LeetCode
目录
常用代码短
获取26个字母
const letters = []
for (let i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
letters.push(String.fromCharCode((97 + i)));
}
const bigLetters = []
for (let i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
bigLetters.push(String.fromCharCode((65 + i)));
}- 字符转ASCII码:用
charCodeAt(); - ASCII码砖字符:用
fromCharCode(); - 大写字母A 到Z 的值是从65 到90;
- 小写a到z 是从91 到 122;
'a'.charCodeAt() // 97Math对象方法
Math.floor(x): 向下取证。Math.ceil(x): 向上取证。Math.round(x): 把数四舍五入为最接近的整数。
1.和问题
两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[]}
*/
// 暴力求解
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
let s = 0, e = 0
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (s + e > 0) break
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++ ) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] === target) {
s = i, e= j
break
}
}
}
return [s, e]
};
// 利用hash表
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
const map = new Map()
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const val = target - nums[i]
if(map.has(val)) return [map.get(val), i]
else map.set(nums[i], i)
}
return []
};var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
let i = nums.length;
while(i > 1) {
let last = nums.pop();
if (nums.indexOf(target - last) > -1) {
return [nums.indexOf(target - last), nums.length]
}
i--
}
};三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
var threeSum = function(nums) {
const { length } = nums
const res = []
nums = nums.sort((a,b) => a - b)
for(let i = 0; i < length - 2; i++) {
const set = new Set()
while(nums[i] === nums[i-1]) { i++ } // 去重
const first = nums[i]
let j = i + 1
while(j < length) {
const third = nums[j]
const second = 0 - first - third
if(set.has(second)) {
res.push([first, second, third])
set.add(third)
j++
while (nums[j] === nums[j-1]) {j++} // 去重
} else {
set.add(third)
j++
}
}
}
return res
};解题思路: 先数组排序,排序完后遍历数组,以 nums[i] 作为第一个数 first ,以 nums[i+1] 作为第二个数 second ,将 nums[nums.length - 1] 作为第三个数 last ,判断三数之和是否为 0 ,
<0,则 second 往后移动一位(nums 是增序排列),继续判断>0,则 last 往前移动一位(nums 是增序排列),继续判断- ===0 ,则进入结果数组中,并且 second 往后移动一位, last 往前移动一位,继续判断下一个元组
- 直至 second >= last 结束循环,此时,
nums[i]作为第一个数的所有满足条件的元组都已写入结果数组中了,继续遍历数组,直至 i === nums.length - 2 (后面需要有 second 、 last )
时间复杂度:O(n^2), n 为数组长度
const threeSum = function(nums) {
if(!nums || nums.length < 3) return []
const result = []
// 排序
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break
// 去重
if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i-1]) continue
let second = i + 1
let last = nums.length - 1
while(second < last){
const sum = nums[i] + nums[second] + nums[last]
if(!sum){
// sum 为 0
result.push([nums[i], nums[second], nums[last]])
// 去重
while (second<last && nums[second] === nums[second+1]) second++
while (second<last && nums[last] === nums[last-1]) last--
second ++
last --
}
else if (sum < 0) second ++
else if (sum > 0) last --
}
}
return result
};// https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/345e2ed5f81d4017bbb8cc6055b0b711 数组中相加和为0的三元组
/**
*
* @param num int整型一维数组
* @return int整型二维数组
*/
function threeSum( num ) {
// write code here
const res = []
const len = num.length
num.sort((a,b) => a - b)
// console.log(num)
for(let i = 0; i < len - 2; i++){
let head = i + 1
let tail = len - 1
while(head < tail){
let sum = num[i] + num[head] + num[tail]
if(sum > 0)
tail--
else if(sum < 0)
head++
else{
res.push([num[i], num[head], num[tail]])
while(head + 1 < tail && num[head + 1] === num[head]) head++
while(tail - 1 > head && num[tail + 1] === num[tail]) tail--
head++
tail--
}
}
while(i < len - 2 && num[i+1] === num[i]) i++
}
return res
}四数之和
三数之和再套一层循环
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var fourSum = function(nums, target) {
const { length } = nums, res = []
nums = nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
for(let i = 0; i < length - 3; i++) {
if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i-1]) continue
for(let j = i + 1; j < length -2; j++) {
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] === nums[j-1]) continue
let L = j + 1, R = length - 1
while(L < R) {
const sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[L] + nums[R]
if(sum === target) {
res.push([nums[i], nums[j], nums[L], nums[R]])
while(L < R && nums[L] === nums[L+1]) L++
while(L < R && nums[R] === nums[R-1]) R--
R--
L++
}
else if(sum > target) R--
else L++
}
}
}
return res
};N数之和
请用算法实现,从给定的无需、不重复的数组A中,取出N个数,使其相加和为M。并给出算法的时间、空间复杂度,如:
var arr = [1, 4, 7, 11, 9, 8, 10, 6];
var N = 3;
var M = 27;
// Result:
Result = [7, 11, 9], [11, 10, 6], [9, 8, 10]使用二进制位运算
// 参数依次为目标数组、选取元素数目、目标和
const search = (arr, count, sum) => {
// 计算某选择情况下有几个 1,也就是选择元素的个数
const getCount = num => {
let count = 0
while(num) {
num &= (num - 1)
count++
}
return count
}
let len = arr.length, bit = 1 << len, res = []
// 遍历所有的选择情况
for(let i = 1; i < bit; i++){
// 满足选择的元素个数 === count
if(getCount(i) === count){
let s = 0, temp = []
// 每一种满足个数为 N 的选择情况下,继续判断是否满足 和为 M
for(let j = 0; j < len; j++){
// 建立映射,找出选择位上的元素
if(i & 1 << (len - 1 -j)) {
s += arr[j]
temp.push(arr[j])
}
}
// 如果这种选择情况满足和为 M
if(s === sum) {
res.push(temp)
}
}
}
return res
}2.回文
回文数
判断一个整数是否是回文数。回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
示例 1:
输入: 121
输出: true
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isPalindrome = function(x) {
if (x < 0) return false
if (x === 0) return true
return x === parseInt(String(x).split('').reverse().join(''))
};双指针
var isPalindrome = function(x) {
if(x < 0) return false
const str = String(x)
let left = 0, right = str.length -1
while(left < right) {
if(str[left] === str[right]) {
left++
right--
} else return false
}
return true
};var isPalindrome = function(x: number): boolean {
// 特殊情况:
// 如上所述,当 x < 0 时,x 不是回文数。
// 同样地,如果数字的最后一位是 0,为了使该数字为回文,
// 则其第一位数字也应该是 0
// 只有 0 满足这一属性
if (x < 0 || (x % 10 === 0 && x !== 0)) {
return false;
}
let revertedNumber: number = 0;
while (x > revertedNumber) {
revertedNumber = revertedNumber * 10 + x % 10;
x = Math.floor(x / 10);
}
// 当数字长度为奇数时,我们可以通过 revertedNumber/10 去除处于中位的数字。
// 例如,当输入为 12321 时,在 while 循环的末尾我们可以得到 x = 12,revertedNumber = 123,
// 由于处于中位的数字不影响回文(它总是与自己相等),所以我们可以简单地将其去除。
return x === revertedNumber || x === Math.floor(revertedNumber / 10);
};回文排列
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var canPermutePalindrome = function(s) {
const map = new Map()
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if(map.has(s[i])) {
map.delete(s[i])
}
else map.set(s[i], 1)
}
return map.size === 0 || map.size === 1
};回文子串个数
- 暴力求解,找出所有子串,看是否是回文
function isPalindromic(s) {
let i = 0, j = s.length - 1
while(i <= j) {
if(s[i] !== s[j]) return false
i++
j--
}
return true
}
var countSubstrings = function(s) {
let count = 0
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
for(let j = i; j < s.length; j++) {
if(isPalindromic(s.slice(i, j+1))) {
count++
}
}
}
return count
};- 中心扩展法
var countSubstrings = function(s) {
let num = 0
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
count(s, i, i) //回文串长度为奇数
count(s, i, i+1) //回文串长度为偶数
}
function count(s, start, end) {
while(start >= 0 && end < s.length && s[start] === s[end]) {
num++
start--
end++
}
}
return num
};const countSubstrings = (s) => {
const len = s.length;
let count = 0;
const dp = new Array(len);
for (let j = 0; j < len; j++) {
for (let i = 0; i <= j; i++) {
if (s[i] === s[j] && (j - i <= 1 || dp[i + 1])) {
dp[i] = true;
count++;
} else {
dp[i] = false;
}
}
}
return count;
};回文链表
- 使用快慢指针找到中间节点
- 从中间节点翻转链表
- 从头和翻转链表比较
var isPalindrome = function(head) {
let slow = head
let fast = head
while(fast && fast.next) {
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
}
let anotherHead = reverseLink(slow)
if(!anotherHead) return false
while(anotherHead) {
if(anotherHead.val === head.val) {
anotherHead = anotherHead.next
head = head.next
}
else return false
}
return true
};
function reverseLink(head) {
let prev = null
while(head) {
let next = head.next
head.next = prev
prev = head
head = next
}
return prev
}3.字符串
比较版本号
/**
* @param {string} version1
* @param {string} version2
* @return {number}
*/
var compareVersion = function(version1, version2) {
let v1 = version1.split('.')
let v2 = version2.split('.')
let judge = false
if(v2.length > v1.length) {
temp = v1
v1 = v2
v2 = temp
judge = true
}
for(let i = 0; i < v1.length; i++) {
let s1 = v1[i]
let s2 = v2[i]
s2 = s2 === undefined ? 0 : parseInt(s2) // parseInt(0001) = 1 parseInt(undefined) = NaN
s1 = parseInt(s1)
if(s1 === s2) continue
else if(s1 > s2) return judge ? -1 : 1
else return judge ? 1: -1
}
return 0
};有效的括号
使用栈
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function(s) {
const stack = []
for(let i = 0; i < s.length;i++) {
const char = s[i]
if(char === '(') stack.push(')')
else if(char === '{') stack.push('}')
else if(char === '[') stack.push(']')
else if(stack.length === 0 || stack.pop() !== char) return false
}
return stack.length === 0
};括号生成
回溯,死抓三个要点
- 选择 在这里,每次最多两个选择,选左括号,或右括号,“选择”会展开出一棵解的空间树。 用 DFS 的方式遍历这棵树,找出所有的解,这个过程叫回溯。
- 约束条件 即,什么情况下可以选左括号,什么情况下可以选右括号。 利用约束做“剪枝”,即,去掉不会产生解的选项,即,剪去不会通往合法解的分支。 比如(),现在左右括号各剩一个,再选)就成了()),这是错的选择,不能让它成为选项(不落入递归):
if (right > left) { // 右括号剩的比较多,才能选右括号
dfs(str + ')', left, right - 1);
}- 目标 构建出一个用尽 n 对括号的合法括号串。意味着,当构建的长度达到 2*n,就可以结束递归(不用继续选了)。
var generateParenthesis = function (n) {
const res = [];
const dfs = (lRemain, rRemain, str) => { // 左右括号所剩的数量,str是当前构建的字符串
if (str.length === 2 * n) { // 字符串构建完成
res.push(str); // 加入解集
return; // 结束当前递归分支
}
if (lRemain > 0) { // 只要左括号有剩,就可以选它,然后继续做选择(递归)
dfs(lRemain - 1, rRemain, str + "(");
}
if (lRemain < rRemain) { // 右括号比左括号剩的多,才能选右括号
dfs(lRemain, rRemain - 1, str + ")"); // 然后继续做选择(递归)
}
};
dfs(n, n, ""); // 递归的入口,剩余数量都是n,初始字符串是空串
return res;
};最长有效括号
hard
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses/solution/shou-hua-tu-jie-zhan-de-xiang-xi-si-lu-by-hyj8/
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {number}
*/
var longestValidParentheses = function(s) {
let maxLength = 0
const stack = []
stack.push(-1)
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
const char = s[i]
if(char === '(') {
stack.push(i)
} else {
stack.pop()
if(stack.length === 0) {
stack.push(i)
} else {
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, i - stack[stack.length - 1])
}
}
}
return maxLength
};最长回文子串
回文串就是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
中心扩展法
// https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/gao-pin-mian-shi-xi-lie/zui-chang-hui-wen-zi-chuan
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {string}
*/
var longestPalindrome = function(s) {
let res = ''
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
let s1 = palidrome(s, i, i)
let s2 = palidrome(s, i, i+1)
let temp = (s1.length > s2.length ? s1 : s2 )
res = temp.length > res.length ? temp : res
}
return res
};
function palidrome (s, l, r) {
while(l > -1 && r < s.length && s[l] === s[r]) {
l--
r++
}
return s.slice(l+1, r)
}动态规划
状态定义: dp[i,j]:字符串s从索引i到j的子串是否是回文串
- true:
s[i,j]是回文串 - false:
s[i,j]不是回文串
转移方程: dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] && s[i] == s[j]
s[i] == s[j]:说明当前中心可以继续扩张,进而有可能扩大回文串的长度- dp[i+1][j-1]:true
- 说明
s[i,j]的子串s[i+1][j-1]也是回文串 - 说明,i是从最大值开始遍历的,j是从最小值开始遍历的
- 说明
- 特殊情况
- j - i < 2:意即子串是一个长度为0或1的回文串
总结: dp[i][j] = s[i] == s[j] && ( dp[i+1][j-1] || j - i < 2)
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {string}
*/
var longestPalindrome = function(s) {
let n = s.length;
let res = '';
let dp = Array.from(new Array(n),() => new Array(n).fill(0));
for(let i = n-1;i >= 0;i--){
for(let j = i;j < n;j++){
dp[i][j] = s[i] === s[j] && (j - i < 2 || dp[i+1][j-1]);
if(dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > res.length){
res = s.substring(i,j + 1);
}
}
}
return res;
};
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/solution/5-zui-chang-hui-wen-zi-chuan-by-alexer-660/分割回文串
中等难度
回文串+回溯
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/solution/shou-hua-tu-jie-san-chong-jie-fa-hui-su-q5zjt/
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var partition = function(s) {
const res = []
function backTrack(temp, start) {
if(start === s.length) {
res.push([...temp])
return
}
for (let i = start; i < s.length; i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, start, i)) {
temp.push(s.slice(start, i + 1))
backTrack(temp, i + 1)
temp.pop()
}
}
}
backTrack([], 0)
return res
};
function isPalindrome(s, l, r) {
while(l < r) {
if(s[l] !== s[r]) {
return false
}
l++
r--
}
return true
}动态规化 + 回溯。
var partition = function(s) {
const n = s.length
if (n === 0) return []
const res = [], dp = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill(0))
for(let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 动规
for (let j = i; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = s[i] === s[j] && (j - i < 2 || dp[i+1][j-1])
}
}
function backTrack(path, start) { // 回溯
if (start === n) res.push([...path])
for(let i = start; i < n; i++) {
if (!dp[start][i]) continue
path.push(s.substring(start, i + 1))
backTrack(path, i + 1)
path.pop()
}
}
backTrack([], 0)
return res
};分割回文串2
-- hard 两次动态规划
最长不含重复字符的子字符串
滑动窗口解法,可以维护一个数组或下标

var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let str = '';
let max = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
const findIndex = str.indexOf(s[i]);
if(findIndex === -1) {
str = str + s[i];
} else {
str = str.slice(findIndex + 1) + s[i];
}
max = Math.max(max, str.length);
}
return max;
};左右指针控制滑动窗口,i相当于右指针
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
if (s.length <= 1) return s.length
let left = 0
let res = ''
for(let right = 1; right < s.length; right++) {
let newLeft = left
const char = s[right]
while(newLeft < right) {
if(s[newLeft] === char) {
left = newLeft + 1
break
}
newLeft++
}
res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1)
}
return res
};var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
if(!s) return 0
let res = 1
let left = 0
for(let i = 1; i< s.length; i++) {
let findIndex = s.slice(left, i).indexOf(s[i]) // 在left-i中找是否有重复的s[i]
if(findIndex > -1) {
left = left + findIndex + 1
}
res = Math.max(res, i - left + 1)
}
return res
};
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let map = new Map(), max = 0, left = 0
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if(map.has(s[i])) {
left = Math.max(map.get(s[i]) + 1, left)
}
max = Math.max(max, i - left + 1)
map.set(s[i], i)
}
return max
}点击查看代码
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let arr = [], max = 0
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
let index = arr.indexOf(s[i])
if(index !== -1) {
arr.splice(0, index+1);
}
arr.push(s.charAt(i))
max = Math.max(arr.length, max)
}
return max
};
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let index = 0, max = 0
for(let i = 0, j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
index = s.substring(i, j).indexOf(s[j])
if(index !== -1) {
i = i + index + 1
}
max = Math.max(max, j - i + 1)
}
return max
};
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let map = new Map(), max = 0
for(let i = 0, j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
if(map.has(s[j])) {
i = Math.max(map.get(s[j]) + 1, i)
}
max = Math.max(max, j - i + 1)
map.set(s[j], j)
}
return max
};最长公共前缀
点击查看代码
/**
* @param {string[]} strs
* @return {string}
*/
var longestCommonPrefix = function(strs) {
if (strs.length === 0) return ''
let result = strs[0]
for (let i=0;i < strs.length;i++) {
while(result) {
if ((strs[i].length >= result.length) && (strs[i].slice(0, result.length) === result)) break;
result = result.slice(0, result.length -1)
}
if (result === '') break;
}
return result
};字符串比较大小时会转换成ASCII码逐一比较。
var longestCommonPrefix = function(strs) {
if(strs.length === 0) return ''
let res = ''
let min = 0; max = 0
for(let i = 1; i < strs.length; i++) {
if(strs[i] < strs[min]) min = i
if(strs[i] > strs[max]) max = i
}
let minStr = strs[min]
while(minStr) {
if(minStr === strs[max].slice(0, minStr.length)) return minStr
else minStr = minStr.slice(0, minStr.length -1)
}
return minStr
};翻转字符串里的单词
点击查看代码
var reverseWords = function(s) {
let result = s.split(' ').filter(v => v && v.trim())
return result.reverse().join(' ')
};
var reverseWords = function(s) {
return s.trim().split(/\s+/).reverse().join(' ');
};字符串相加
点击查看代码
function solve( s , t ) {
// write code here
let i = s.length, j = t.length, res = '', temp = 0
while(i || j) {
i ? temp = temp + parseInt(s[--i]) : ''
j ? temp = temp + parseInt(t[--j]) : ''
if(temp > 9) {
res = String(temp - 10) + res
temp = 1
} else {
res = String(temp) + res
temp = 0
}
}
if(temp) res = '1' + res
return res
}
/**
* @param {string} num1
* @param {string} num2
* @return {string}
*/
var addStrings = function(num1, num2) {
let i = num1.length, j = num2.length, temp = 0, result = ''
while(i || j) {
i ? temp += +num1[--i] : ''
j ? temp += +num2[--j] : ''
result = temp % 10 + result
if (temp > 9) temp = 1
else temp = 0
}
if (temp) result = 1 + result
return result
};字符串相乘
- 0乘以任何数 = 0
- 两数相乘,乘积的长度一定 <= 两数长度之和
- 被乘数的一位 与 乘数的每一位相乘,乘积不会超过 9 x 9 = 81,不超过两位
- 每次只考虑两位,乘积 与 个位 相加
- 个位保留余数
- 十位保留取整,取整直接舍弃小数点,用0 |效率,高于parseInt
- while循环,删除多余的0
var multiply = function(num1, num2) {
if (num1 === '0' || num2 === '0') {
return '0'
}
let dp = new Array(num1.length + num2.length).fill(0)
for(let i = num1.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for(let j = num2.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
let temp = num1[i] * num2[j] + dp[i + j + 1]
if(temp > 9) {
dp[i + j] += parseInt(String(temp)[0])
dp[i + j + 1] = parseInt(String(temp)[1])
} else {
dp[i + j + 1] = temp
}
}
}
while(dp[0] === 0) {
dp.shift()
}
return dp.join('')
};点击查看代码
let multiply = function(num1, num2) {
if(num1 === '0' || num2 === '0') return "0"
// 用于保存计算结果
let res = []
// 从个位数开始逐位相乘
for(let i = 0 ; i < num1.length; i++){
// num1 尾元素
let tmp1 = +num1[num1.length-1-i]
for(let j = 0; j < num2.length; j++){
// num2尾元素
let tmp2 = +num2[num2.length-1-j]
// 判断结果集索引位置是否有值
let pos = res[i+j] ? res[i+j]+tmp1*tmp2 : tmp1*tmp2
// 赋值给当前索引位置
res[i+j] = pos%10
// 是否进位 这样简化res去除不必要的"0"
pos >=10 && (res[i+j+1]=res[i+j+1] ? res[i+j+1]+Math.floor(pos/10) : Math.floor(pos/10));
}
}
return res.reverse().join("");
}替换后的最长重复字符
/**
如: s = "AABABBA", k = 1
max 记录窗口内相同字符最多的次数
遍历字符串, 窗口往右扩张
一旦 窗口大小 大于 max + k, 则窗口左边收缩 (因为窗口内最多可替换 k个其他字符 为 出现最多的字符)
窗口扩张: left: 0, right: 0, 窗口: [ A ]ABABBA
窗口扩张: left: 0, right: 1, 窗口: [ AA ]BABBA
窗口扩张: left: 0, right: 2, 窗口: [ AAB ]ABBA
窗口扩张: left: 0, right: 3, 窗口: [ AABA ]BBA
移动左边: left: 1, right: 4, 窗口: A[ ABAB ]BA
移动左边: left: 2, right: 5, 窗口: AA[ BABB ]A
移动左边: left: 3, right: 6, 窗口: AAB[ ABBA ]
遍历完后, 只要看窗口大小即可
**/
var characterReplacement = function(s, k) {
if (!s) return 0
let max = 0
let left = 0
let right = 1
const map = new Map([[s[0], 1]])
while(right < s.length) {
const char = s[right]
if(map.has(char)) map.set(char, map.get(char) +1)
else map.set(char, 1)
max = Math.max(max, map.get(char))
if(right - left + 1 > max + k) {
map.set(s[left], map.get(s[left]) - 1)
left++
}
right++
}
return s.length - left
};
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var characterReplacement = function(s, k) {
if (!s) return 0
let codes = Array(26).fill(0) // 记录窗口内各字符出现次数
let i = 0
let max = 0
for(let j = 0; j < s.length; j++){
let n = s[j].charCodeAt() - 65
codes[n] += 1
max = Math.max(max, codes[n])
if (j - i + 1 > max + k) { // 移动左边
codes[ s[i].charCodeAt() - 65 ] -= 1
i++
}
}
return s.length - i
};
/**
作者:shetia
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-repeating-character-replacement/solution/ti-huan-hou-de-zui-chang-zhong-fu-zi-fu-a6fuv/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
**/最长公共子串
/**
* longest common substring
* @param str1 string字符串 the string
* @param str2 string字符串 the string
* @return string字符串
*/
function LCS( str1 , str2 ) {
// write code here
if(str1.length > str2.length) {
let temp = str1
str1 = str2
str2 = temp
}
let left = 0, right = 0
let res = ''
while(right < str1.length) {
right++
let str = str1.slice(left, right)
if(str2.indexOf(str) === -1) {
left++
} else {
res = str.length > res.length ? str : res
}
}
return res
}最长公共子序列
对于两个字符串求子序列的问题,都是用两个指针i和j分别在两个字符串上移动,大概率是动态规划思路。
先是自顶向下的递归解法,使用memo备忘录。
核心dp函数的递归框架:
function dp(i, j) {
dp(i + 1, j + 1); // #1
dp(i, j + 1); // #2
dp(i + 1, j); // #3
}想从dp(i, j)转移到dp(i+1, j+1),有不止一种方式,可以直接走#1,也可以走#2 -> #3,也可以走#3 -> #2。
这就是重叠子问题,如果不用memo备忘录消除子问题,那么dp(i+1, j+1)就会被多次计算,这是没有必要的。
var longestCommonSubsequence = function(text1, text2) {
const n = text1.length
const m = text2.length
const memo = Array.from(new Array(n), () => new Array(m).fill(-1))
function dp(s1, i, s2, j) {
if(i === n || j === m) return 0
// 如果之前计算过,则直接返回备忘录中的答案
if (memo[i][j] !== -1) {
return memo[i][j]
}
// 根据 s1[i] 和 s2[j] 的情况做选择
if (s1[i] === s2[j]) {
// s1[i] 和 s2[j] 必然在 lcs 中
memo[i][j] = 1 + dp(s1, i + 1, s2, j + 1)
} else {
// s1[i] 和 s2[j] 至少有一个不在 lcs 中
memo[i][j] = Math.max(
dp(s1, i + 1, s2, j),
dp(s1, i, s2, j + 1)
)
}
return memo[i][j]
}
return dp(text1, 0, text2, 0)
};/**
* @param {string} text1
* @param {string} text2
* @return {number}
*/
var longestCommonSubsequence = function(text1, text2) {
let n = text1.length;
let m = text2.length;
let dp = Array.from(new Array(n+1),() => new Array(m+1).fill(0));
for(let i = 1;i <= n;i++){
for(let j = 1;j <= m;j++){
if(text1[i-1] == text2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}else{
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[n][m];
};两个字符串的删除操作
计算将两个字符串变得相同的最少删除次数, 其实删除的结果就是他们的最长公共子序列
那么,要计算删除的次数,就可以通过最长公共子序列的长度推导出来:
var minDistance = function(word1, word2) {
const n = word1.length
const m = word2.length
const longMax = longestCommonSubsequence(word1, word2)
return m - longMax + n - longMax
};两个字符串的最小ASCII删除和
var minimumDeleteSum = function(s1, s2) {
const n = s1.length
const m = s2.length
let s1_TotalAsc = 0
let s2_TotalAsc = 0
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s1_TotalAsc += s1[i].charCodeAt()
}
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
s2_TotalAsc += s2[j].charCodeAt()
}
if(n === 0 || m === 0) {
return n === 0 ? s2_TotalAsc : s1_TotalAsc
}
let longSum = 0
const dp = Array.from(new Array(n + 1), () => new Array(m + 1).fill(0))
for(let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(let j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if(s1[i-1] === s2[j-1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + s1[i-1].charCodeAt()
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j])
}
longSum = Math.max(longSum, dp[i][j])
}
}
return s1_TotalAsc + s2_TotalAsc - 2 * longSum
};最小覆盖子串
难度:困难
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solution/js-hua-dong-chuang-kou-by-jsyt/
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string} t
* @return {string}
*/
var minWindow = function(s, t) {
let windows = {}, needs = {}, l = 0, r = 0, count = 0, start = -1, minLen = Infinity;
[...t].forEach(c => needs[c] ? needs[c]++ : needs[c] = 1)
let keyLen = Object.keys(needs).length;
while (r < s.length) {
let c1 = s[r++];
windows[c1] ? windows[c1]++ : windows[c1] = 1;
if (windows[c1] === needs[c1]) count++;
while(count === keyLen) {
if (r - l < minLen) {
start = l;
minLen = r - l;
}
let c2 = s[l++];
if (windows[c2]-- === needs[c2]) count--;
}
}
return start === -1 ? "" : s.substr(start, minLen)
};字符串的排列
回溯算法
/**
* @param {string} str
* @return {string[]}
*/
var permutation = function(str) {
const length = str.length
const res = new Set()
const set = new Set()
function backTrack(path) {
if(path.length === length) res.add(path)
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if(set.has(i)) continue
set.add(i)
backTrack(path + str[i])
set.delete(i)
}
}
backTrack('')
return Array.from(res)
};4.二叉树
做二叉树的问题,关键是把题目的要求细化,搞清楚根节点应该做什么,然后剩下的事情抛给前/中/后序的遍历框架就行了。比如对于一般的构造二叉树的题目,是要想怎么构造出根节点。所以应该是前序遍历。
/* 二叉树遍历框架 */
function traverse(root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left)
// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right)
// 后序遍历
}中序遍历的非递归实现
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/solution/shou-hua-tu-jie-zhong-xu-bian-li-fan-xiang-de-by-x/
const inorderTraversal = (root) => {
const res = [];
const stack = [];
while (root) { // 能压入栈的左子节点都压进来
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
while (stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop(); // 栈顶的节点出栈
res.push(node.val); // 在压入右子树之前,处理它的数值部分(因为中序遍历)
node = node.right; // 获取它的右子树
while (node) { // 右子树存在,执行while循环
stack.push(node); // 压入当前root
node = node.left; // 不断压入左子节点
}
}
return res;
};路径总和
递归: 深度优先遍历
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false
if(root.left === null && root.right === null && root.val === targetSum) return true
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
};广度优先遍历: 父节点的值是targetSum - root.val
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false
let stack = [root]
root.val = targetSum - root.val
while(stack.length) {
const nextNodes = []
for(let i = 0; i < stack.length; i++) {
let node = stack[i]
if(node.left === null && node.right === null && node.val === 0) {
return true
}
if(node.left) {
node.left.val = node.val - node.left.val
nextNodes.push(node.left)
}
if(node.right) {
node.right.val = node.val - node.right.val
nextNodes.push(node.right)
}
}
stack = nextNodes
}
return false
};二叉树的层序遍历
bfs
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(root == null) return []
let queue = [root]
const res = []
while(queue.length) {
const nodesLevels = []
const newQueue = []
queue.forEach(node => {
nodesLevels.push(node.val)
if (node.left) newQueue.push(node.left)
if (node.right) newQueue.push(node.right)
})
res.push(nodesLevels)
queue = newQueue
}
return res
};dfs
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(root == null) return []
const res = []
const dfs = (node, step) => {
if(node === null) return
if(!res[step]) res[step] = []
res[step].push(node.val)
dfs(node.left, step + 1)
dfs(node.right, step + 1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return res
};二叉树的序列化与反序列化
前序遍历法,后续遍历法差不多一样,而中序遍历的方式行不通,因为无法实现反序列化方法deserialize。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {string}
*/
const splitStr = ','
const nullStr = '#'
var serialize = function(root) {
let res = ''
function help(node) {
if(node === null) {
res = res + nullStr + splitStr
return
}
res = res + node.val + splitStr
help(node.left)
help(node.right)
}
help(root)
return res.slice(0, res.length - 1) // 末尾多一个,
};
/**
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*
* @param {string} data
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var deserialize = function(data) {
const nodes = data.split(splitStr)
function help(nodes) {
if (nodes.length === 0) return null
const node = nodes.shift()
if (node === nullStr) return null
const root = new TreeNode(parseInt(node))
root.left = help(nodes)
root.right = help(nodes)
return root
}
return help(nodes)
};
/**
* Your functions will be called as such:
* deserialize(serialize(root));
*/验证二叉树的前序序列化
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/verify-preorder-serialization-of-a-binary-tree/solution/pai-an-jiao-jue-de-liang-chong-jie-fa-zh-66nt/
/**
* @param {string} preorder
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidSerialization = function(preorder) {
const nodes = preorder.split(',')
const stack = []
for(let i = 0; i < nodes.length;i++) {
stack.push(nodes[i])
while(stack.length > 2 && stack[stack.length - 1] === '#' && stack[stack.length - 2] === '#' && stack[stack.length - 3] !== '#') {
stack.pop()
stack.pop()
stack.pop()
stack.push('#')
}
}
return stack.length === 1 && stack.pop() === '#'
};从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
先构造根节点,接着思考如何构造左右节点,而构造左右节点也是构造根节点。剩下的就是分割数组
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if (preorder.length === 0) return null
const root = new TreeNode(preorder[0])
const inorderRootIndex = inorder.findIndex(v => v === preorder[0])
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1,inorderRootIndex + 1), inorder.slice(0, inorderRootIndex))
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(inorderRootIndex+1), inorder.slice(inorderRootIndex+1))
return root
};从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
/**
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @param {number[]} postorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
if(inorder.length === 0) return null
const rootValue = postorder[postorder.length -1]
const root = new TreeNode(rootValue)
const inorderFindIndex = inorder.findIndex(v => v === rootValue) // 1
root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, inorderFindIndex), postorder.slice(0, inorderFindIndex))
root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(inorderFindIndex+1), postorder.slice(inorderFindIndex, postorder.length -1))
return root
};对称二叉树
递归
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
function check(left, right) {
if(left === null && right === null) return true
else if(left && right) {
return left.val === right.val && check(left.left, right.right) && check(left.right, right.left)
} else return false
}
if(root === null) return true
return check(root.left, root.right)
};迭代
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if (!root) return true;
let stack = [];
stack.push(root.left, root.right);
while (stack.length) {
const right = stack.pop();
const left = stack.pop();
if (left === null && right === null) {
// 节点为空什么都不做
} else if (left && right && left.val === right.val) {
//左左节点和对称右右节点入栈
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
//左右节点和对称右左节点入栈
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};翻转二叉树
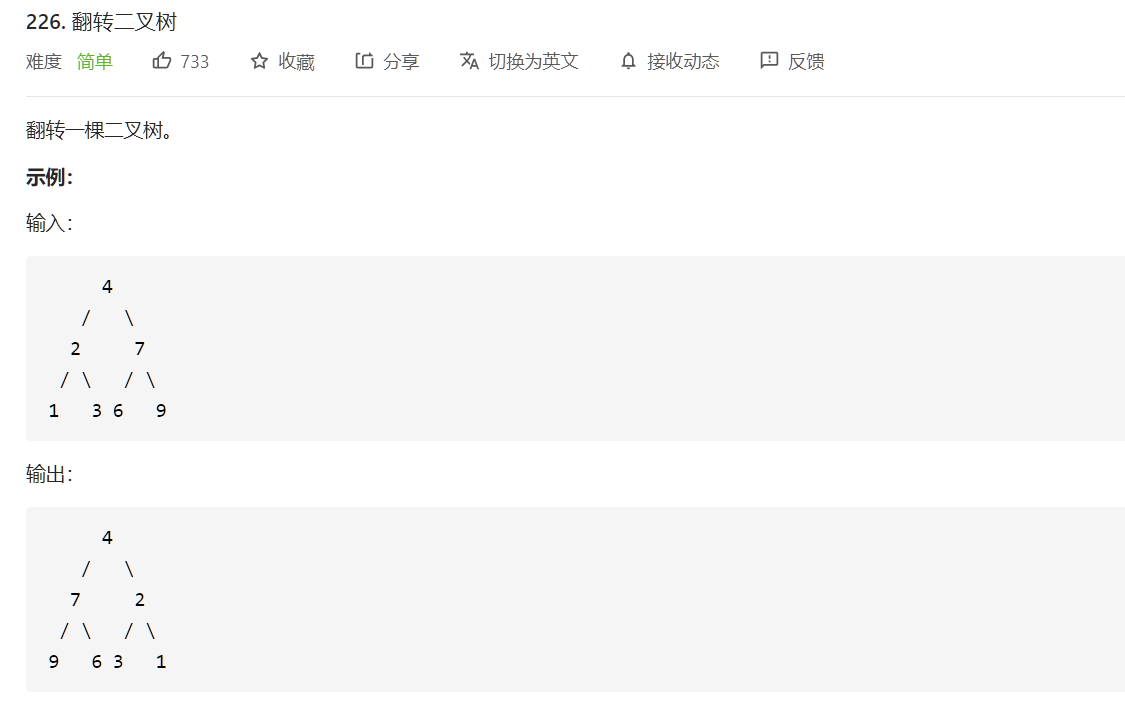
var invertTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
let temp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = temp
invertTree(root.right)
invertTree(root.left)
return root
};填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
var connect = function(root) {
if(root === null) return null
connectTowNode(root.left, root.right)
return root
};
function connectTowNode(left, right) {
if (left === null || right === null) {
return
}
left.next = right
connectTowNode(left.left,left.right)
connectTowNode(right.left,right.right)
connectTowNode(left.right, right.left)
}二叉树展开为链表

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var flatten = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
flatten(root.left)
flatten(root.right)
let left = root.left, right = root.right
root.right = left
root.left = null
let node = root
while(node.right !== null) {
node = node.right
}
node.right = right
};
var flatten2 = function(root) {
while(root){
let p=root.left;
if(p){
while(p.right) p=p.right;
p.right=root.right;
root.right=root.left;
root.left=null
}
root=root.right;
}
};
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/solution/114er-cha-shu-zhan-kai-wei-lian-biao-chao-jian-dan/二叉树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(root === null) return null
if(root === q || root === p) return root
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if(left && right) return root
else if (left) return left
else if(right) return right
else return null
};// https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/e0cc33a83afe4530bcec46eba3325116
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param o1 int整型
* @param o2 int整型
* @return int整型
*/
function lowestCommonAncestor( root , o1 , o2 ) {
// write code here
if(root === null) return -1
if(root.val === o1 || root.val === o2) return root.val
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, o1,o2)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, o1,o2)
if (left !== -1 && right !== -1) return root.val;
else if (left != -1) return left;
else if (right != -1) return right;
else return -1;
}二叉树的最大深度
// bfs
const maxDepth = (root) => {
if (root == null) return 0;
const queue = [root];
let depth = 1;
while (queue.length) {
// 当前层的节点个数
const levelSize = queue.length;
// 逐个让当前层的节点出列
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
// 当前出列的节点
const cur = queue.shift();
// 左右子节点入列
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left);
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right);
}
// 当前层所有节点已经出列,如果队列不为空,说明有下一层节点,depth+1
if (queue.length) depth++;
}
return depth;
};
// 动态规划思路 - DFS
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) return 0
const leftMax = maxDepth(root.left)
const rightMax = maxDepth(root.right)
// 根据左右子树的最大深度推出原二叉树的最大深度
return 1 + Math.max(leftMax, rightMax)
};最大二叉树
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function(nums) {
if(nums.length === 0) return null
const [max, leftArray, rightArray] = getBuildResult(nums)
const root = new TreeNode(max)
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(leftArray)
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(rightArray)
return root
};
function getBuildResult(arr) {
const max = Math.max(...arr)
const maxIndex = arr.findIndex(v => v === max)
return [
max,
arr.slice(0, maxIndex),
arr.slice(maxIndex+1)
]
}寻找重复的子树
1.拼接字符串使二叉树序列化
2.用Map存放每个子树以及出现的次数
3.递归得到所有的子树
var findDuplicateSubtrees = function(root) {
const treeMap = new Map()
const result = []
function traversal(root) {
if(!root) {
return '#'
}
const left = traversal(root.left)
const right = traversal(root.right)
const subtree = `${left},${right},${root.val}`
if(treeMap.get(subtree)) {
treeMap.set(subtree, treeMap.get(subtree)+1)
} else {
treeMap.set(subtree, 1)
}
if(treeMap.get(subtree) === 2) {
result.push(root)
}
return subtree
}
traversal(root)
return result
};- 二分查找
二叉树的直径
var diameterOfBinaryTree = function(root) {
let maxLength = 0;
function trverse(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
const leftMax = trverse(root.left);
const rightMax = trverse(root.right);
const max = leftMax + rightMax;
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, max);
return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax) + 1;
}
trverse(root);
return maxLength;
};求二叉树中最大路径和
var maxPathSum = function(root) {
let res = -Infinity
function help(node) {
if (node === null) return 0
let left = Math.max(0, help(node.left))
let right = Math.max(0, help(node.right))
res = Math.max(res, left + right + node.val)
return Math.max(left, right) + node.val
}
help(root)
return res
};求根节点到叶节点数字之和
dfs
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
let arr = []
function help(node, str) {
if(!node) return
str = str + node.val
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
if(str) arr.push(str)
return
}
help(node.left, str)
help(node.right, str)
}
help(root, '')
return arr.reduce((prev, curr) => parseInt(curr) + parseInt(prev), 0)
};
// 官方的
const dfs = (root, prevSum) => {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
const sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum;
} else {
return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum);
}
}
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
};bfs
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
let sum = 0;
const nodeQueue = [];
const numQueue = [];
nodeQueue.push(root);
numQueue.push(root.val);
while (nodeQueue.length) {
const node = nodeQueue.shift();
const num = numQueue.shift();
const left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left === null && right === null) {
sum += num;
} else {
if (left !== null) {
nodeQueue.push(left);
numQueue.push(num * 10 + left.val);
}
if (right !== null) {
nodeQueue.push(right);
numQueue.push(num * 10 + right.val);
}
}
}
return sum;
};5.二叉搜索树
BST(Binary Search Tree) 的特性
- 对于 BST 的每一个节点node,左子树节点的值都比node的值要小,右子树节点的值都比node的值大。
- 对于 BST 的每一个节点node,它的左侧子树和右侧子树都是 BST。
从做算法题的角度来看 BST,除了它的定义,还有一个重要的性质:BST 的中序遍历结果是有序的(升序)。
interface TreeNode {
left: null | TreeNode,
right: null | TreeNode,
val: number
}
function traverse(root:TreeNode) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
// 中序遍历代码位置
console.log(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
var kthSmallest = function(root, k) {
let res = null
let rank = 0
function treverse(node) {
if (node === null) return
treverse(node.left)
rank++
if (rank === k) {
res = node.val
return
}
treverse(node.right)
}
treverse(root)
return res
}迭代
let kthSmallest = function(root, k) {
let stack = []
let node = root
while(node || stack.length) {
// 遍历左子树
while(node) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.left
}
node = stack.pop()
if(--k === 0) {
return node.val
}
node = node.right
}
return null
}把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
var convertBST = function(root) {
let prevSum = 0
function help(node) {
if (node === null) return
help(node.right)
node.val = node.val + prevSum
prevSum = node.val
help(node.left)
}
help(root)
return root
};迭代版本
var convertBST1 = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
let prevSum = 0
let stack = []
let curr = root
while(curr) {
stack.push(curr)
curr = curr.right
}
while(stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop()
node.val = node.val + prevSum
prevSum = node.val
node = node.left
while(node) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.right
}
}
return root
};
const convertBST = (root) => {
let sum = 0;
let stack = [];
let cur = root;
while (cur) { // 右子节点先不断压栈
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
while (stack.length) { // 一直到清空递归栈
cur = stack.pop(); // 位于栈顶的节点出栈
sum += cur.val; // 做事情
cur.val = sum; // 做事情
cur = cur.left; // 找左子节点
while (cur) { // 存在,让左子节点压栈
stack.push(cur); //
cur = cur.right; // 让当前左子节点的右子节点不断压栈
}
}
return root;
};恢复二叉搜索树
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/recover-binary-search-tree/solution/tu-jie-hui-fu-yi-ge-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-hyj8/
var recoverTree = function(root) {
let prev = new TreeNode(-Infinity)
let err1 = null, err2 = null
function trverseTree(node) {
if(node === null) return
trverseTree(node.left)
if(err1 === null && prev.val > node.val) {
err1 = prev
}
if(err1 !== null && prev.val > node.val) {
err2 = node
}
prev = node
trverseTree(node.right)
}
trverseTree(root)
let temp = err1.val
err1.val = err2.val
err2.val = temp
};判断BST的合法性
function isValidBST(root) {
/* 限定以 root 为根的子树节点必须满足 max.val > root.val > min.val */
function isValidBST(root, min, max) {
// base case
if (root === null) return true
// 若 root.val 不符合 max 和 min 的限制,说明不是合法 BST
if (min !== null && root.val <= min.val) return false
if (max !== null && root.val >= max.val) return false
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root) && isValidBST(root.right, root, max)
}
return isValidBST(root, null, null)
}中序遍历
var isValidBST = function(root) {
let stack = [];
let inorder = -Infinity;
while (stack.length || root !== null) {
while (root !== null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
// 如果中序遍历得到的节点的值小于等于前一个 inorder,说明不是二叉搜索树
if (root.val <= inorder) {
return false;
}
inorder = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
};在BST中搜索一个数
function isInBST(root, target) {
if (root === null) return true
if (root.val === target) return true
if (root.val > target) return isInBST(root.left, target)
if (root.val < target) return isInBST(root.right, target)
}不同的二叉搜索树
动态规划
假设n个节点存在二叉排序树的个数是G(n),令f(i)为以i为根的二叉搜索树的个数
即有:G(n) = f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + f(4) + ... + f(n)
n为根节点,当i为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为[1,2,3,...,i-1],右子树节点个数为[i+1,i+2,...n],所以当i为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为i-1个,右子树节点为n-i,即f(i) = G(i-1)*G(n-i),
上面两式可得:G(n) = G(0)*G(n-1)+G(1)*(n-2)+...+G(n-1)*G(0)
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var numTrees = function(n) {
const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}6.链表
反转链表
var reverseList = function(head) {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
while (curr) {
const next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
};两个链表的第一个公共结点
A和B两个链表长度可能不同,但是A+B和B+A的长度是相同的,所以遍历A+B和遍历B+A一定是同时结束。 如果A,B相交的话A和B有一段尾巴是相同的,所以两个遍历的指针一定会同时到达交点 如果A,B不相交的话两个指针就会同时到达A+B(B+A)的尾节点
A' + R = A ; B' + R = B ; A' + R + B' = A + B' = A' + B ; 其中 R 是重复部分。A‘ 和 B' 是各链表的开头不重复的部分。
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
if(!headA || !headB) return null
let pA= headA, pB = headB
while(pA !== pB) {
pA = pA === null ? headB : pA.next
pB = pB === null ? headA : pB.next
}
return pA
};环形链表
快慢指针
var hasCycle = function(head) {
// 使用hash表,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
// let cache = new Set()
// while(head) {
// if (cache.has(head)) {
// return true
// } else {
// cache.add(head)
// }
// head = head.next
// }
// return false
// 使用快慢指针表,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
let slow = head
let fast = head
while(fast && fast.next) {
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if (slow === fast) {
return true
}
}
return false
};链表中环的入口节点
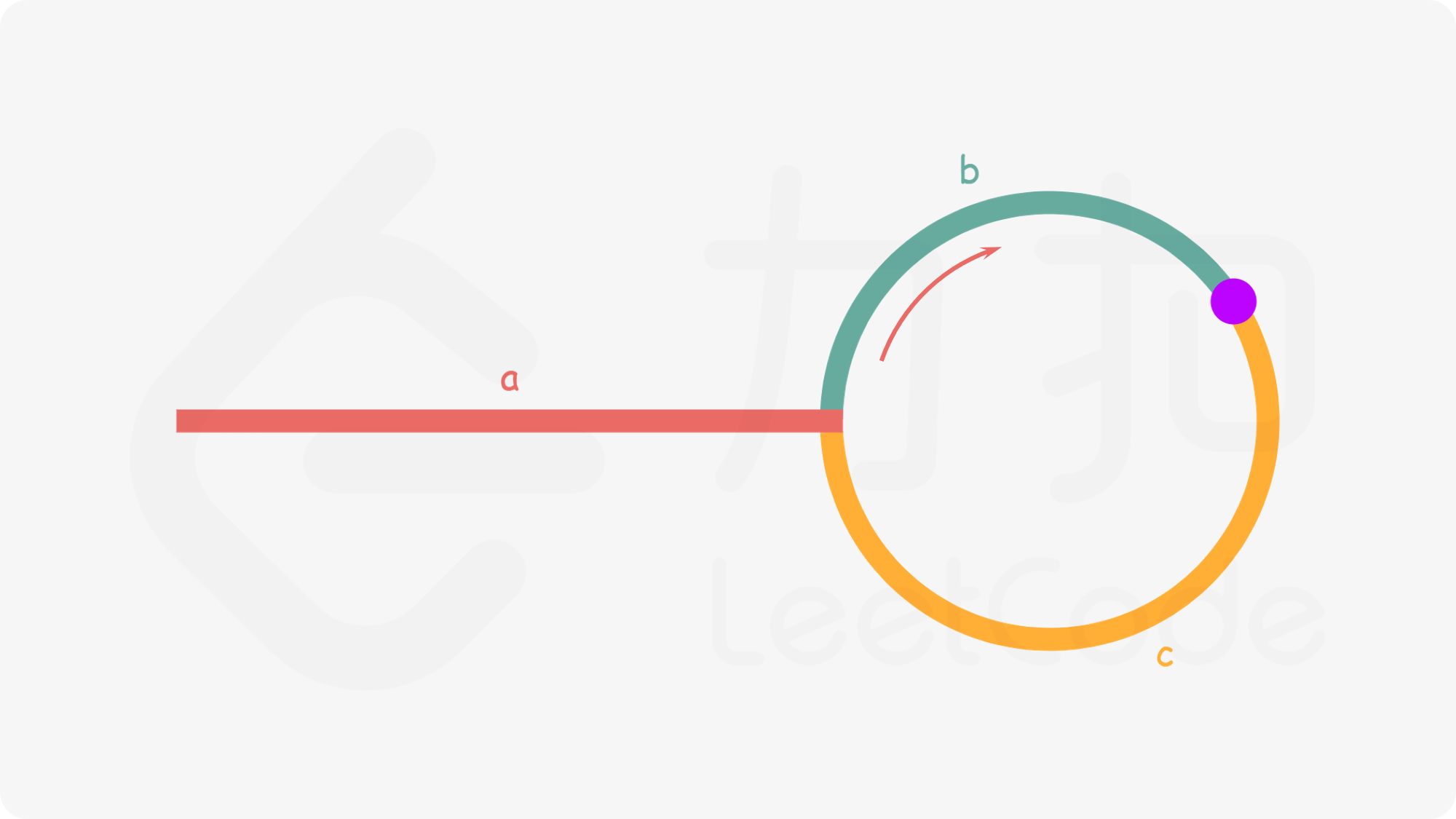 快慢指针:慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走2步,如果有环肯定相遇。
快慢指针:慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走2步,如果有环肯定相遇。
slow * 2 = fast;
slow = a + b;
fast = a + n(c + b) + b= a + (n+1)b + nc; fast是走了n圈环,slow还没有走完一圈就相遇了
a + (n+1)b + nc = 2(a+b) ⟹ a = c + (n−1)(b+c)
a = c + (n-1)(b+c)从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n-1圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离。
var detectCycle = function(head) {
// const set = new Set()
// let res = null
// while(head) {
// if(set.has(head)) return head
// set.add(head)
// head = head.next
// }
// return res
if (head === null) {
return null;
}
let slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if (fast === slow) {
let ptr = head;
while (ptr !== slow) {
ptr = ptr.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return null;
};链表的中间结点
快慢指针
var middleNode = function(head) {
let slow = head
let fast = head
while(fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return slow
};寻找链表的倒数第k个元素
快慢指针
让快指针先走 k 步,然后快慢指针开始同速前进。这样当快指针走到链表末尾 null 时,慢指针所在的位置就是倒数第 k 个链表节点
var getKthFromEnd = function(head, k) {
let slow = head
let fast = head
while(k > 0) {
fast = fast.next
k--
}
while(fast) {
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
}
return slow
};k个一组翻转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
const stack = []
let preHead = new ListNode(0)
let pre = preHead
// 循环链接后续反转链表
while(true) {
let count = 0
let temp = head
while(temp && count < k) {
stack.push(temp)
temp = temp.next
count++
}
// 不够k个,直接链接剩下链表返回
if(count !== k) {
pre.next = head;
break;
}
// 出栈即是反转
while(stack.length > 0) {
pre.next = stack.pop()
pre = pre.next
}
head = temp
}
return preHead.next
};排序链表
时间复杂度要求O(log n), 常数级空间复杂度
v1: O(n*n)
var sortList = function(head) {
if(head === null) return null
let newHead = new ListNode(head.val)
while(head.next) {
let node = head.next
let temp = newHead
let prev = null
while(temp && temp.val < node.val) {
prev = temp
temp = temp.next
}
if(prev) {
prev.next = new ListNode(node.val, temp)
} else {
newHead = new ListNode(node.val, temp)
}
head = head.next
}
return newHead
};合并有序链表
mine
var mergeTwoLists = function(list1, list2) {
let pre = new ListNode(-Infinity);
const root = pre;
while(list1 || list2) {
if (list1 && list2) {
if (list1.val > list2.val) {
// 其实可以直接 pre.next = list2
pre.next = new ListNode(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
pre = pre.next;
} else {
pre.next = new ListNode(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
} else if (list1) {
pre.next = list1;
list1 = null;
} else {
pre.next = list2;
list2 = null;
}
}
return root.next;
};递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
if(l1 === null){
return l2;
}
if(l2 === null){
return l1;
}
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}迭代
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
const prehead = new ListNode(-1);
let prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 === null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
};合并k个有序链表
转为数组
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
return lists.reduce((prev, list) => {
while(list) {
prev.push(list)
list = list.next
}
return prev
}, []).sort((a, b) => a.val - b.val).reduceRight((prev, node) => {
node.next = prev
return node
}, null)
};类似数组归并排序似的合并
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
/* 分而治之 */
if (lists.length <= 1) return lists[0] || null;
const newLists = [];
for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i += 2) {
newLists.push(merge(lists[i], lists[i + 1] || null));
}
return mergeKLists(newLists);
};
const merge = (list_1, list_2) => {
const sentinelNode = new ListNode(0);
let p = sentinelNode;
while (list_1 && list_2) {
if (list_1.val < list_2.val) {
p.next = list_1;
list_1 = list_1.next;
} else {
p.next = list_2;
list_2 = list_2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = list_1 ? list_1 : list_2;
return sentinelNode.next;
};链表求和
// mine
var addTwoNumbers = function(h1, h2) {
const res = new ListNode(Infinity)
let curr = res
let prevMoreVal = 0
while(h1 && h2) {
let val = h1.val + h2.val + prevMoreVal
if (val > 9) {
const str = String(val)
prevMoreVal = parseInt(str.slice(0, 1))
val = parseInt(str.slice(1,2))
} else prevMoreVal = 0
curr.next = new ListNode(val)
curr = curr.next
h1 = h1.next
h2 = h2.next
}
if(h1) curr.next = h1
else if (h2) curr.next = h2
let prev = curr
curr = curr.next
while(curr) {
let val = curr.val + prevMoreVal
if(val > 9) {
prevMoreVal = 1
val = val - 10
} else prevMoreVal = 0
prev.next = new ListNode(val)
prev = prev.next
curr = curr.next
}
if(prevMoreVal > 0) {
prev.next = new ListNode(prevMoreVal)
}
return res.next
};
// better
var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) {
let dummy =new ListNode();
let curr=dummy;
let carry=0;
while(l1 !==null || l2 !==null){
let sum=0;
if(l1!==null){
sum+=l1.val;
l1=l1.next;
}
if(l2!==null){
sum+=l2.val;
l2=l2.next;
}
sum+=carry;
curr.next=new ListNode(sum%10);
carry=Math.floor(sum/10);
curr=curr.next;
}
if(carry>0){
curr.next=new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummy.next;
};数位是正向存放的
function addInList( head1 , head2 ) {
// write code here
function reverNode(head) {
let prev = null
while(head) {
const temp = head.next
head.next = prev
prev = head
head = temp
}
return prev
}
let h1 = reverNode(head1)
let h2 = reverNode(head2)
const res = new ListNode(Infinity)
let curr = res
let prevMoreVal = 0
while(h1 && h2) {
let val = h1.val + h2.val + prevMoreVal
if (val > 9) {
const str = String(val)
prevMoreVal = parseInt(str.slice(0, 1))
val = parseInt(str.slice(1,2))
} else prevMoreVal = 0
curr.next = new ListNode(val)
curr = curr.next
h1 = h1.next
h2 = h2.next
}
if(h1) curr.next = h1
else if (h2) curr.next = h2
let prev = curr
curr = curr.next
while(curr) {
let val = curr.val + prevMoreVal
if(val > 9) {
prevMoreVal = 1
val = val - 10
} else prevMoreVal = 0
prev.next = new ListNode(val)
prev = prev.next
curr = curr.next
}
if(prevMoreVal > 0) {
prev.next = new ListNode(prevMoreVal)
}
return reverNode(res.next)
}删除排序链表中的重复元素
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
const prevHead = new ListNode(0, head)
while(head) {
let next = head.next
while(head && next && head.val === next.val) {
next = next.next
}
head.next = next
head = next
}
return prevHead.next
};删除排序链表中的重复元素II
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
let prevHead = new ListNode(0, head)
let prev = prevHead
while(prev) {
let curr = prev.next
while(curr && curr.next && curr.val === curr.next.val) {
curr = curr.next
}
if(prev.next !== curr) { // 找到了重复的,应该还要删除curr
prev.next = curr.next
} else {
prev = curr
}
}
return prevHead.next
};7.动态规划
凑零钱问题
var coinChange = function(coins, amount) {
let dp = new Array(amount + 1).fill(Infinity)
dp[0] = 0
for (let i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (let coin of coins) {
if (i - coin >= 0) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1)
}
}
}
return dp[amount] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[amount]
}最长递增子序列
就是给定一个无序的数组,在这个数组中找出,递增并且最长的子数组
- dp表定义:
dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的「上升子序列」的长度, 这个定义中nums[i]必须被选取,且必须是这个子序列的最后一个元素; - 动态规划,状态转移方程
dp[i] = Max(dp[i],dp[j]+1)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var lengthOfLIS = function(nums) {
const { length } = nums
if (!length) return 0
let dp = new Array(length).fill(1)
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
for(let j = 0;j < i;j++){
if(nums[j] < nums[i]){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
return Math.max(...dp)
};
// 返回子序列
function LIS( arr ) {
// write code here
const length = arr.length
if(length === 0) return []
const dp = Array.from(new Array(length), () => [])
let res = [arr[0]]
dp[0] = [arr[0]]
for(let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
dp[i].push(arr[i])
for(let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if(arr[j] < arr[i]) {
let temp = [...dp[j], arr[i]]
if(temp.length > dp[i].length) dp[i] = temp
}
}
if(dp[i].length > res.length) res = dp[i]
}
return res
}维护一个列表 tails,其中每个元素 tails[k]tails[k] 的值代表 长度为 k+1的子序列尾部元素的值。 如 [1,4,6]序列,长度为 1,2,3 的子序列尾部元素值分别为 tails = [1,4,6]。
时间复杂度 O(NlogN)
var lengthOfLIS = function(nums) {
const tails = new Array(nums.length).fill(-Infinity)
tails[0] = nums[0]
let res = 1 // 最长递增子序列res
for(let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] > tails[res - 1]) { // 比之前最长子序列的末位值都要大时
tails[res] = nums[i]
res++
continue
}
let left = 0, right = res
while(left < right) { // 二分查找,tails中找到第一个比 nums[i] 大的数 tails[left] ,并更新d[left]=nums[i]。
const mid = Math.floor((left + right)/2)
if(tails[mid] < nums[i]) left = left + 1
else right = mid
}
tails[left] = nums[i]
}
return res
};
function LIS( arr ) {
// write code here
const length = arr.length
if(length === 0) return []
const dp = new Array(length)
const tails = new Array(length).fill(-Infinity)
tails[0] = arr[0]
dp[0] = 1
let count = 1
for(let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if(arr[i] > tails[count - 1]) {
tails[count++] = arr[i]
dp[i] = count
} else {
let left = 0, right = count
while(left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right)/2)
if(arr[i] > tails[mid]) {
left = left + 1
} else right = mid
}
tails[left] = arr[i]
dp[i] = left + 1
}
}
let res = new Array(count);
for(let i=length-1; i>=0; i--){
if(dp[i]===count){
res[--count] = arr[i];
}
}
return res;
}贪心 + 二分查找
贪心: 同样是长度为 2 的序列,[1,2] 一定比 [1,4] 好,因为它更有潜力。即想要组成最长的递增子序列, 就要让这个子序列中上升的尽可能的慢,这样才能更长。
var lengthOfLIS = function(nums) {
let len = nums.length
if (len <= 1) {
return len
}
let tails = [nums[0]]
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 当前遍历元素 nums[i] 大于 前一个递增子序列的 尾元素时,追加到后面即可
if (nums[i] > tails[tails.length - 1]) {
tails.push(nums[i])
} else {
// 否则,查找递增子序列中第一个大于当前值的元素,用当前遍历元素 nums[i] 替换它
// 递增序列,可以使用二分查找
let left = 0
let right = tails.length - 1
while (left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right)/2)
// let mid = (left + right) >> 1
if (tails[mid] < nums[i]) {
left = mid + 1
} else {
right = mid
}
}
tails[left] = nums[i]
}
}
return tails.length
};编辑距离
// 递归-超时
var minDistance = function(s1, s2) {
let m = s1.length
let n = s2.length
// 返回 s1[0..i] 和 s2[0..j] 的最小编辑距离
function dp(i, j) {
if (i === -1) return j + 1
if (j === -1) return i + 1
if (s1[i] === s2[j]) return dp(i -1, j - 1) // 什么多不做
else {
return Math.min(
dp(i, j - 1) + 1, // 插入
dp(i-1, j) + 1, // 删除
dp(i -1, j -1) + 1 // 替换
)
}
}
return dp(m -1, n -1)
};
// 优化 加备忘录
var minDistance = function(s1, s2) {
let m = s1.length
let n = s2.length
const memo = Array.from(new Array(m), () => new Array(n).fill(null))
function dp(i, j) {
if (i === -1) return j + 1
if (j === -1) return i + 1
if(memo[i][j] !== null) return memo[i][j]
if (s1[i] === s2[j]) return memo[i][j] = dp(i -1, j - 1) // 什么多不做
else {
return memo[i][j] = Math.min(
dp(i, j - 1) + 1, // 插入
dp(i-1, j) + 1, // 删除
dp(i -1, j -1) + 1 // 替换
)
}
}
return dp(m - 1, n - 1)
};
// DP table 是自底向上求解,递归解法是自顶向下求解:
// 动态规划使用dp表
// dp 函数的 base case 是i,j等于 -1,而数组索引至少是 0,所以 dp 数组会偏移一位,dp[..][0]和dp[0][..]对应 base case。
var minDistance = function(s1, s2) {
let m = s1.length
let n = s2.length
const dp = Array.from(new Array(m+1), () => new Array(n+1).fill(null))
// base case
for(let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i
}
for(let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = j
}
// 自底向上求解
for(let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for(let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(s1[i-1] === s2[j-1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]
else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(
dp[i][j - 1] + 1, // 插入
dp[i-1][j] + 1, // 删除
dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 // 替换
)
}
}
}
return dp[m][n]
};
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/solution/dong-tai-gui-hua-xiang-jie-xiang-jin-zhu-a8e5/
/**
* @param {string} word1
* @param {string} word2
* @return {number}
* 定义 dp[i][j]的含义为:当字符串 word1 的长度为 i,字符串 word2 的长度为 j 时,
* 将 word1 转化为 word2 所使用的最少操作次数为 dp[i][j]
*
*/
var minDistance = function(word1, word2) {
let n1 = word1.length;
let n2 = word2.length;
let dp = new Array(n1 + 1)
for (let i = 0; i < n1 + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = new Array(n2 + 1).fill(0)
}
// dp[0...n2]的初始值
for (let j = 0; j <= n2; j++)
dp[j] = j;
// dp[j] = min(dp[j-1], pre, dp[j]) + 1
for (let i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
let temp = dp[0];
// 相当于初始化
dp[0] = i;
for (let j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
// pre 相当于之前的 dp[i-1][j-1]
let pre = temp;
temp = dp[j];
// 如果 word1[i] 与 word2[j] 相等。第 i 个字符对应下标是 i-1
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)){
dp[j] = pre;
} else {
dp[j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[j - 1], pre), dp[j]) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[n2];
};买卖股票的最佳时机
一次交易
DP思想:
- 记录【今天之前买入的最小值】
- 计算【今天之前最小值买入,今天卖出的获利】,也即【今天卖出的最大获利】
- 比较【每天的最大获利】,取最大值即可
/**
* @param {number[]} prices
* @return {number}
*/
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
if(prices.length <= 1) return 0
let min = prices[0], max = 0
for(let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - min)
min = Math.min(min, prices[i])
}
return max
};买卖股票的最佳时机II
无数次交易但不能同时参与多笔交易
// 动态规划
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
const length = prices.length
let max = 0, min = -Infinity
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
let temp = max
max = Math.max(max, min + prices[i])
min = Math.max(min, temp - prices[i])
}
return max
};贪心,贪心算法只能用于计算最大利润,计算的过程并不是实际的交易过程。
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
const length = prices.length
let ans = 0
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if(prices[i] > prices[i-1]) { // 只要有利润就卖出
ans += (prices[i] - prices[i-1])
}
}
return ans
};跳跃游戏
动态规划,状态转移方程,下一步是不是能到达,要看上一步的包含上一个节点的最大跳跃步数
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {boolean}
*/
var canJump = function(nums) {
let res = true
let prevMax = 1
for(let i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) {
if(prevMax > 0) {
prevMax = Math.max(nums[i], prevMax - 1)
} else return false
}
return res
};爬楼梯
动态规划思路: 要考虑第爬到第n阶楼梯时候可能是一步,也可能是两步。
- 计算爬上n-1阶楼梯的方法数量。因为再爬1阶就到第n阶
- 计算爬上n-2阶楼梯体方法数量。因为再爬2阶就到第n阶 那么f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2);
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
if(n === 1) return 1
if(n === 2) return 2
let a = 1, b = 2
for(let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
let temp = a + b
a = b
b = temp
}
return b
};单词拆分
var wordBreak = function(s, wordDict) {
const { length } = s
const dp = new Array(length + 1).fill(false)
const set = new Set(wordDict)
dp[0] = true
for(let i = 1; i <= length; i++) {
for(let j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (dp[i] === true) break;
if (dp[j] === false) continue;
const suffix = s.slice(j,i)
if(set.has(suffix ) && dp[j]) {
dp[i] = true
break
}
}
}
return dp[length]
};目标和
- dfs,类似于二叉树的遍历
var findTargetSumWays = function(nums, S) {
let count = 0
function dfs(i, sum) {
if(i === nums.length) {
if (sum === S) count++
return
}
dfs(i+1, sum + nums[i])
dfs(i+1, sum - nums[i])
}
dfs(0, 0)
return count
};- 动态规划
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} S
* @return {number}
*/
var findTargetSumWays = function (nums, S) {
// nums 长度不足以循环时
if (nums.length < 2) {
// 考虑正负值的情况
if (nums[0] !== S && -nums[0] !== S) {
return 0
} else {
return 1
}
}
// 获得nums的总和
const sum = nums.reduce((sum, cur) => sum + cur, 0)
// 因为是非负整数数组,如果全部加起来还要比目标小直接返回0
if (sum < Math.abs(S)) return 0
// 初始化 dp
let dp = Array.from({ length: nums.length }, () => new Array(sum * 2 + 1).fill(0))
// 初始化第一行,考虑 0 的情况
if (nums[0] === 0) {
dp[0][sum] = 2
} else {
dp[0][sum + nums[0]] = 1
dp[0][sum - nums[0]] = 1
}
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < sum * 2 + 1; j++) {
// 判断边界情况
const l = (j - nums[i] < 0) ? 0 : dp[i - 1][j - nums[i]]
const r = (j + nums[i] > sum * 2) ? 0 : dp[i - 1][j + nums[i]]
// 转移方程
dp[i][j] = l + r
// 如果已经到达了目标位置【最后一行的 S 值】,就可以返回了,可以少循环几次
if (i === nums.length - 1 && j === S + sum) {
return dp[i][j]
}
}
}
};
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/target-sum/solution/jing-dian-0-1bei-bao-by-rodrick278-7ohy/8.数组
连续子数组的最大和
暴力求解:时间复杂度O(n^2),空间复杂度O(1)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
var max = -Infinity
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, nums[i])
let prev = nums[i]
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
prev = prev + nums[j]
max = Math.max(max, prev)
}
}
return max
};动态规划: 连续数组,每次循环包括自身,比较自身和i-1的最大连续数组和,得到i的最大连续数组和
以nums[i]为结尾的「最大子数组和」为dp[i]。
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lian-xu-zi-shu-zu-de-zui-da-he-lcof/solution/mian-shi-ti-42-lian-xu-zi-shu-zu-de-zui-da-he-do-2/
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let sum = nums[0]
let prevSum = nums[0]
for(let i = 1; i < nums.length;i++) {
prevSum = Math.max(nums[i], prevSum + nums[i])
sum = Math.max(prevSum, sum)
}
return sum
};乘积最大子数组
var maxProduct = function(nums) {
const length = nums.length
let min = nums[0]
let max = nums[0]
let res = nums[0]
for(let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
let temp = min
min = Math.min(nums[i], Math.min(nums[i] * min, nums[i] * max))
max = Math.max(nums[i], Math.max(nums[i] * temp, nums[i] * max))
res = Math.max(max, res)
}
return res
};合并两个有序数组
mine: 插入后交换
/**
* @param {number[]} A
* @param {number} m
* @param {number[]} B
* @param {number} n
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify A in-place instead.
*/
var merge = function(A, m, B, n) {
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let b = B[i]
if(A[m - 1 + i] <= b || m === 0) A[m+i] = b
else {
let swapFlag = false
let lastV = 0
for(let j = 0; j < m + i + 1; j++) {
if(swapFlag) {
let temp = A[j]
A[j] = lastV
lastV = temp
} else {
if(A[j] > b && !swapFlag) {
swapFlag = true
lastV = A[j]
A[j] = b
}
}
}
}
}
};把 A 和 B 中的所有元素,从大到小依次放入 A 中
var merge = function(nums1, m, nums2, n) {
let count = m + n
while(m > 0 || n > 0) {
if(n === 0) break
let a = m === 0 ? -Infinity : nums1[m- 1]
let b = nums2[n - 1]
if(b>= a) {
nums1[count - 1] = b
n--
} else {
nums1[count - 1] = a
m--
}
count--
}
};全排列
回溯算法
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var permute = function(nums) {
const res = []
backtrack([])
function backtrack(track) {
if (track.length === nums.length) {
res.push([...track])
return
}
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (track.includes(nums[i])) continue
track.push(nums[i])
backtrack(track)
track.pop()
}
}
return res
};最长湍流子数组
/**
* @param {number[]} arr
* @return {number}
*/
var maxTurbulenceSize = function(arr) {
if (arr.length === 1) return 1
let max = 1
for(let i = 0, p = 1,q = 1; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
if (i%2 === 0) { // 偶数
if(arr[i] < arr[i+1]) {
p++
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
q = 1
} else if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]) {
q++
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
p = 1
} else {
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
q = 1
p = 1
}
} else{ // 基数
if(arr[i] < arr[i+1]) {
q++
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
p = 1
} else if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]) {
p++
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
q = 1
} else {
max = Math.max(max, p, q)
q = 1
p = 1
}
}
}
return max
};数组中的第K个最大元素
暴力循环
var findKthLargest = function(nums, k) {
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
let temp = i
for(let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if(nums[j] > nums[temp]) {
temp = j
}
}
if(i === k - 1) return nums[temp]
if(temp !== i) {
nums[temp] = nums[i] // 只需要把小的数放到没有排序的那边
}
}
};快排
// 参考快排序的快速查找
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) {
function swap(a, b) {
let temp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = temp;
}
// 查找nums[start]正确的排序位置
// 直到找到排在第k-1位的。就是所求结果
function findLocation(start, end) {
if (start === end) return nums[start];
let i = start;
let j = end + 1;
while (true) {
while (nums[++i] > nums[start]) if (i === end) break;
while (nums[--j] < nums[start]) if (j === start) break;
if (i < j) swap(i, j) // 交换左右边元素,保证左分支元素 大于 右分支元素
if (i >= j) {
swap(start, j)
break
}
}
// 找到所求元素
if (j === k - 1) return nums[j];
// j>k-1 从nums[j]的左边分支开始查找
// 否则 从右边分支查找
if (j > k - 1) return findLocation(start, j - 1);
else return findLocation(j + 1, end);
}
return findLocation(0, nums.length - 1)
};const findKthLargest = (nums, k) => {
const n = nums.length;
const quick = (l, r) => {
if (l > r) return;
let random = Math.floor(Math.random() * (r - l + 1)) + l; // 随机选取一个index
swap(nums, random, r); // 将它和位置r的元素交换,让 nums[r] 作为 pivot 元素
/**
* 我们选定一个 pivot 元素,根据它进行 partition
* partition 找出一个位置:它左边的元素都比pivot小,右边的元素都比pivot大
* 左边和右边的元素的是未排序的,但 pivotIndex 是确定下来的
*/
let pivotIndex = partition(nums, l, r);
/**
* 我们希望这个 pivotIndex 正好是 n-k
* 如果 n - k 小于 pivotIndex,则在 pivotIndex 的左边继续找
* 如果 n - k 大于 pivotIndex,则在 pivotIndex 的右边继续找
*/
if (n - k < pivotIndex) {
quick(l, pivotIndex - 1);
} else {
quick(pivotIndex + 1, r);
}
/**
* n - k == pivotIndex ,此时 nums 数组被 n-k 分成两部分
* 左边元素比 nums[n-k] 小,右边比 nums[n-k] 大,因此 nums[n-k] 就是第K大的元素
*/
};
quick(0, n - 1); // 让n-k位置的左边都比 nums[n-k] 小,右边都比 nums[n-k] 大
return nums[n - k];
};
function partition(nums, left, right) {
let pivot = nums[right]; // 最右边的元素作为 pivot 元素
let pivotIndex = left; // pivotIndex 初始为 left
for (let i = left; i < right; i++) { // 逐个考察元素,和 pivot 比较
if (nums[i] < pivot) { // 如果当前元素比 pivot 小
swap(nums, i, pivotIndex); // 将它交换到 pivotIndex 的位置
pivotIndex++;
}
} // 循环结束时,pivotIndex左边都是比pivot小的
swap(nums, right, pivotIndex); // pivotIndex和right交换,更新pivot元素
return pivotIndex; // 返回 pivotIndex 下标
}
function swap(nums, p, q) {
const temp = nums[p];
nums[p] = nums[q];
nums[q] = temp;
}最小K个数
使用大顶堆
大顶堆方法,初始化一个长度为 k 的数组为大顶堆,遍历 arr,如果遇到比堆顶数小的数,就拿它替换掉堆顶的数,将这个数重新堆化一下,最终返回这个堆即可
function GetLeastNumbers_Solution(input, k)
{
function findMaxIndex(arr) {
let maxIndex = 0
for(let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i] > arr[maxIndex]) {
maxIndex = i
}
}
return maxIndex
}
// write code here
if(k === 0 || k > input.length) return []
let res = input.slice(0, k)
for(let i = k; i < input.length;i++) {
const maxIndex = findMaxIndex(res)
if(input[i] < res[maxIndex]) {
res[maxIndex] = input[i]
}
}
return res.sort((a, b) => a -b)
}长度最小的子数组
暴力
var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) {
let n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
let ans = Infinity;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let sum = 0;
for (let j = i; j < n; j++) {
sum += nums[j];
if (sum >= target) {
ans = Math.min(ans, j - i + 1);
break;
}
}
}
return ans == Infinity ? 0 : ans;
};滑动窗口
var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) {
let n = nums.length
if (n === 0) return 0
let start = 0, end = 0, sum = 0, res = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER
while(end < n) {
sum = sum + nums[end]
while((sum - nums[start]) >= target) {
sum = sum - nums[start]
start++
}
if(sum >= target) {
res = Math.min(res, end - start + 1)
}
end++
}
return res === Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ? 0 : res
};合并区间
/**
* @param {number[][]} intervals
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var merge = function(intervals) {
const res = []
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]) // 先排序
let prev = intervals[0]
for(let i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
let curr = intervals[i]
if(prev[1] >= curr[0]) { // 有重合
prev[1] = Math.max(curr[1], prev[1])
} else {
res.push(prev) // 不重合,prev推入res数组
prev = curr
}
}
res.push(prev)
return res
};和为K的子数组
var subarraySum = function(nums, k) {
// 暴力求解
// let res = 0
// for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// let sum = 0
// for(let j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
// sum = sum + nums[j]
// if(sum === k) res++
// }
// }
// return res
let count = 0
let map = new Map() // 记录key是sum的出现了多少次
map.set(0, 1) // 和为0的连续子数组出现1次`
let sum = 0
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length;i++) {
sum += nums[i]
if(map.has(sum-k)) count += map.get(sum-k) // 如果sum - k map里有,证明存在有多少个和为k的子数组
map.set(sum, map.has(sum) ? map.get(sum) + 1 : 1)
}
return count
};优美子数组
前缀和
var numberOfSubarrays = function(nums, k) {
let count = 0
const map = new Map()
let countSum = 0
map.set(0, 1)
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] % 2 !== 0) { // 奇数
countSum++
}
map.set(countSum, map.has(countSum) ? map.get(countSum) + 1 : 1)
if(map.has(countSum - k)) {
count += map.get(countSum - k)
}
}
return count
};连续的子数组和
最短无序连续子数组
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var findUnsortedSubarray = function(nums) {
let min = Infinity, max = -Infinity
let flag = false
for(let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] < nums[i - 1]) flag = true
if(flag) {
min = Math.min(min, nums[i])
}
}
flag = false
for(let j = nums.length - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) flag = true
if(flag) {
max = Math.max(max, nums[j])
}
}
let l, r;
for (l = 0; l < nums.length; l++) {
if (min < nums[l]) break;
}
for (r = nums.length - 1; r >= 0; r--) {
if (max > nums[r]) break;
}
return r - l < 0 ? 0 : r - l + 1;
};9.二维数组
N x N二维数组翻转90度
给定 matrix =
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
],
原地旋转输入矩阵,使其变为:
[
[7,4,1],
[8,5,2],
[9,6,3]
]对于矩阵中第 ii 行的第 jj 个元素,在旋转后,它出现在倒数第 ii 列的第 jj 个位置。由于矩阵中的行列从 00 开始计数,因此对于矩阵中的元素 matrix[row][col],在旋转后,它的新位置为 [col][n−row−1]。
var rotate = function(matrix) {
const n = matrix.length
var map = new Map()
// [col][n−row−1]
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(var j =0; j < n; j++) {
var key = j + '&' + (n - i -1)
map.set(key, matrix[i][j])
}
}
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(var j =0; j < n; j++) {
var key = i + '&' + j
matrix[i][j] = map.get(key)
}
}
};
var rotate2 = function(matrix){
const n = matrix.length
const map = new Map()
// [col][n−row−1]
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
const row = j
const col = n - i - 1
const key = row + '-' + col
if (map.has(i + '-' + j)) {
if (!map.has(key)) map.set(key, matrix[row][col])
matrix[row][col] = map.get(i + '-' + j)
} else {
if (!map.has(key)) map.set(key, matrix[row][col])
matrix[row][col] = matrix[i][j]
}
}
}
}先以对角线(左上<—>右下)为轴进行翻转,再对每行左右翻转即可。
var rotate = function(matrix) {
const n = matrix.length
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
[matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]] = [matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]]
}
}
const mid = Math.floor(n/2)
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < mid; j++) {
[matrix[i][j], matrix[i][n - 1 - j]] = [matrix[i][n - 1 - j], matrix[i][j]]
}
}
};执行用时为 60 ms 的范例
var rotate3 = function (matrix) {
//let newMatrix = []
let len = matrix.length
for (let l = 0; l < len; l++) {
let newL = []
for (let n = 0; n < len; n++) {
newL.unshift(matrix[n][l])
}
matrix.push(newL)
//newMatrix.push(newL)
//console.log(newMatrix)
}
matrix.splice(0, matrix.length / 2)
//matrix = newMatrix
};二维数组中的查找
从左下角开始比较,对行列进行位移
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var findNumberIn2DArray = function(matrix, target) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
let row = matrix.length - 1
let col = 0
while(row >=0 && col <= matrix[0].length -1) {
let val = matrix[row][col]
if(target > val) {
col++
} else if(target < val) {
row--
} else {
return true
}
}
return false
};螺旋矩阵
- 一层层向里处理,按顺时针依次遍历:上、右、下、左
- 不再形成“环”了,就会剩下一行或一列,然后单独判断 4 个边界
- 上边界 top : 0
- 下边界 bottom : matrix.length - 1
- 左边界 left : 0
- 右边界 right : matrix[0].length - 1 矩阵不一定是方阵
- top < bottom && left < right 是循环的条件
- 无法构成“环”了,就退出循环,退出时可能是这 3 种情况之一:
- top == bottom && left < right —— 剩一行
- top < bottom && left == right —— 剩一列
- top == bottom && left == right —— 剩一项(也是一行/列) 处理剩下的单行或单列
- 因为是按顺时针推入结果数组的,所以
- 剩下的一行,从左至右 依次推入结果数组
- 剩下的一列,从上至下 依次推入结果数组 代码
- 每个元素访问一次,时间复杂度 O(m*n),m、n 分别是矩阵的行数和列数
- 空间复杂度 O(m*n)
var spiralOrder = function (matrix) {
if (matrix.length === 0) return []
const res = []
let top = 0, bottom = matrix.length - 1, left = 0, right = matrix[0].length - 1
while (top < bottom && left < right) {
for (let i = left; i < right; i++) res.push(matrix[top][i]) // 上层
for (let i = top; i < bottom; i++) res.push(matrix[i][right]) // 右层
for (let i = right; i > left; i--) res.push(matrix[bottom][i])// 下层
for (let i = bottom; i > top; i--) res.push(matrix[i][left]) // 左层
right--
top++
bottom--
left++ // 四个边界同时收缩,进入内层
}
if (top === bottom) // 剩下一行,从左到右依次添加
for (let i = left; i <= right; i++) res.push(matrix[top][i])
else if (left === right) // 剩下一列,从上到下依次添加
for (let i = top; i <= bottom; i++) res.push(matrix[i][left])
return res
};托普利茨矩阵
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isToeplitzMatrix = function(matrix) {
const res = true
const maxRow = matrix.length, maxCol = matrix[0].length
for(let i = 1; i < maxRow; i++) {
for(j = 1; j < maxCol; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j] !== matrix[i -1][j-1]) return false
}
}
return true
};不同路径
递归加memo
/**
* @param {number} m
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
const memo = Array.from(new Array(m), () => new Array(n).fill(null))
memo[0][0] = 1
function dp(i, j) {
if(memo[i][j] !== null) return memo[i][j]
if(i === 0 || j === 0) return memo[i][j] = 1
return memo[i][j] = dp(i - 1, j) + dp(i, j -1)
}
return dp(m -1, n -1)
};动态规划
var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
const dp = Array.from(new Array(m), () => new Array(n).fill(1))
for(let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for(let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i -1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1]
};最小路径和
递归加memo
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var minPathSum = function(grid) {
const rows = grid.length, cloumns = grid[0].length
const memo = Array.from(new Array(rows), () => new Array(cloumns).fill(null))
memo[0][0] = grid[0][0]
function dp(row, cloumn) {
if(memo[row][cloumn] !== null) return memo[row][cloumn]
if(row === 0) return memo[row][cloumn] = grid[row][cloumn] + dp(row,cloumn - 1)
if(cloumn === 0) return memo[row][cloumn] = grid[row][cloumn] + dp(row-1,cloumn)
return memo[row][cloumn] = grid[row][cloumn] + Math.min(dp(row - 1, cloumn), dp(row, cloumn -1))
}
return dp(rows -1, cloumns -1)
};动态规划
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var minPathSum = function(grid) {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length
const dp = Array.from(new Array(m), () => new Array(n).fill(null))
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]
for(let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = grid[i][0] + dp[i-1][0]
}
for(let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[0][i] = grid[0][i] + dp[0][i-1]
}
for(let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for(let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + Math.min(dp[i -1][j], dp[i][j-1])
}
}
return dp[m-1][n -1]
};二分查找
二分查找
function binarySearch(arr, target){
let low = 0
let high = arr.length - 1
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high)/2)
const midValue = arr[mid]
if (midValue > target) {
high = mid - 1
} else if (midValue < target) {
low = mid + 1
} else {
return mid
}
}
return -1
}求平方根
根据平方数的性质——连续n个奇数相加的结果一定是平方数。
设第一个奇数为a,共有n个连续奇数。 用等差数列求和公式 S=an+[(n-1)n/2]*2 =n^2+(a-1)n 所以若第一个奇数为1的话就一定是一个数的平方,否则不是。
如:9=1+3+5; 16=1+3+5+7; 所以,不断的进行奇数相加,并判断x大小即可。代码如下:
var mySqrt = function(x) {
let i = 1
let res = 0
while(x >= 0) {
x -= i
res++
i += 2
}
return res - 1
};二分查找,由于 x平方根的整数部分是满足k*k <= x的最大k值, 可以对 kk 进行二分查找
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sqrtx/solution/cong-ji-ben-de-er-fen-fa-shuo-qi-jie-jue-xde-ping-/
const mySqrt = function(x) {
if (x < 2) return x
let left = 1, mid, right = Math.floor(x / 2);
while (left <= right) {
mid = Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2)
if (mid * mid === x) return mid
if (mid * mid < x) {
left = mid + 1
}else {
right = mid - 1
}
}
return right
}寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
时间复杂度是 O(logN)
思路:
第一步:基于二分法的思路,先找mid
第二步:若mid > first element ,说明什么?说明mid的左侧是升序,最小值肯定不在mid左边,此时,我们需要在mid的右边找,所以 left = mid + 1
第三步:若mid < first element ,说明什么?说明最小值肯定在mid左边,此时,我们需要在mid的左边找,所以 right = mid - 1
第四步:终止条件是什么?分两种情况讨论:
1、若mid > mid + 1,此时mid + 1就是最小值,返回结果 2、若mid < mid - 1,此时mid就是最小值,返回结果
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sqrtx/solution/cong-ji-ben-de-er-fen-fa-shuo-qi-jie-jue-xde-ping-/
var findMin = function(nums) {
const { length } = nums
if(length === 1) return nums[0]
let left = 0, right = length - 1, mid
if(nums[right] > nums[left]) return nums[0]
while(left <= right) {
mid = Math.floor((left + right)/2)
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
return nums[mid + 1]
}
if (nums[mid] < nums[mid - 1]) {
return nums[mid]
}
if (nums[mid] > nums[0]) {
left = mid + 1
} else {
right = mid - 1
}
}
return null
};搜索旋转排序数组
时间复杂度要求O(log n)
思路:如果中间的数小于最右边的数,则右半段是有序的,若中间数大于最右边数,则左半段是有序的,只要在有序的半段里用首尾两个数组来判断目标值是否在这一区域内,这样就可以确定保留哪半边了
var search = function(nums, target) {
// for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// if(target === nums[i]) {
// return i
// }
// }
// return -1
let left = 0, right = nums.length - 1
while(left <= right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right)/2)
if(target === nums[mid]) return mid
else if(nums[mid] < nums[right]){
if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right])
left = mid+1
else
right = mid-1
} else{
if(nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid])
right = mid-1
else
left = mid+1
}
}
return -1
};双指针
盛最多水的容器
/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
var maxArea = function(height) {
const n = height.length
let left = 0, right = n - 1
let res = 0
while(left < right) {
if(height[left] < height[right]) {
res = Math.max(res, (right - left) * height[left])
left++
} else {
res = Math.max(res, (right - left) * height[right])
right--
}
}
return res
};在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[]}
*/
var searchRange = function(nums, target) {
let l = 0
let r = nums.length -1
let findIndex = -1
while(l <= r) {
const mid = Math.floor((l + r)/2)
if(nums[mid] === target) {
findIndex = mid
} if(nums[mid] > target) {
r = mid -1
} else {
l = mid + 1
}
}
const res = [findIndex, findIndex]
if(findIndex === -1) return res
l = findIndex
r = findIndex
while(l> 0 && nums[l-1] === target) {
res[0] = --l
}
while(r < nums.length - 1 && nums[r+1] === target) {
res[1] = ++r
}
return res
};接雨水
/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
var trap = function (height) {
let n = height.length
if (n === 0) return 0
let res = 0
let left_max = [], right_max = []
//记录左边数组的最大值
left_max[0] = height[0]
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
left_max[i] = Math.max(left_max[i - 1], height[i])
}
//记录右边数组的最大值
right_max[n - 1] = height[n - 1]
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
right_max[i] = Math.max(right_max[i + 1], height[i])
}
//统计每一列的面积之和
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res += Math.min(left_max[i], right_max[i]) - height[i]
}
return res
}双指针
/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
// myself
var trap = function(height) {
const { length } = height
let res = 0
let left = 0, right = length - 1
let left_max = 0, right_max = 0
while(left < right) {
if(height[left] < height[right]) {
res += Math.max(left_max - height[left], 0)
left_max = Math.max(height[left], left_max)
left++
} else {
res += Math.max(right_max - height[right], 0)
right_max = Math.max(right_max, height[right])
right--
}
}
return res
};
var trap = function (height) {
let left = 0;
let right = height.length - 1;
let res = 0;
let leftMax = 0;
let rightMax = 0;
while (left < right) {
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
leftMax = Math.max(height[left], leftMax);
res += leftMax - height[left];
left++;
} else {
rightMax = Math.max(height[right], rightMax);
res += rightMax - height[right];
right--;
}
}
return res;
};设计LRU缓存结构
思路: 双链表+哈希表, 哈希表存取数据都是o(1), 双链表先预设表头和表尾。
map结构刚好符合,且是有序存放的,但Map.prototype.keys()返回的是遍历器
class LRUCache {
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity
this.cache = new Map()
}
get (key) {
if(this.cache.has(key)) {
const value = this.cache.get(key)
this.cache.delete(key)
this.cache.set(key, value)
return value
}
else return -1
}
put (key, value) {
if(this.cache.has(key)) {
this.cache.delete(key)
this.cache.set(key, value)
} else {
const size = this.cache.size
if(size === this.capacity) {
const keys = this.cache.keys()
const key = keys.next().value
this.cache.delete(key)
}
this.cache.set(key, value)
}
}
}/**
* lru design
* @param operators int整型二维数组 the ops
* @param k int整型 the k
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
function LRU( operators , k ) {
// write code here
const res = []
const map = new Map()
operators.forEach(arr => {
const opt = arr.shift()
if(opt === 1) {
const value = arr.pop()
const key = arr.pop()
if(map.has(key)) {
map.delete(key)
map.set(key, value)
} else {
if(map.size === k) {
const keys = map.keys()
map.delete(keys.next().value)
}
map.set(key, value)
}
} else {
const key = arr.pop()
if(map.has(key)) {
const value = map.get(key)
map.delete(key)
map.set(key, value)
res.push(value)
} else res.push(-1)
}
})
return res
}
module.exports = {
LRU : LRU
};扑克牌中的顺子
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isStraight = function(nums) {
//从小到大排序
const minSort = nums.sort((a,b)=> a-b);
//记录每个数字之间大差值,反正不能大于4
let sum = 0;
//不能超过4
for(let i = 0; i<4;i++){
//忽略0也就是王
if(minSort[i] == 0){
continue
}
//如果扑克牌(非0)重复,说明不是顺子
else if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]){
return false
}else{
//差值记录
sum = sum + nums[i+1] - nums[i]
}
}
//如果超过4,说明不是顺子。
return sum<5
};扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
/**
* @constructor
* @param {NestedInteger[]} nestedList
*/
var NestedIterator = function(nestedList) {
// 通过生成器函数递归遍历嵌套数组
var generator = function * (arr) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i].isInteger()) {
yield arr[i].getInteger()
} else {
yield* generator(arr[i].getList())
}
}
};
// 初始化迭代器
this.iterator = generator(nestedList);
// 调用迭代器的 next 方法,返回 {value: val, done: true/false},value 为返回的值,done 表示是否遍历完
this.nextVal = this.iterator.next();
};
/**
* @this NestedIterator
* @returns {boolean}
*/
NestedIterator.prototype.hasNext = function() {
return !this.nextVal.done;
};
/**
* @this NestedIterator
* @returns {integer}
*/
NestedIterator.prototype.next = function() {
var value = this.nextVal.value;
// 调用迭代器的 next 方法,更新 nextVal 的值
this.nextVal = this.iterator.next();
return value;
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator will be called like this:
* var i = new NestedIterator(nestedList), a = [];
* while (i.hasNext()) a.push(i.next());
*/计算器
计算器1
基本计算器
var calculate = function(s) {
const n = s.length
let res = 0
let sign = 1
const ops = [1]
let i = 0
while(i < n) {
const ch = s[i]
switch(ch) {
case ' ':
break;
case '+':
sign = ops[ops.length -1]
break
case '-':
sign = -ops[ops.length -1] // 比如2个减好久要逆转为+
break
case '(':
ops.push(sign)
break
case ')':
ops.pop()
break
default:
let j = i
let chNew = ''
while(j < n && !(isNaN(Number(s[j]))) && s[j] !== ' ') { // 可能是9989这种不是一位的字符串数字的处理
chNew = chNew + s[j]
j++
}
res += parseInt(chNew) * sign
i = j
if(i > 0) i--
}
i++
}
return res
};基本计算器2
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {number}
*/
var calculate = function(s) {
s = s.trim()
const length = s.length
const stack = []
let prevSign = '+'
let prevNum = 0
for(let i = 0; i < length + 1; i++) {
const char = s[i]
if(char === ' ') continue
if (!isNaN(Number(char))) {
// 获取正确的数字
let j = i + 1
let chNew = char
while(j < length && !(isNaN(Number(s[j]))) && s[j] !== ' ') { // 可能是9989这种不是一位的字符串数字的处理
chNew = chNew + s[j]
j++
}
i = j
if(i > 0) i--
prevNum = parseInt(chNew)
} else {
switch(prevSign) {
case '+':
stack.push(prevNum)
break
case '-':
stack.push(-prevNum)
break
case '*':
stack.push(stack.pop() * prevNum)
break
default:
stack.push(stack.pop() / prevNum | 0)
}
prevSign = char
prevNum = 0
}
}
let ans = 0
while (stack.length) {
ans += stack.pop()
}
return ans;
};电话号码的字母组合
思路: dfs(回溯),bfs
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/solution/shou-hua-tu-jie-liang-chong-jie-fa-dfshui-su-bfsya/
/**
* @param {string} digits
* @return {string[]}
*/
var letterCombinations = function(digits) {
if(digits.length === 0) {
return []
}
const dictionary = {
2: 'abc',
3: 'def',
4: 'ghi',
5: 'jkl',
6: 'mno',
7: 'pqrs',
8: 'tuv',
9: 'wxyz'
}
const treeLength = digits.length
const res = []
const dfs = (str, pos) => {
if(pos > treeLength - 1) {
res.push(str)
return
}
const charts = dictionary[digits[pos]]
for(let i = 0; i < charts.length; i++) {
dfs(str + charts[i], pos + 1)
}
}
dfs('', 0)
return res
};bfs解法,类似二叉树的层次遍历
var letterCombinations = function(digits) {
if(digits.length === 0) return []
const dictionary = { '2': 'abc', '3': 'def', '4': 'ghi', '5': 'jkl', '6': 'mno', '7': 'pqrs', '8': 'tuv', '9': 'wxyz' }
const queue = []
queue.push('')
for(let i = 0; i < digits.length; i++) {
const nodeLevelLength = queue.length
const words = dictionary[digits[i]]
for(let j = 0; j < nodeLevelLength; j++) {
let str = queue.shift()
for( let letter of words) {
queue.push(str + letter)
}
}
}
return queue
};下一个排列
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
*/
var nextPermutation = function(nums) {
if(nums.length < 2) return
for(let i = nums.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]) { //找到相邻升序
for(let j = nums.length - 1; j >= i; j--) { // 找到最右边大于nums[i-1]的数,并交换,原本最右边[i, nums.length -1]肯定降序
if(nums[j] > nums[i-1]) {
swap(nums, i-1, j)
// reverse nums[i:end]
for(let k = i, p = nums.length - 1; k < p; k++, p--) {
swap(nums, k, p)
}
return
}
}
}
}
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
};
function swap (nums, i, j) {
const temp = nums[i]
nums[i] = nums[j]
nums[j] = temp
}岛屿数量
- dfs
重点是将节点重置为0,并把上下左右的是1的都重置为0
/**
* @param {character[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var numIslands = function(grid) {
let res = 0
let row = grid.length
let cloumn = grid[0].length
if(!row * cloumn) return 0
for(let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < cloumn; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] === '1') {
res++
dfs(grid, i, j)
}
}
}
return res
};
function dfs (grid, i, j) {
let row = grid.length
let cloumn = grid[0].length
grid[i][j] = '0'
if((i - 1) >= 0 && grid[i-1][j] === '1') dfs(grid, i-1, j)
if((i + 1) < row && grid[i + 1][j] === '1') dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
if((j - 1) >= 0 && grid[i][j - 1] === '1') dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
if((j + 1) < cloumn && grid[i][j + 1] === '1') dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
}