range.start + leadingSpaceLength;
}
if (range.end != null) {
data.end = range.end + leadingSpaceLength;
}
}
(tip ? tips : errors).push(data);
};
}
// merge custom modules
if (options.modules) {
finalOptions.modules =
(baseOptions.modules || []).concat(options.modules);
}
// merge custom directives
if (options.directives) {
finalOptions.directives = extend(
Object.create(baseOptions.directives || null),
options.directives
);
}
// copy other options
for (var key in options) {
if (key !== 'modules' && key !== 'directives') {
finalOptions[key] = options[key];
}
}
}
finalOptions.warn = warn;
var compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions);
{
detectErrors(compiled.ast, warn);
}
compiled.errors = errors;
compiled.tips = tips;
return compiled
}
return {
compile: compile,
compileToFunctions: createCompileToFunctionFn(compile)
}
}
}this.$set() 与this.$del
- 判断是数组则调用splice方法触发响应式更新
- 对象则调用
defineReactive$$1设置getter和setter,并通过target获取初始化时的Observer及__ob__对象,调用ob.dep.notify()通知更新。
注意这个__ob__中dep怎么添加的
observe(data)方法中new Observer(value)(value及data), new的时候这里也new Dep(),这个和defineReactive$$1中建的dep不一样,执行 def(value, '__ob__', this);把__ob__定义成属性给这个对象和数组, 而这个__ob__中的dep怎么添加watcher的?在defineReactive$$1调用var childOb = !shallow && observe(val);获取ob,然后在getter中
var childOb = !shallow && observe(val);
get: function reactiveGetter () {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend();
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend(); // !!!!这里
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
}
return value
},点击查看代码
/**
* Set a property on an object. Adds the new property and
* triggers change notification if the property doesn't
* already exist.
*/
function set (target, key, val) {
if (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target)
) {
warn(("Cannot set reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: " + ((target))));
}
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key);
target.splice(key, 1, val);
return val
}
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val;
return val
}
var ob = (target).__ob__;
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
warn(
'Avoid adding reactive properties to a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'at runtime - declare it upfront in the data option.'
);
return val
}
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val;
return val
}
defineReactive$$1(ob.value, key, val);
ob.dep.notify();
return val
}
/**
* Delete a property and trigger change if necessary.
*/
function del (target, key) {
if (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target)
) {
warn(("Cannot delete reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: " + ((target))));
}
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.splice(key, 1);
return
}
var ob = (target).__ob__;
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
warn(
'Avoid deleting properties on a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'- just set it to null.'
);
return
}
if (!hasOwn(target, key)) {
return
}
delete target[key];
if (!ob) {
return
}
ob.dep.notify();
}
/**
* Define a reactive property on an Object.
*/
function defineReactive$$1 (
obj,
key,
val,
customSetter,
shallow
) {
var dep = new Dep();
var property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
var getter = property && property.get;
var setter = property && property.set;
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key];
}
var childOb = !shallow && observe(val);
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend();
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend();
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) { return }
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
dep.notify();
}
});
}数组响应式变化原理
事实上,Object.defineProperty 本身是可以监控到数组下标的变化的,只是在 Vue 的实现中,从性能 / 体验的性价比考虑,放弃了这个特性。 数组就是个对象的封装,index就是key,如果劫持了get和set,调用arr[0]和arr[0] = 1是会触发getter和setter的。但是对于新push的值,类似于object之前没有定义key,是没有劫持到的。 而且比如unshift方法,数组会依次读取并复制到下一位,所以会多次触发getter和setter
使用
Object.create复制Array的原型对象prototype得到arrayMethods, 遍历一个7个数组方法的数组,包括push,pop,shift,unshift,splice,sort,reverse这些能改变数组的方法,使用函数劫持,再遍历使用Object.defineProperty重写复制的原型对象arrayMethods对应方法的value,即重写方法,使用Array.prototype 的原函数方法apply获取并返回结果,同时通过var ob = this.__ ob__获取Observer,调用ob.dep.notify(),通知更新; 在Observe构造函数中,判断如果data的value如果是数组,1、如果该数组有__proto__属性,则直接把arrayMethods赋值给__proto__2、如果没有,则调用copyAugment,遍历arrayMethods把方法直接赋值给该数组 3、遍历该数组,递归调用observe方法new Observer进行依赖收集
点击查看代码
/**
* Define a property.
*/
function def (obj, key, val, enumerable) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
value: val,
enumerable: !!enumerable,
writable: true,
configurable: true
});
}
var arrayProto = Array.prototype;
var arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto);
var methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
];
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// cache original method
var original = arrayProto[method];
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator () {
var args = [], len = arguments.length;
while ( len-- ) args[ len ] = arguments[ len ];
var result = original.apply(this, args);
var ob = this.__ob__;
var inserted;
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args;
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2);
break
}
if (inserted) { ob.observeArray(inserted); }
// notify change
ob.dep.notify();
return result
});
});
var Observer = function Observer (value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
if (Array.isArray(value)) { // 数组的处理
if (hasProto) { // var hasProto = '__proto__' in {};
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods);
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys); // var arrayKeys = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arrayMethods);
}
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
this.walk(value);
}
};
/**
* Augment a target Object or Array by intercepting
* the prototype chain using __proto__
*/
function protoAugment (target, src) {
/* eslint-disable no-proto */
target.__proto__ = src;
/* eslint-enable no-proto */
}
/**
* Augment a target Object or Array by defining
* hidden properties.
*/
/* istanbul ignore next */
function copyAugment (target, src, keys) {
for (var i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) {
var key = keys[i];
def(target, key, src[key]);
}
}Vue中$nextTick源码解析
Vue 在更新 DOM 时是异步执行的。只要侦听到数据变化,Vue 将开启一个队列,并缓冲在同一事件循环中发生的所有数据变更。如果同一个 watcher 被多次触发,只会被推入到队列中一次。 这种在缓冲时去除重复数据对于避免不必要的计算和 DOM 操作是非常重要的。然后,在下一个的事件循环“tick”中,Vue 刷新队列并执行实际 (已去重的) 工作。 Vue 在内部对异步队列尝试使用原生的 Promise.then、MutationObserver 和 setImmediate,如果执行环境不支持,则会采用 setTimeout(fn, 0) 代替。 vue更新Dom也会把更新队列添加到nextTick中去执行
总结描述
事件循环是在执行执行完宏任务后(script是第一个宏任务),执行完所有的微任务,再执行GUI渲染,然后开启事件队列中的下一个宏任务。 当执行this.xx = 'xx' 时,背后更新Dom的回调会加到callback数组中,当执行完脚本,会执行微任务队列,这时就会遍历callback运行所有的回调函数。
nextTick中维护了一个callbacks队列,一个pending锁,一个timerFunc。
- 这个timerFunc就是根据浏览器环境判断得出的一个能够产生微任务或降级为宏任务的api调用,比如promise.then。
- callbacks队列的作用是收集当前正在执行的宏任务中所有的nextTick回调,等当前宏任务执行完之后好一次性for循环执行完。
- 试想如果没有callback队列的话,每次调用nextTick都去创建一个timerFunc微任务(假设支持),那么也就不需要pending锁了。
- 现在有了callbacks队列的情况下就只需要创建一个timerFunc微任务,那问题是什么时候创建该微任务呢? 这里就要讲到pending了,在pending为false的时候表示第一次添加cb到callbacks中,这时候创建一个timerFunc微任务,并加锁。 后面调用nextTick就只是往callbacks添加回调。 等当前宏任务之后完之后,就会去执行timerFunc清空callbacks队列,并设置pending为false,一切归零
js 引擎线程和 GUI 渲染线程是互斥的,执行 js 引擎线程运行的时候,GUI 渲染线程是被挂起的。在执行 $nextTick 的时候,DOM 树已经被更新了,只是新的 DOM 还没有给被GUI 渲染,所以可以拿到 更新后的 DOM。
点击查看代码
var isUsingMicroTask = false;
var callbacks = [];
var pending = false;
function flushCallbacks () {
pending = false;
var copies = callbacks.slice(0);
callbacks.length = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]();
}
}
// Here we have async deferring wrappers using microtasks.
// In 2.5 we used (macro) tasks (in combination with microtasks).
// However, it has subtle problems when state is changed right before repaint
// (e.g. #6813, out-in transitions).
// Also, using (macro) tasks in event handler would cause some weird behaviors
// that cannot be circumvented (e.g. #7109, #7153, #7546, #7834, #8109).
// So we now use microtasks everywhere, again.
// A major drawback of this tradeoff is that there are some scenarios
// where microtasks have too high a priority and fire in between supposedly
// sequential events (e.g. #4521, #6690, which have workarounds)
// or even between bubbling of the same event (#6566).
var timerFunc;
// The nextTick behavior leverages the microtask queue, which can be accessed
// via either native Promise.then or MutationObserver.
// MutationObserver has wider support, however it is seriously bugged in
// UIWebView in iOS >= 9.3.3 when triggered in touch event handlers. It
// completely stops working after triggering a few times... so, if native
// Promise is available, we will use it:
/* istanbul ignore next, $flow-disable-line */
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
var p = Promise.resolve();
timerFunc = function () {
p.then(flushCallbacks);
// In problematic UIWebViews, Promise.then doesn't completely break, but
// it can get stuck in a weird state where callbacks are pushed into the
// microtask queue but the queue isn't being flushed, until the browser
// needs to do some other work, e.g. handle a timer. Therefore we can
// "force" the microtask queue to be flushed by adding an empty timer.
if (isIOS) { setTimeout(noop); }
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available,
// e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4
// (#6466 MutationObserver is unreliable in IE11)
var counter = 1;
var observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks);
var textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter));
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
});
timerFunc = function () {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2;
textNode.data = String(counter);
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// Fallback to setImmediate.
// Technically it leverages the (macro) task queue,
// but it is still a better choice than setTimeout.
timerFunc = function () {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks);
};
} else {
// Fallback to setTimeout.
timerFunc = function () {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0);
};
}
function nextTick (cb, ctx) {
var _resolve;
callbacks.push(function () {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick');
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx);
}
});
if (!pending) {
pending = true;
timerFunc();
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
_resolve = resolve;
})
}
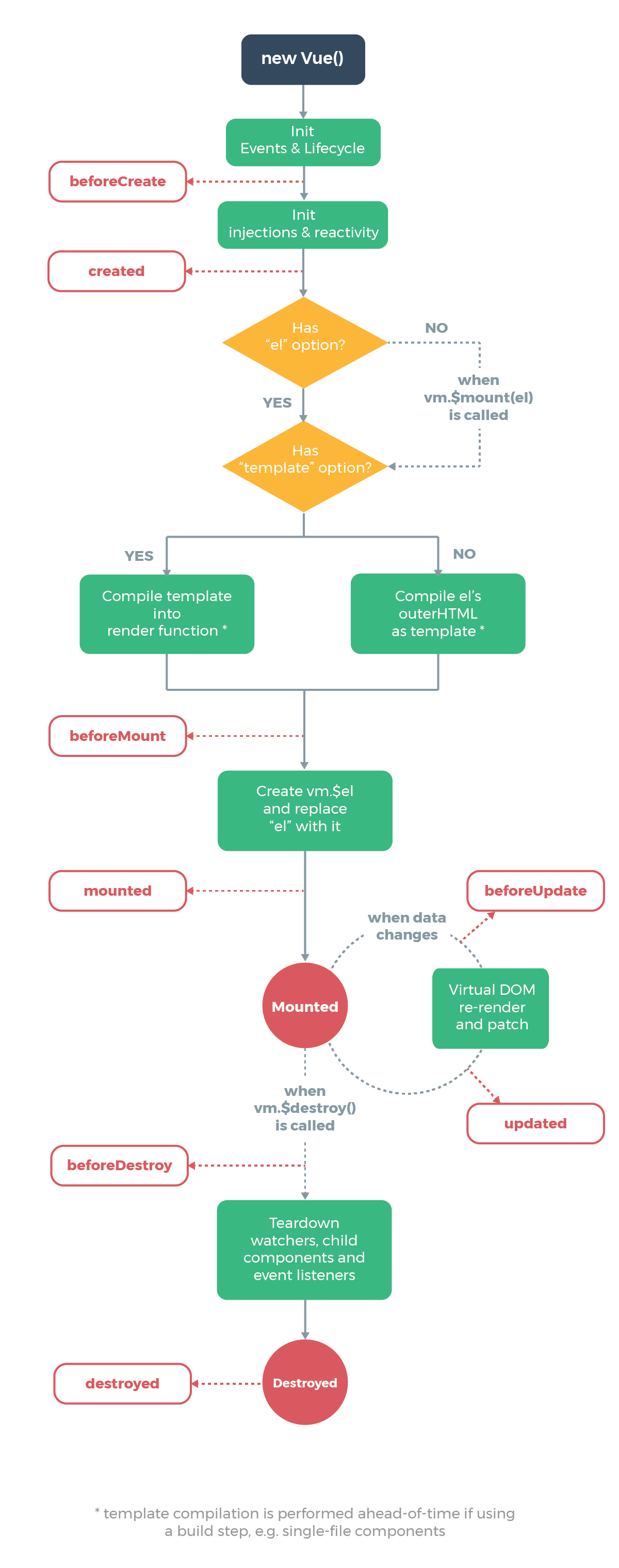
}生命周期
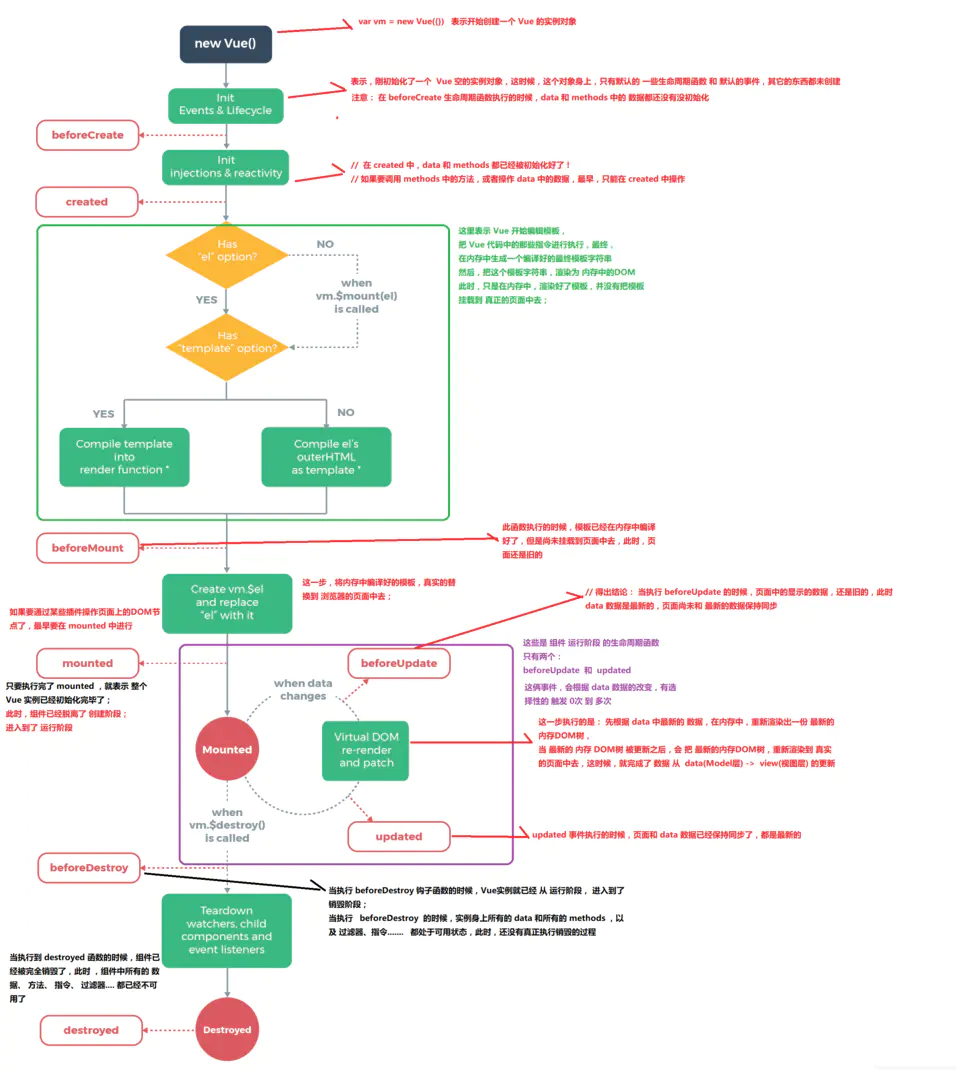
initLifecycle(vm);initEvents(vm);initRender(vm);,initLifecycle:初始化参数,找到父节点,设置子节点,$refs为空数组,初始化组件变量,_isMounted,_isDestroyed等,initEvents:初始化事件,如果 _parentListeners 存在的话,更新组件的事件监听;beforeCreate之前合并配置,初始化生命周期,初始化事件中心,初始化渲染created之前调用initInjections,initState,initProvide,初始化 data、props、computed、watcher;beforeMount(渲染dom前):判断$options中是否有挂载el,即检查是否有渲染位置。有的话执行vm.$mount(vm.$options.el),注意这个$mount()执行的是11879行的方法,先var mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;保存之前的,在最后mount.call(this, el, hydrating), 在$mount()中,会判断options是否有render,没有就开始编译模板,模板parse,optimize,generate,后得到render的字符串表达式,通过new Function生成render function接着到
mountComponent,callHook(vm, 'beforeMount');执行了
beforeMount钩子函数后,为组件new Watcher, 在new Watcher的时候,其实就是执行了updateComponent,调用了_render方法得到Vdom,_update中patch,实现了dom的渲染,即在执行完vm._update()把 VNode patch 到真实 DOM 后,执行mounted钩子。beforeUpdate: 实际上是在watcher.run()之前调用了watcher.before();触发了这个beforeUpdate,其他没做什么。数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 打补丁之前。,beforeUpdate是针对视图层,视图层的数据发生改变才会触发(废话,只有访问了数据的get才会收集依赖)在watcher.run之后调用了
callUpdatedHooks, 因为有多个组件的时候,会有很多个 watcher ,在这里,就是检查当前的得 watcher 是哪个,是当前的话,就直接执行当前 updated 钩子。beforeDestroy(卸载组件前): 在卸载前,检查是否已经被卸载,如果已经被卸载,就直接 return 出去;执行
beforeDestroy钩子destroyed前: 从父级组件那里删除自己,
vm._watcher.teardown()拆解观察者,把所有有关自己痕迹的地方,都给删除掉。
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before: function before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate');
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */);
function callUpdatedHooks (queue) {
var i = queue.length;
while (i--) {
var watcher = queue[i];
var vm = watcher.vm;
if (vm._watcher === watcher && vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'updated');
}
}
}点击查看代码
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
var vm = this;
// a uid
vm._uid = uid$3++;
var startTag, endTag;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (config.performance && mark) {
startTag = "vue-perf-start:" + (vm._uid);
endTag = "vue-perf-end:" + (vm._uid);
mark(startTag);
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true;
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options);
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
);
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
{
initProxy(vm);
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm;
initLifecycle(vm);
initEvents(vm);
initRender(vm);
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate');
initInjections(vm); // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm);
initProvide(vm); // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created');
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false);
mark(endTag);
measure(("vue " + (vm._name) + " init"), startTag, endTag);
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el);
}
};Vue事件绑定原理
原生事件绑定是通过addEventListener绑定给真实元素的,组件事件绑定是通过Vue自定义的$on实现的。
抽象组件
常用的transition和keep-alive就是一个抽象组件。抽象组件是无状态的,同样也是“不存在的”,它自己并不会被渲染为实际的DOM,而是直接返回以及操作它的子元素。
vue函数式组件functional
什么是函数式组件: 没有管理任何状态,也没有监听任何传递给它的状态,也没有生命周期方法,它只是一个接受一些 prop 的函数。简单来说是 一个无状态(没有响应式数据)和无实例的组件(没有 this 上下文)
函数式组件和普通的对象类型的组件不同,是通过createFunctionalComponent创建,它不会被看作成一个真正的组件,在 patch 过程中,如果遇到一个节点是组件 vnode,会递归执行子组件的初始化过程;而函数式组件的 render 生成的是普通的 vnode,不会有递归子组件的过程,因此渲染开销会低很多。 因此,函数式组件也不会有状态,不会有响应式数据,生命周期钩子函数这些东西。可以把它当成把普通组件模板中的一部分 DOM 剥离出来,通过函数的方式渲染出来,是一种在 DOM 层面的复用。
Vue.component('my-component', {
functional: true,
// Props 是可选的
props: {
// ...
},
// 为了弥补缺少的实例
// 提供第二个参数作为上下文
render: function(createElement, context) {
// ...
}
})或者单文件定义函数式组件(2.5版本后)
<template functional>
<button
class="btn btn-primary"
v-bind="data.attrs"
v-on="listeners">
<slot/>
</button>
</template>function createComponent (
Ctor,
data,
context,
children,
tag
) {
if (isUndef(Ctor)) {
return
}
var baseCtor = context.$options._base;
// 省略N行
// functional component
if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) { // 在此判断是否是函数式组件,如果是return 自定义render函数返回的Vnode,跳过底下初始化的流程
return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children)
}
// 省略N行
// install component management hooks onto the placeholder node
installComponentHooks(data); // 正常的组件是在此进行初始化方法(包括响应数据和钩子函数的执行)
// return a placeholder vnode
var name = Ctor.options.name || tag;
var vnode = new VNode(
("vue-component-" + (Ctor.cid) + (name ? ("-" + name) : '')),
data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context,
{ Ctor: Ctor, propsData: propsData, listeners: listeners, tag: tag, children: children },
asyncFactory
);
return vnode
}正是因为函数式组件精简了很多例如响应式和钩子函数的处理,因此渲染性能会有一定的提高,所以如果业务组件是一个纯展示且不需要有响应式数据状态的处理的,那函数式组件会是一个非常好的选择。
和正常自定义组件的区别?
- 不维护响应数据
- 无钩子函数
- 没有instance实例, 所以在组件内部没有办法像传统组件一样通过this来访问组件属性
在一些展示组件。例如, buttons, tags, cards,或者页面是静态文本,就很适合使用函数式组件。
该应用于以下场景:
- 需要通过编程实现在多种组件中选择一种。
- children、props 或者 data 在传递给子组件之前,处理它们。
插槽和作用域插槽
具名插槽: 实际上就是实现组件children内容按name分发
作用域插槽
作用:让插槽内容能够访问子组件中的数据。
使用
- 子组件
v-bind提供可访问的数据 - 在父组件中使用子组件时,插槽容器上通过slot-scope来接收 子组件中插槽抛出来的数据。自 2.6.0 起有所更新, 使用
v-slot
父级模板里的所有内容都是在父级作用域中编译的;子模板里的所有内容都是在子作用域中编译的。
slot和slot-scope在组件内部被统一整合成了 函数- 他们的渲染作用域都是 子组件
- 并且都能通过
this.$slotScopes去访问
编译过程
- 普通插槽
<!-- 场景设置 -->
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div>
<test>我是slot中的内容</test>
</div>
<!-- 子组件:test -->
<main>
我在子组件中
<slot></slot>
</main>父组件先解析,将test作为子组件处理,生成这样的节点
{
tag: 'div',
children: [{
tag: 'test',
children: ['插入slot中']
}]
}子组件解析,slot作为一个占位符,会被解析成一个函数
{
tag: 'main',
children: [
'我在子组件里面',
// 不传递插槽的名称默认就是default, 如果传了就是传入的名称
_t('default')
]
}- 作用域插槽
<!-- 场景设置 -->
<!-- 父组件 -->
<div>
<test>
<template slot-scope="slotProps">
插入slot中{{slotProps}}
</template>
</test>
</div>
<!-- 子组件:test -->
<main>
我在子组件中
<slot :child="child"></slot>
</main>
data() {
return { child: 123 }
}父组件先解析
{
tag: 'div',
children: [{
tag: 'test',
scopeSlots: {
default(slotProps) {
return ['插入slot中' + slotProps]
}
}
}]
}子组件解析,slot作为一个占位符,会被解析成一个函数
{
tag: 'main',
children: [
'我在子组件中',
// 这里的{ child: 123 }就是传递给插槽中的数据
_t('default', { child: 123 })
]
}最终会解析成
{
tag: 'main',
children: [
'我在子组件里面',
'插入slot 中 {child:123}'
]
}computed和watch
在initState时initComputed和initWatch
- 1.实例上定义
_computedWatchers对象,用于存储“计算属性Watcher”; - 2.获取计算属性的
getter,需要判断是函数声明还是对象声明; - 3.创建“计算属性Watcher”,
getter作为参数传入,它会在依赖属性更新时进行调用,并对计算属性重新取值。需要注意 Watcher 的 lazy 配置,这是实现缓存的标识; - 4.
defineComputed对计算属性进行数据劫持;
computed核心是computedGetter里的执行,获取缓存的_computedWatchers,具体如下:
function computedGetter(){
var watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) { // 初始化时这里依赖属性是先收集的computed的watcher
watcher.evaluate()
}
if (Dep.target) { // 这里其实是给依赖的属性的dep添加渲染的watcher(如果已经添加会有去重校验不再添加)
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}
}
Watcher.prototype.evaluate = function evaluate () {
this.value = this.get();
this.dirty = false;
};watcher.dirty 是实现计算属性缓存的触发点,watcher.evaluate是对计算属性重新求值,依赖属性收集“渲染Watcher”,计算属性求值后会将值存储在 value 中,get 返回计算属性的值; dirty为false返回上次的求值结果watcher.value,为true执行watcher.evaluate()重新求职。实际上是defineReactive中的get方法的dep.depend()将computed的watcher推入依赖data的dep的sub队列中,这正是依赖data的修改可以触发dirty=true的原因
计算属性更新的路径
- computed使用的响应式的值更新
- 同时通知
computed watcher和渲染 watcher更新 computed watcher把dirty设置为true- 视图渲染读取到
computed的值,由于dirty所以computed watcher重新求值
ComputedWatcher 和普通 Watcher 的区别:
- 用
lazy为true标示为它是一个计算Watcher 计算Watcher的get和set是在初始化(initComputed)时经过 defineComputed() 方法重写了的- 当它所依赖的属性发生改变时虽然也会调用ComputedWatcher.update(),但是因为它的lazy属性为true,所以只执行把dirty设置为true这一个操作,并不会像其它的Watcher一样执行queueWatcher()或者run()
- 当有用到这个ComputedWatcher的时候,例如视图渲染时调用了它时,才会触发ComputedWatcher的get,但又由于这个get在初始化时被重写了,其内部会判断dirty的值是否为true来决定是否需要执行evaluate()重新计算
- 因此才有了这么一句话:当计算属性所依赖的属性发生变化时并不会马上重新计算(只是将dirty设置为了true而已),而是要等到其它地方读取这个计算属性的时候(会触发重写的get)时才重新计算,因此它具备懒计算特性。
点击查看代码
var computedWatcherOptions = { lazy: true };
function initComputed (vm, computed) {
// $flow-disable-line
var watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null);
// computed properties are just getters during SSR
var isSSR = isServerRendering();
for (var key in computed) {
var userDef = computed[key];
var getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get;
if (getter == null) {
warn(
("Getter is missing for computed property \"" + key + "\"."),
vm
);
}
if (!isSSR) {
// create internal watcher for the computed property.
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
);
}
// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the
// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined
// at instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef);
} else {
if (key in vm.$data) {
warn(("The computed property \"" + key + "\" is already defined in data."), vm);
} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {
warn(("The computed property \"" + key + "\" is already defined as a prop."), vm);
}
}
}
}
function defineComputed (
target,
key,
userDef
) {
var shouldCache = !isServerRendering();
if (typeof userDef === 'function') {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = shouldCache
? createComputedGetter(key)
: createGetterInvoker(userDef);
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = noop;
} else {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = userDef.get
? shouldCache && userDef.cache !== false
? createComputedGetter(key)
: createGetterInvoker(userDef.get)
: noop;
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = userDef.set || noop;
}
if (sharedPropertyDefinition.set === noop) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function () {
warn(
("Computed property \"" + key + "\" was assigned to but it has no setter."),
this
);
};
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition);
}
function createComputedGetter (key) {
return function computedGetter () {
var watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key];
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) { // 开始时初始化的dirty为true,执行evaluate,及执行watcher的get,这一步相当于,依赖的data的dep收集了这个watcher
watcher.evaluate();
}
if (Dep.target) { // 收集了渲染watcher
watcher.depend();
}
return watcher.value
}
}
}
function createGetterInvoker(fn) {
return function computedGetter () {
return fn.call(this, this)
}
}
function initMethods (vm, methods) {
var props = vm.$options.props;
for (var key in methods) {
{
if (typeof methods[key] !== 'function') {
warn(
"Method \"" + key + "\" has type \"" + (typeof methods[key]) + "\" in the component definition. " +
"Did you reference the function correctly?",
vm
);
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
warn(
("Method \"" + key + "\" has already been defined as a prop."),
vm
);
}
if ((key in vm) && isReserved(key)) {
warn(
"Method \"" + key + "\" conflicts with an existing Vue instance method. " +
"Avoid defining component methods that start with _ or $."
);
}
}
vm[key] = typeof methods[key] !== 'function' ? noop : bind(methods[key], vm);
}
}
function initWatch (vm, watch) {
for (var key in watch) {
var handler = watch[key];
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
for (var i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i]);
}
} else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler);
}
}
}
function createWatcher (
vm,
expOrFn,
handler,
options
) {
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler;
handler = handler.handler;
}
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
handler = vm[handler];
}
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)
}Vue中组件生命周期调用顺序
组件的调用顺序都是先父后子,渲染完成的顺序是先子后父 组件的销毁操作是先父后子,销毁完成的顺序是先子后父
- 加载渲染过程(在父组件mounted执行子组件beforeCreate到mounted的过程) 父beforeCreate->父created->父beforeMount->子beforeCreate->子created->子beforeMount- >子mounted->父mounted
- 子组件更新过程 父beforeUpdate->子beforeUpdate->子updated->父updated
- 父组件更新过程 父 beforeUpdate -> 父 updated
- 销毁过程 父beforeDestroy->子beforeDestroy->子destroyed->父destroyed
- 路由守卫beforeRouteEnter的next回调会在组件mounted后执行
视图渲染过程
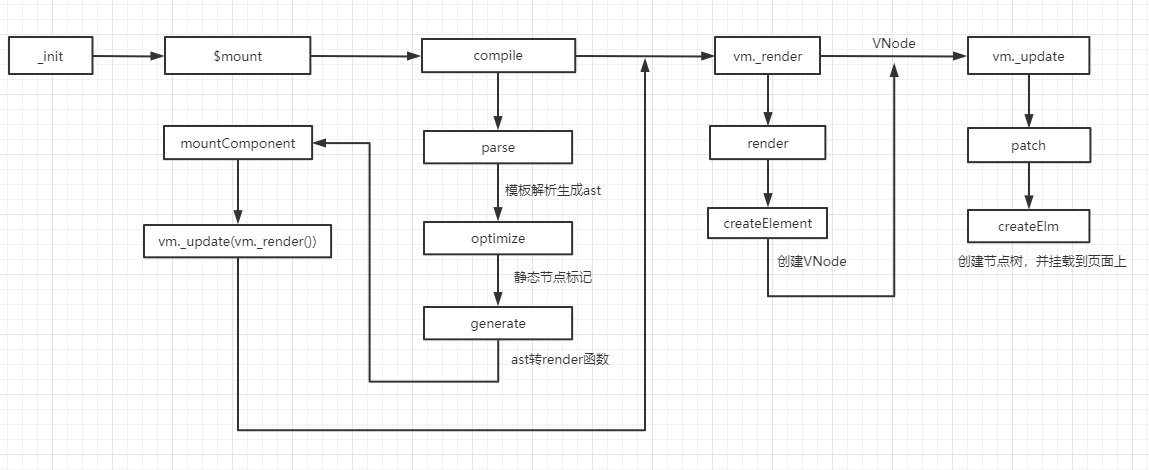
vue Diff
对比 oldVnode 和 vnode(patch)
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, parentElm) {
if (!oldVnode) {
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
} else if (!vnode) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
} else {
if (sameVnode(oldVNode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVNode, vnode);
} else {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);
addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);
}
}
}- 1、没有旧节点
没有旧节点,说明是页面刚开始初始化的时候,此时,根本不需要比较了,直接全部都是新建,所以只调用
createElm
- 2、旧节点 和 新节点 自身一样(不包括其子节点)
通过
sameVnode判断节点是否一样,旧节点 和 新节点自身一样时,直接调用patchVnode去处理这两个节点; 当两个Vnode自身一样的时候,我们需要做什么? 首先,自身一样,我们可以先简单理解,是 Vnode 的两个属性tag和key一样; 那么,我们是不知道其子节点是否一样的,所以肯定需要比较子节点; 所以,patchVnode其中的一个作用,就是比较子节点。
- 3、旧节点 和 新节点自身不一样
当两个节点不一样的时候,不难理解,直接创建新节点,删除旧节点
点击查看代码
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && (
(
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
) || (
isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) &&
a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory &&
isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error)
)
)
)
}
function sameInputType (a, b) {
if (a.tag !== 'input') { return true }
var i;
var typeA = isDef(i = a.data) && isDef(i = i.attrs) && i.type;
var typeB = isDef(i = b.data) && isDef(i = i.attrs) && i.type;
return typeA === typeB || isTextInputType(typeA) && isTextInputType(typeB)
}
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode)) { invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode); }
return
}
var isInitialPatch = false;
var insertedVnodeQueue = [];
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true;
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else {
var isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType);
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly);
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR);
hydrating = true;
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true);
return oldVnode
} else {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
'<p>, or missing <tbody>. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
);
}
}
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode);
}
// replacing existing element
var oldElm = oldVnode.elm;
var parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm);
// create new node
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
);
// update parent placeholder node element, recursively
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
var ancestor = vnode.parent;
var patchable = isPatchable(vnode);
while (ancestor) {
for (var i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor);
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm;
if (patchable) {
for (var i$1 = 0; i$1 < cbs.create.length; ++i$1) {
cbs.create[i$1](emptyNode, ancestor);
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
var insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert;
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (var i$2 = 1; i$2 < insert.fns.length; i$2++) {
insert.fns[i$2]();
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor);
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent;
}
}
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0);
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode);
}
}
}
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch);
return vnode.elm
}patchVnode(比较两个Vnode 的子节点)
总的来说,这个函数的作用是
1、Vnode 是文本节点,则更新文本(文本节点不存在子节点)
2、Vnode 有子节点,则处理比较更新子节点, 此时有3种情况。
1、新旧节点 都有子节点,而且不一样,调用
updateChildren(细节很多)2、只有新节点(不用比较,直接创建出所有新DOM,并且添加进父节点的)
3、只有旧节点(把所有的旧节点删除,也就是直接把DOM 删除)
两个节点值得比较时,会调用patchVnode函数
点击查看代码
// 逻辑提取
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return;
}
if (vnode.isStatic && oldVnode.isStatic && vnode.key === oldVnode.key) {
vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance;
return;
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
const oldCh = oldVnode.children;
const ch = vnode.children;
if (vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text);
} else {
if (oldCh && ch && (oldCh !== ch)) {
updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch);
} else if (ch) {
if (oldVnode.text) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '');
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1);
} else if (oldCh) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (oldVnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
}
}
function patchVnode (
oldVnode,
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
ownerArray,
index,
removeOnly
) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
if (isDef(vnode.elm) && isDef(ownerArray)) {
// clone reused vnode
vnode = ownerArray[index] = cloneVNode(vnode);
}
var elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true;
}
return
}
// reuse element for static trees.
// note we only do this if the vnode is cloned -
// if the new node is not cloned it means the render functions have been
// reset by the hot-reload-api and we need to do a proper re-render.
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance;
return
}
var i;
var data = vnode.data;
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode);
}
var oldCh = oldVnode.children;
var ch = vnode.children;
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) { cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode); }
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) { i(oldVnode, vnode); }
}
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
if (oldCh !== ch) { updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly); }
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
{
checkDuplicateKeys(ch);
}
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) { nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, ''); }
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1);
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '');
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text);
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) { i(oldVnode, vnode); }
}
}const el = vnode.el = oldVnode.el 这是很重要的一步,让vnode.el引用到现在的真实dom,当el修改时,vnode.el会同步变化。
节点的比较有5种情况:
额外:在当新老 VNode 节点都是 isStatic(静态的),并且 key 相同时,只要将 componentInstance 与 elm 从老 VNode 节点“拿过来”即可。这里的 isStatic 也就是前面提到过的「编译」的时候会将静态节点标记出来,这样就可以跳过比对的过程。
if (oldVnode === vnode),他们的引用一致,可以认为没有变化。
if(oldVnode.text !== null && vnode.text !== null && oldVnode.text !== vnode.text),文本节点的比较,需要修改,则会调用Node.textContent = vnode.text。
if( oldCh && ch && oldCh !== ch ), 两个节点都有子节点,而且它们不一样,这样我们会调用updateChildren函数比较子节点,这是diff的核心,见下updateChildren。
else if (ch),只有新的节点有子节点,调用createEle(vnode),vnode.el已经引用了老的dom节点,createEle函数会在老dom节点上添加子节点。
else if (oldCh),新节点没有子节点,老节点有子节点,直接删除老节点。
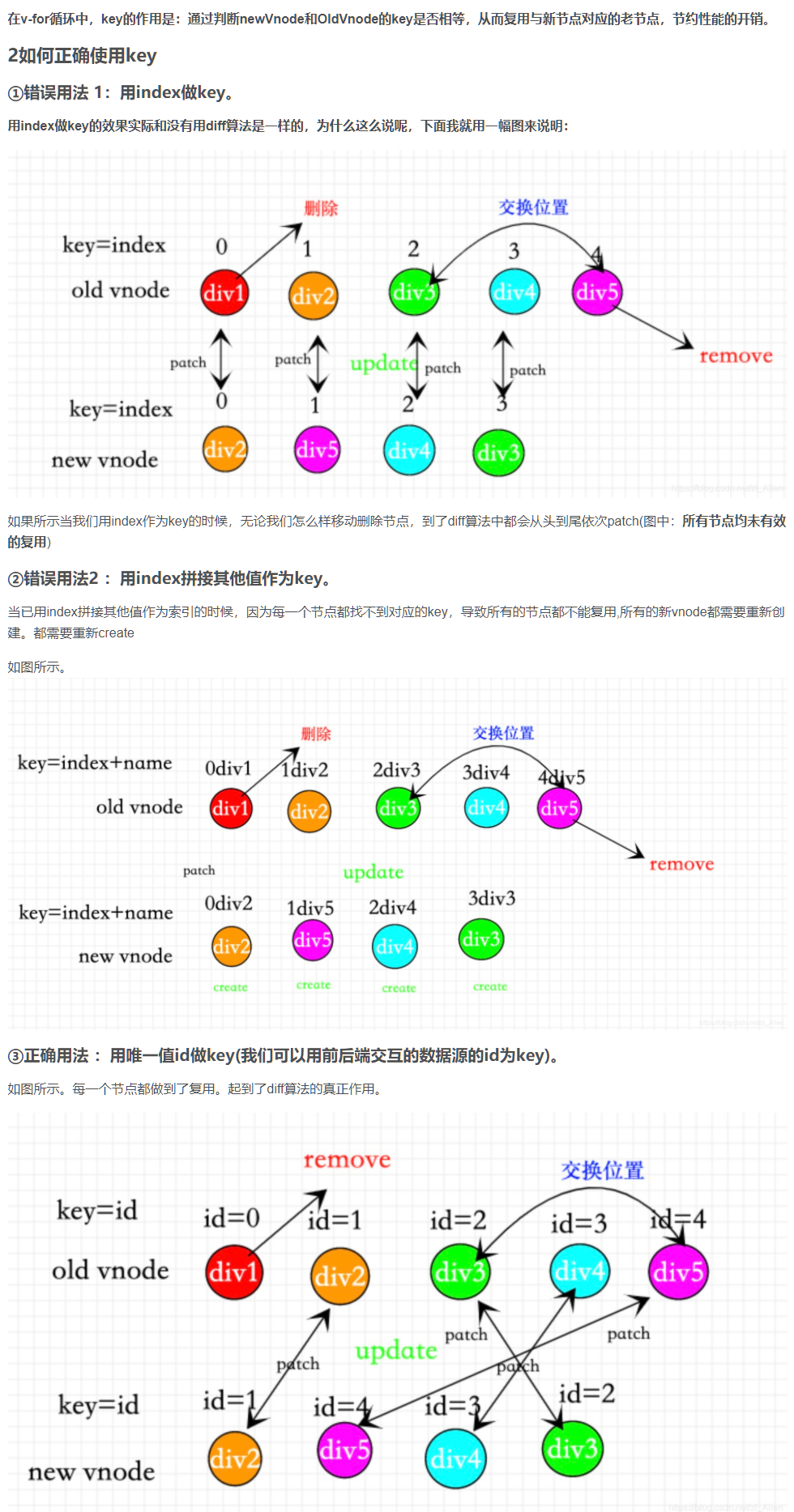
Vue中key属性的作用
当 Vue.js 用
v-for正在更新已渲染过的元素列表时,它默认用“就地复用”策略。如果数据项的顺序被改变,Vue 将不会移动 DOM 元素来匹配数据项的顺序, 而是简单复用此处每个元素,并且确保它在特定索引下显示已被渲染过的每个元素。————官方文档
用 index 做为 key
- 虽然找到了以index为key的节点复用了,在进行
patchVnode的时候, 但是props变了,vue会改变props,更新这个响应式的值,触发dep.notify,触发子组件视图的重新渲染等一套很重的逻辑。
然后,还会额外的触发以下几个钩子,假设我们的组件上定义了一些dom的属性或者类名、样式、指令,那么都会被全量的更新。
- updateAttrs
- updateClass
- updateDOMListeners
- updateDOMProps
- updateStyle
- updateDirectives
简单说就是性能损耗
- 节点删除场景:可能导致错误删除
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(value, index) in arr" :key="index">
<test :index='index'/>
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="this.handleDelete">delete</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
arr: [1, 2, 3]
};
},
methods: {
handleDelete() {
this.arr.splice(0, 1); // 删除的第一项,实际删除的最后一项, 如果props传的value,可以正确删除
}
},
components: {
test: {
props: ['index'],
template: "<li>{{Math.random()}} - {{ index }} </li>"
}
}
};
</script>updateChildren
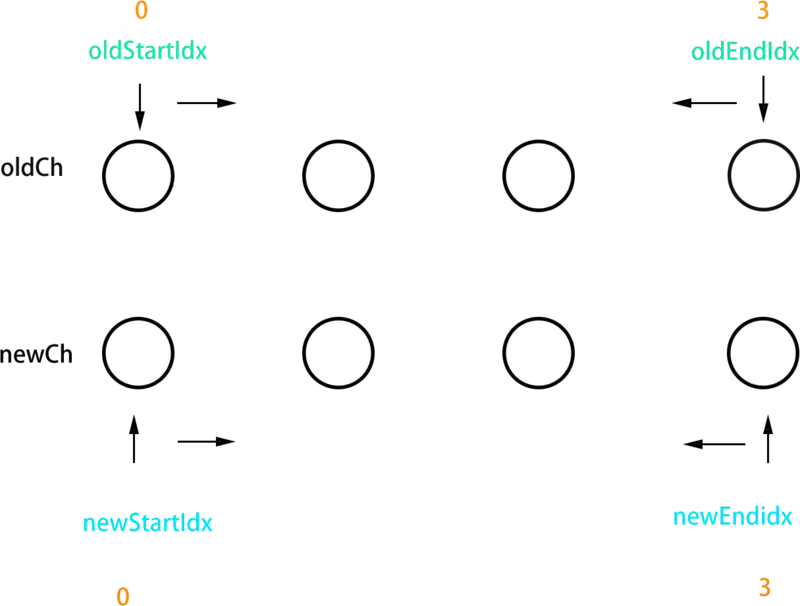
过程可以概括为:oldCh和newCh各有两个头尾的变量StartIdx和EndIdx,它们的2个变量相互比较,一共有4种比较方式。如果4种比较都没匹配,如果设置了key,就会用key进行比较,在比较的过程中,变量会往中间靠,一旦StartIdx>EndIdx表明oldCh和newCh至少有一个已经遍历完了,就会结束比较。
- 旧节点
oldStartVnode或oldEndVnode为undefined或null,则index++
- 旧节点
- 新旧开始和结束节点比较,四种情况其实是指定key的时候,判定为同一个VNode,则直接patchVnode即可,分别比较oldCh以及newCh的两头节点2*2=4种情况
- oldStartVnode === newStartVnode =》 patchVnode
- oldEndVnode === newEndVnode =》 patchVnode
- oldStartVnode === newEndVnode =》 pathVode 并且,oldStartVnode移动到右边,即把旧的开始节点插入到旧的结束节点后面。就是老
VNode节点的头部与新VNode节点的尾部是同一节点的时候,将oldStartVnode.elm这个节点直接移动到oldEndVnode.elm这个节点的后面即可。然后oldStartIdx向后移动一位,newEndIdx向前移动一位。 - oldEndVnode === newStartVnode =》 pathVode 并且,oldEndVnode移动到左边,即把旧的结束节点插入到旧的开始节点前面。就是老
VNode节点的尾部与新VNode节点的头部是同一节点的时候,将oldEndVnode.elm插入到oldStartVnode.elm前面。同样的,oldEndIdx向前移动一位,newStartIdx向后移动一位。 - 生成一个key与旧VNode的key对应的哈希表, 如果找不到key,则创建插入。如果找到了节点,同时它符合
sameVnode,则将这两个节点进行patchVnode,将该位置的老节点赋值undefined(之后如果还有新节点与该节点key相同可以检测出来提示已有重复的 key ),同时将newStartVnode.elm插入到oldStartVnode.elm的前面。同理,newStartIdx往后移动一位。
- while结束时,如果是
oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx,说明老节点已经遍历完了,新节点比老节点多,所以这时候多出来的新节点需要一个一个创建出来加入到真实DOM中。newStartIdx > newEndIdx,则说明新节点已经遍历完了,老节点多余新节点,这个时候需要将多余的老节点从真实DOM中移除
点击查看代码
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, elmToMove, refElm
// removeOnly is a special flag used only by <transition-group>
// to ensure removed elements stay in correct relative positions
// during leaving transitions
const canMove = !removeOnly
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
/*前四种情况其实是指定key的时候,判定为同一个VNode,则直接patchVnode即可,分别比较oldCh以及newCh的两头节点2*2=4种情况*/
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
/*
生成一个key与旧VNode的key对应的哈希表(只有第一次进来undefined的时候会生成,也为后面检测重复的key值做铺垫)
比如childre是这样的 [{xx: xx, key: 'key0'}, {xx: xx, key: 'key1'}, {xx: xx, key: 'key2'}] beginIdx = 0 endIdx = 2
结果生成{key0: 0, key1: 1, key2: 2}
*/
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
/*如果newStartVnode新的VNode节点存在key并且这个key在oldVnode中能找到则返回这个节点的idxInOld(即第几个节点,下标)*/
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key) ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key] : null
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element
/*newStartVnode没有key或者是该key没有在老节点中找到则创建一个新的节点*/
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm)
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
/*获取同key的老节点*/
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !elmToMove) {
/*如果elmToMove不存在说明之前已经有新节点放入过这个key的DOM中,提示可能存在重复的key,确保v-for的时候item有唯一的key值*/
warn(
'It seems there are duplicate keys that is causing an update error. ' +
'Make sure each v-for item has a unique key.'
)
}
if (sameVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode)) {
/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*/
/*如果新VNode与得到的有相同key的节点是同一个VNode则进行patchVnode*/
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
/*因为已经patchVnode进去了,所以将这个老节点赋值undefined,之后如果还有新节点与该节点key相同可以检测出来提示已有重复的key*/
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
/*当有标识位canMove实可以直接插入oldStartVnode对应的真实DOM节点前面*/
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, newStartVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
// same key but different element. treat as new element
/*当新的VNode与找到的同样key的VNode不是sameVNode的时候(比如说tag不一样或者是有不一样type的input标签),创建一个新的节点*/
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm)
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
/*全部比较完成以后,发现oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx的话,说明老节点已经遍历完了,新节点比老节点多,所以这时候多出来的新节点需要一个一个创建出来加入到真实DOM中*/
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
/*如果全部比较完成以后发现newStartIdx > newEndIdx,则说明新节点已经遍历完了,老节点多余新节点,这个时候需要将多余的老节点从真实DOM中移除*/
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}
vue3.0 diff
点击查看代码
const patchChildren: PatchChildrenFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized = false
) => {
const c1 = n1 && n1.children
const prevShapeFlag = n1 ? n1.shapeFlag : 0
const c2 = n2.children
const { patchFlag, shapeFlag } = n2
// fast path
if (patchFlag > 0) {
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.KEYED_FRAGMENT) {
// this could be either fully-keyed or mixed (some keyed some not)
// presence of patchFlag means children are guaranteed to be arrays
patchKeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
return
} else if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.UNKEYED_FRAGMENT) {
// unkeyed
patchUnkeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
return
}
}
// children has 3 possibilities: text, array or no children.
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
// text children fast path
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
unmountChildren(c1 as VNode[], parentComponent, parentSuspense)
}
if (c2 !== c1) {
hostSetElementText(container, c2 as string)
}
} else {
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
// prev children was array
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
// two arrays, cannot assume anything, do full diff
patchKeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// no new children, just unmount old
unmountChildren(c1 as VNode[], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
}
} else {
// prev children was text OR null
// new children is array OR null
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
hostSetElementText(container, '')
}
// mount new if array
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
}
}
}
const patchUnkeyedChildren = (
c1: VNode[],
c2: VNodeArrayChildren,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
c1 = c1 || EMPTY_ARR
c2 = c2 || EMPTY_ARR
const oldLength = c1.length
const newLength = c2.length
const commonLength = Math.min(oldLength, newLength)
let i
for (i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
patch(
c1[i],
nextChild,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
if (oldLength > newLength) {
// remove old
unmountChildren(
c1,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
true,
false,
commonLength
)
} else {
// mount new
mountChildren(
c2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
commonLength
)
}
}
// can be all-keyed or mixed
const patchKeyedChildren = (
c1: VNode[],
c2: VNodeArrayChildren,
container: RendererElement,
parentAnchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
let i = 0
const l2 = c2.length
let e1 = c1.length - 1 // prev ending index
let e2 = l2 - 1 // next ending index
// 1. sync from start
// (a b) c
// (a b) d e
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i]
const n2 = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
break
}
i++
}
// 2. sync from end
// a (b c)
// d e (b c)
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1]
const n2 = (c2[e2] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[e2] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[e2]))
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
break
}
e1--
e2--
}
// 3. common sequence + mount
// (a b)
// (a b) c
// i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2
// (a b)
// c (a b)
// i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0
if (i > e1) {
if (i <= e2) {
const nextPos = e2 + 1
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? (c2[nextPos] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
while (i <= e2) {
patch(
null,
(c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i])),
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
i++
}
}
}
// 4. common sequence + unmount
// (a b) c
// (a b)
// i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1
// a (b c)
// (b c)
// i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1
else if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
i++
}
}
// 5. unknown sequence
// [i ... e1 + 1]: a b [c d e] f g
// [i ... e2 + 1]: a b [e d c h] f g
// i = 2, e1 = 4, e2 = 5
else {
const s1 = i // prev starting index
const s2 = i // next starting index
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
const keyToNewIndexMap: Map<string | number | symbol, number> = new Map()
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (nextChild.key != null) {
if (__DEV__ && keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {
warn(
`Duplicate keys found during update:`,
JSON.stringify(nextChild.key),
`Make sure keys are unique.`
)
}
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}
// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer present
let j
let patched = 0
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1
let moved = false
// used to track whether any node has moved
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0
// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>
// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1
// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has
// no corresponding old node.
// used for determining longest stable subsequence
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched)
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removal
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
continue
}
let newIndex
if (prevChild.key != null) {
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
} else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
if (
newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&
isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j] as VNode)
) {
newIndex = j
break
}
}
}
if (newIndex === undefined) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
} else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex
} else {
moved = true
}
patch(
prevChild,
c2[newIndex] as VNode,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
patched++
}
}
// 5.3 move and mount
// generate longest stable subsequence only when nodes have moved
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1
// looping backwards so that we can use last patched node as anchor
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex] as VNode
const anchor =
nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? (c2[nextIndex + 1] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// mount new
patch(
null,
nextChild,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (moved) {
// move if:
// There is no stable subsequence (e.g. a reverse)
// OR current node is not among the stable sequence
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, MoveType.REORDER)
} else {
j--
}
}
}
}
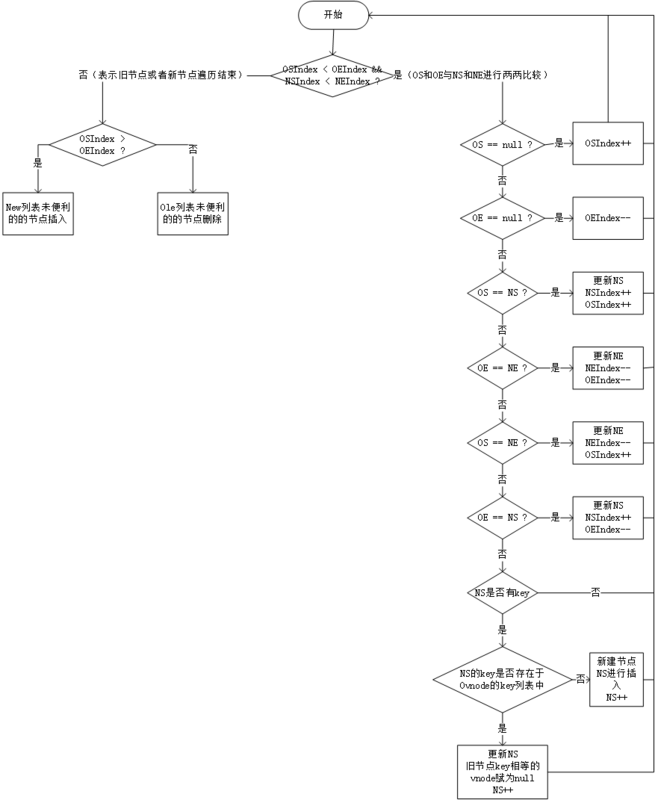
}在 Vue3 中将采用另外一种核心 Diff 算法,它借鉴于 ivi 和 inferno。
该算法其中有两个理念。第一个是相同的前置与后置元素的预处理;第二个则是最长递增子序列,此思想与React的diff类似又不尽相同。
patchChildren的过程中,存在 patchUnkeyedChildren和patchKeyedChildren
patchUnkeyedChildren
- 比较新老children的length获取最小值 然后对于公共部分,进行从新patch工作。
- 如果老节点数量大于新的节点数量 ,移除多出来的节点。
- 如果新的节点数量大于老节点的数量,从新 mountChildren新增的节点。
patchKeyedChildren
const i = 0;
const e1 = oldNodes.length - 1;
const e2 = newNodes.length - 1;- 第一步从头开始向尾diff,从头对比找到有相同的节点
patch,发现不同,立即跳出 (i++) - 第二步从尾开始往前diff,如果第一步没有
patch完,立即,从后往前开始patch,如果发现不同立即跳出循环(e1--,e2--) - 新节点mount,如果
i > e1 && i <= e2,对于剩下的节点全部以新的vnode处理(这种情况说明已经patch完相同的vnode)(i++) - 旧节点unmount,如果
i>e2 && i<=e1,对于超出的节点全部卸载(这种情况说明已经patch完相同的vnode)(i++) - 情况只剩下新老节点都还有剩余,没有patch完相同的vnode --
unknown sequence不确定序列,及有节点需要移动。- 遍历所有
新节点把索引和对应的key,存入mapkeyToNewIndexMap中,2.0是建立的老节点的mapKey - 根据之前的算出新节点还需要patch的个数,
toBePatched,声明newIndexToOldIndexMap用来存放新节点索引和老节点索引的数组。newIndexToOldIndexMap 数组的index是新vnode的索引 ,value是老vnode的索引。(新旧节点的对应关系) - 遍历老的Vnode,这一步是
unmount卸载不能复用的老节点,并且填充newIndexToOldIndexMap,接下来就是要处理新节点中新增的和复用的且要移动位置的。 - 如果
patched >= toBePatched(即新节点已经处理完了),卸载老节点 - 如果,老节点的key如果在新节点中存在 ,通过key找到对应的
index,否则则是遍历新节点,比较isSame,总之就是想复用节点,并把老节点的index放在newIndexToOldIndexMap中,通过寻找最长增长子序列来做到最小移动
- 遍历所有
核心步骤:
第一步: 通过老节点的key找到对应新节点的index:开始遍历老的节点,判断有没有key, 如果存在key通过新节点的keyToNewIndexMap找到与新节点index,如果不存在key那么会遍历剩下来的新节点试图找到对应index。
第二步:如果存在index证明有对应的老节点,那么直接复用老节点进行patch,没有找到与老节点对应的新节点,删除当前老节点。
第三步:newIndexToOldIndexMap找到对应新老节点关系。
patch了一遍,把所有的老vnode都patch了一遍。
为什么要找最长增长子序列,因为得到的newIndexToOldIndexMap数组表示的是新节点在老的节点的index,在这个数组中依次排放,所以,老节点是增序排的,就不需要移动

双端比较时的优化:
- 判断是否有节点需要移动,将需要移动的节点加入 source 数组中。
- 根据 source 数组计算出一个最长递增子序列(计算出最小的移动)。
- 移动 Dom 操作。
虚拟dom
keep-alive原理
Vue.extend
实现双向绑定Proxy比defineProperty优劣如何
为什么Vue3.0不再使用defineProperty实现数据监听?
数据改变到页面渲染的过程是怎么样的?
- 看下面的图片👇,这是执行click函数改变一个数据之后发生的函数调用栈,从图上的说明可以比较清楚个了解这个响应式过程的大概流程。下面简单讲解一下:
- 改变数据,触发这个被劫持过的数据的setter方法
- 执行这个数据的订阅中心(dep)的notify方法
- update方法里执行queueWatcher方法把watcher推入队列
- 执行nextTick方法开始更新视图
- run方法里设置dep.target为当前订阅对象
- 调用get方法调用当前watcher的getter执行更新方法
- updateComponent方法里调用了render方法开始执行渲染页面
- patch、patchVnode、updateChildren方法都是比较VNode更新渲染的函数,不过重点的diff过程在updateChildren方法里。

vue模板渲染--compile
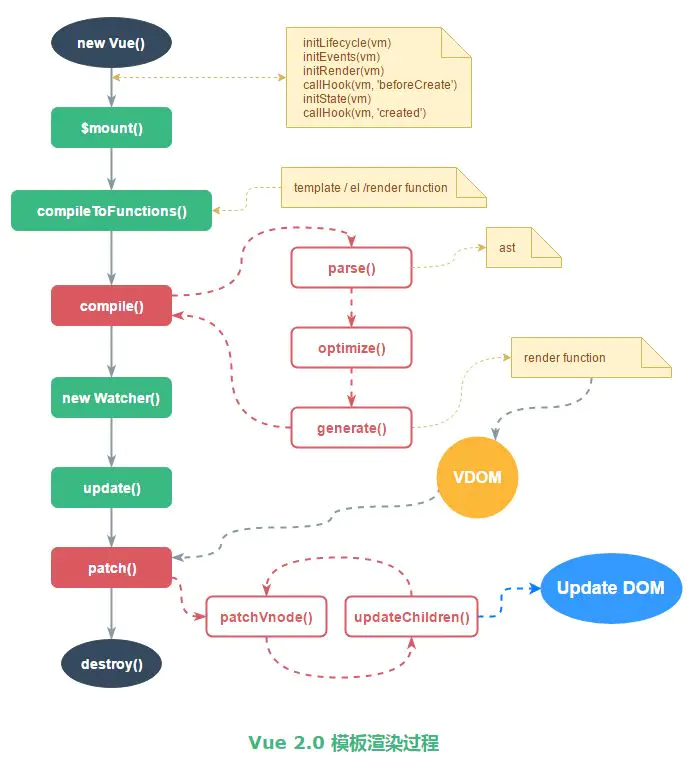
手写Vue-router核心原理
SPA 路由
hash
hash 是 URL 中 hash (#) 及后面的那部分,常用作锚点在页面内进行导航,改变 URL 中的 hash 部分不会引起页面刷新
通过 hashchange 事件监听 URL 的变化, 页面第一次加载完不会触发 hashchange,可以使用window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', ()=>{}),改变 URL 的方式只有这几种:
- 通过浏览器前进后退改变 URL;
- 通过
<a>标签改变 URL; - 通过
window.location改变URL。
DOMContentLoaded 事件在 html文档加载完毕,并且 html 所引用的内联 js、以及外链 js 的同步代码都执行完毕后触发。
当页面 DOM 结构中的 js、css、图片,以及 js 异步加载的 js、css 、图片都加载完成之后,才会触发 load 事件。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<ul>
<ul>
<!-- 定义路由 -->
<li><a href="#/home">home</a></li>
<li><a href="#/about">about</a></li>
<!-- 渲染路由对应的 UI -->
<div id="routeView"></div>
</ul>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
let routerView = routeView
window.addEventListener('hashchange', ()=>{
let hash = location.hash;
routerView.innerHTML = hash
})
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', ()=>{
if(!location.hash){//如果不存在hash值,那么重定向到#/
location.hash="/"
}else{//如果存在hash值,那就渲染对应UI
let hash = location.hash;
routerView.innerHTML = hash
}
})
</script>
</html>history
history 提供了 pushState 和 replaceState 两个方法,这两个方法改变 URL 的 path 部分不会引起页面刷新;
history 提供类似 hashchange 事件的 popstate 事件,但 popstate 事件有些不同:
- 通过浏览器前进后退改变 URL 时会触发 popstate 事件
- 通过
pushState、replaceState或<a>标签改变 URL 不会触发 popstate 事件。 - 好在可以拦截
pushState、replaceState的调用和<a>标签的点击事件来检测URL变化,通过js调用history的back,go,forward方法可触发该事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<ul>
<ul>
<li><a href='/home'>home</a></li>
<li><a href='/about'>about</a></li>
<div id="routeView"></div>
</ul>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
let routerView = routeView
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', onLoad)
window.addEventListener('popstate', ()=>{
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
})
function onLoad () {
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
var linkList = document.querySelectorAll('a[href]')
linkList.forEach(el => el.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
e.preventDefault()
history.pushState(null, '', el.getAttribute('href'))
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
}))
}
</script>
</html>打包懒加载
路由使用import导入,并声明webpackChunkName
const routes = [{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
// 将子组件加载语句封装到一个function中,将function赋给component
component: () => import( /* webpackChunkName: "home" */ '../views/Home.vue')
}
]原理
- 将需要进行懒加载的子模块打包成独立的文件(
children chunk);借助的是es6的import - 借助函数来实现延迟执行子模块的加载代码;
vue-loader原理分析
Vue CLI是如何实现的
Vue组件name属性总结
export default {
name: 'xxx',
components: {}
}- 当项目使用
keep-alive时,可搭配组件name进行缓存过滤 - 递归组件时
- vue-devtools调试工具里显示的组件名称是由vue中组件name决定的