遇到一道二叉树的题目时的通用思考过程是:
是否可以通过遍历一遍二叉树得到答案?如果不能的话,是否可以定义一个递归函数,通过子问题(子树)的答案推导出原问题的答案?
1.二叉树
做二叉树的问题,关键是把题目的要求细化,搞清楚根节点应该做什么,然后剩下的事情抛给前/中/后序的遍历框架就行了。比如对于一般的构造二叉树的题目,是要想怎么构造出根节点。所以应该是前序遍历。
/* 二叉树遍历框架 */
function traverse(root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left)
// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right)
// 后序遍历
}中序遍历的非递归实现
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/solution/shou-hua-tu-jie-zhong-xu-bian-li-fan-xiang-de-by-x/
const inorderTraversal = (root) => {
const res = [];
const stack = [];
while (root) { // 能压入栈的左子节点都压进来
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
while (stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop(); // 栈顶的节点出栈
res.push(node.val); // 在压入右子树之前,处理它的数值部分(因为中序遍历)
node = node.right; // 获取它的右子树
while (node) { // 右子树存在,执行while循环
stack.push(node); // 压入当前root
node = node.left; // 不断压入左子节点
}
}
return res;
};路径总和
递归: 深度优先遍历
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false
if(root.left === null && root.right === null && root.val === targetSum) return true
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
};广度优先遍历: 父节点的值是targetSum - root.val
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root === null) return false
let stack = [root]
root.val = targetSum - root.val
while(stack.length) {
const nextNodes = []
for(let i = 0; i < stack.length; i++) {
let node = stack[i]
if(node.left === null && node.right === null && node.val === 0) {
return true
}
if(node.left) {
node.left.val = node.val - node.left.val
nextNodes.push(node.left)
}
if(node.right) {
node.right.val = node.val - node.right.val
nextNodes.push(node.right)
}
}
stack = nextNodes
}
return false
};二叉树的层序遍历
bfs
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(root == null) return []
let queue = [root]
const res = []
while(queue.length) {
const nodesLevels = []
const newQueue = []
queue.forEach(node => {
nodesLevels.push(node.val)
if (node.left) newQueue.push(node.left)
if (node.right) newQueue.push(node.right)
})
res.push(nodesLevels)
queue = newQueue
}
return res
};dfs
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(root == null) return []
const res = []
const dfs = (node, step) => {
if(node === null) return
if(!res[step]) res[step] = []
res[step].push(node.val)
dfs(node.left, step + 1)
dfs(node.right, step + 1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return res
};二叉树的序列化与反序列化
前序遍历法,后续遍历法差不多一样,而中序遍历的方式行不通,因为无法实现反序列化方法deserialize。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {string}
*/
const splitStr = ','
const nullStr = '#'
var serialize = function(root) {
let res = ''
function help(node) {
if(node === null) {
res = res + nullStr + splitStr
return
}
res = res + node.val + splitStr
help(node.left)
help(node.right)
}
help(root)
return res.slice(0, res.length - 1) // 末尾多一个,
};
/**
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*
* @param {string} data
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var deserialize = function(data) {
const nodes = data.split(splitStr)
function help(nodes) {
if (nodes.length === 0) return null
const node = nodes.shift()
if (node === nullStr) return null
const root = new TreeNode(parseInt(node))
root.left = help(nodes)
root.right = help(nodes)
return root
}
return help(nodes)
};
/**
* Your functions will be called as such:
* deserialize(serialize(root));
*/验证二叉树的前序序列化
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/verify-preorder-serialization-of-a-binary-tree/solution/pai-an-jiao-jue-de-liang-chong-jie-fa-zh-66nt/
/**
* @param {string} preorder
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValidSerialization = function(preorder) {
const nodes = preorder.split(',')
const stack = []
for(let i = 0; i < nodes.length;i++) {
stack.push(nodes[i])
while(stack.length > 2 && stack[stack.length - 1] === '#' && stack[stack.length - 2] === '#' && stack[stack.length - 3] !== '#') {
stack.pop()
stack.pop()
stack.pop()
stack.push('#')
}
}
return stack.length === 1 && stack.pop() === '#'
};从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
先构造根节点,接着思考如何构造左右节点,而构造左右节点也是构造根节点。剩下的就是分割数组
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if (preorder.length === 0) return null
const root = new TreeNode(preorder[0])
const inorderRootIndex = inorder.findIndex(v => v === preorder[0])
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1,inorderRootIndex + 1), inorder.slice(0, inorderRootIndex))
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(inorderRootIndex+1), inorder.slice(inorderRootIndex+1))
return root
};从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
/**
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @param {number[]} postorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
if(inorder.length === 0) return null
const rootValue = postorder[postorder.length -1]
const root = new TreeNode(rootValue)
const inorderFindIndex = inorder.findIndex(v => v === rootValue) // 1
root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, inorderFindIndex), postorder.slice(0, inorderFindIndex))
root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(inorderFindIndex+1), postorder.slice(inorderFindIndex, postorder.length -1))
return root
};对称二叉树
递归
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
function check(left, right) {
if(left === null && right === null) return true
else if(left && right) {
return left.val === right.val && check(left.left, right.right) && check(left.right, right.left)
} else return false
}
if(root === null) return true
return check(root.left, root.right)
};迭代
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if (!root) return true;
let stack = [];
stack.push(root.left, root.right);
while (stack.length) {
const right = stack.pop();
const left = stack.pop();
if (left === null && right === null) {
// 节点为空什么都不做
} else if (left && right && left.val === right.val) {
//左左节点和对称右右节点入栈
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
//左右节点和对称右左节点入栈
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};翻转二叉树
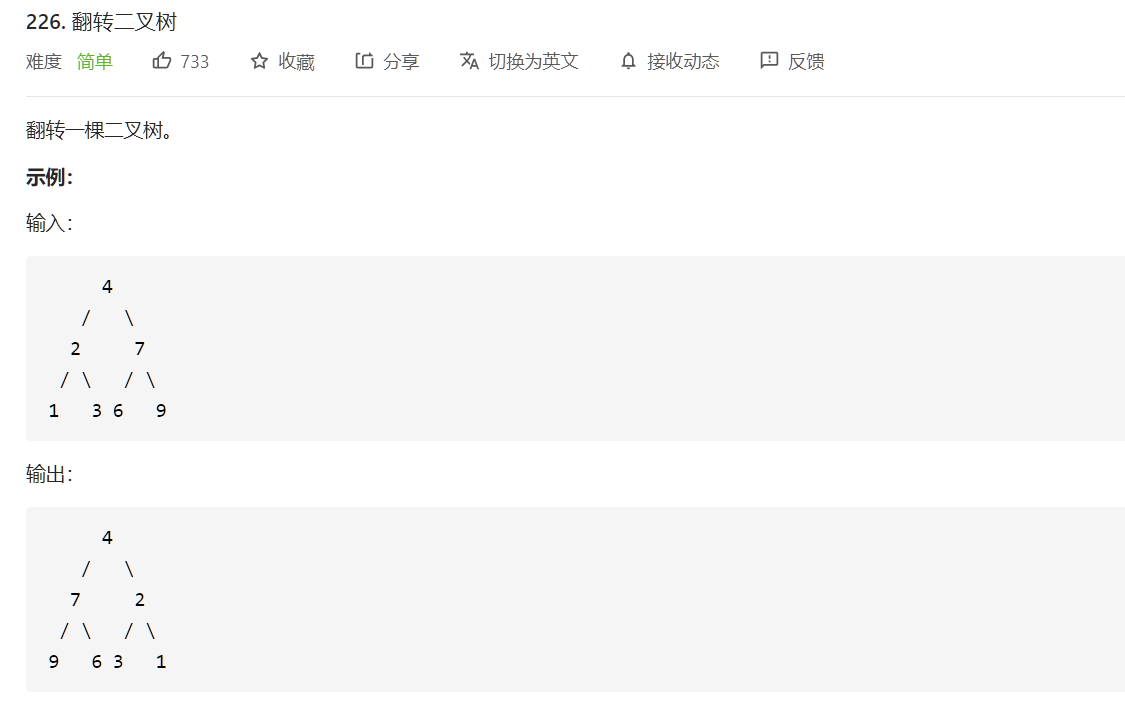
var invertTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
let temp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = temp
invertTree(root.right)
invertTree(root.left)
return root
};填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
var connect = function(root) {
if(root === null) return null
connectTowNode(root.left, root.right)
return root
};
function connectTowNode(left, right) {
if (left === null || right === null) {
return
}
left.next = right
connectTowNode(left.left,left.right)
connectTowNode(right.left,right.right)
connectTowNode(left.right, right.left)
}二叉树展开为链表

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
*/
var flatten = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
flatten(root.left)
flatten(root.right)
let left = root.left, right = root.right
root.right = left
root.left = null
let node = root
while(node.right !== null) {
node = node.right
}
node.right = right
};
var flatten2 = function(root) {
while(root){
let p=root.left;
if(p){
while(p.right) p=p.right;
p.right=root.right;
root.right=root.left;
root.left=null
}
root=root.right;
}
};
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/solution/114er-cha-shu-zhan-kai-wei-lian-biao-chao-jian-dan/二叉树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(root === null) return null
if(root === q || root === p) return root
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if(left && right) return root
else if (left) return left
else if(right) return right
else return null
};// https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/e0cc33a83afe4530bcec46eba3325116
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param o1 int整型
* @param o2 int整型
* @return int整型
*/
function lowestCommonAncestor( root , o1 , o2 ) {
// write code here
if(root === null) return -1
if(root.val === o1 || root.val === o2) return root.val
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, o1,o2)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, o1,o2)
if (left !== -1 && right !== -1) return root.val;
else if (left != -1) return left;
else if (right != -1) return right;
else return -1;
}二叉树的最大深度
// bfs
const maxDepth = (root) => {
if (root == null) return 0;
const queue = [root];
let depth = 1;
while (queue.length) {
// 当前层的节点个数
const levelSize = queue.length;
// 逐个让当前层的节点出列
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
// 当前出列的节点
const cur = queue.shift();
// 左右子节点入列
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left);
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right);
}
// 当前层所有节点已经出列,如果队列不为空,说明有下一层节点,depth+1
if (queue.length) depth++;
}
return depth;
};
// 动态规划思路 - DFS
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) return 0
const leftMax = maxDepth(root.left)
const rightMax = maxDepth(root.right)
// 根据左右子树的最大深度推出原二叉树的最大深度
return 1 + Math.max(leftMax, rightMax)
};最大二叉树
var constructMaximumBinaryTree = function(nums) {
if(nums.length === 0) return null
const [max, leftArray, rightArray] = getBuildResult(nums)
const root = new TreeNode(max)
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(leftArray)
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(rightArray)
return root
};
function getBuildResult(arr) {
const max = Math.max(...arr)
const maxIndex = arr.findIndex(v => v === max)
return [
max,
arr.slice(0, maxIndex),
arr.slice(maxIndex+1)
]
}寻找重复的子树
1.拼接字符串使二叉树序列化
2.用Map存放每个子树以及出现的次数
3.递归得到所有的子树
var findDuplicateSubtrees = function(root) {
const treeMap = new Map()
const result = []
function traversal(root) {
if(!root) {
return '#'
}
const left = traversal(root.left)
const right = traversal(root.right)
const subtree = `${left},${right},${root.val}`
if(treeMap.get(subtree)) {
treeMap.set(subtree, treeMap.get(subtree)+1)
} else {
treeMap.set(subtree, 1)
}
if(treeMap.get(subtree) === 2) {
result.push(root)
}
return subtree
}
traversal(root)
return result
};- 二分查找
二叉树的直径
var diameterOfBinaryTree = function(root) {
let maxLength = 0;
function trverse(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
const leftMax = trverse(root.left);
const rightMax = trverse(root.right);
const max = leftMax + rightMax;
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, max);
return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax) + 1;
}
trverse(root);
return maxLength;
};求二叉树中最大路径和
var maxPathSum = function(root) {
let res = -Infinity
function help(node) {
if (node === null) return 0
let left = Math.max(0, help(node.left))
let right = Math.max(0, help(node.right))
res = Math.max(res, left + right + node.val)
return Math.max(left, right) + node.val
}
help(root)
return res
};求根节点到叶节点数字之和
dfs
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
let arr = []
function help(node, str) {
if(!node) return
str = str + node.val
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
if(str) arr.push(str)
return
}
help(node.left, str)
help(node.right, str)
}
help(root, '')
return arr.reduce((prev, curr) => parseInt(curr) + parseInt(prev), 0)
};
// 官方的
const dfs = (root, prevSum) => {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
const sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum;
} else {
return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum);
}
}
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
};bfs
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
let sum = 0;
const nodeQueue = [];
const numQueue = [];
nodeQueue.push(root);
numQueue.push(root.val);
while (nodeQueue.length) {
const node = nodeQueue.shift();
const num = numQueue.shift();
const left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left === null && right === null) {
sum += num;
} else {
if (left !== null) {
nodeQueue.push(left);
numQueue.push(num * 10 + left.val);
}
if (right !== null) {
nodeQueue.push(right);
numQueue.push(num * 10 + right.val);
}
}
}
return sum;
};2.二叉搜索树
BST(Binary Search Tree) 的特性
- 对于 BST 的每一个节点node,左子树节点的值都比node的值要小,右子树节点的值都比node的值大。
- 对于 BST 的每一个节点node,它的左侧子树和右侧子树都是 BST。
从做算法题的角度来看 BST,除了它的定义,还有一个重要的性质:BST 的中序遍历结果是有序的(升序)。
interface TreeNode {
left: null | TreeNode,
right: null | TreeNode,
val: number
}
function traverse(root:TreeNode) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
// 中序遍历代码位置
console.log(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
var kthSmallest = function(root, k) {
let res = null
let rank = 0
function treverse(node) {
if (node === null) return
treverse(node.left)
rank++
if (rank === k) {
res = node.val
return
}
treverse(node.right)
}
treverse(root)
return res
}迭代
let kthSmallest = function(root, k) {
let stack = []
let node = root
while(node || stack.length) {
// 遍历左子树
while(node) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.left
}
node = stack.pop()
if(--k === 0) {
return node.val
}
node = node.right
}
return null
}把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
var convertBST = function(root) {
let prevSum = 0
function help(node) {
if (node === null) return
help(node.right)
node.val = node.val + prevSum
prevSum = node.val
help(node.left)
}
help(root)
return root
};迭代版本
var convertBST1 = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null
let prevSum = 0
let stack = []
let curr = root
while(curr) {
stack.push(curr)
curr = curr.right
}
while(stack.length) {
let node = stack.pop()
node.val = node.val + prevSum
prevSum = node.val
node = node.left
while(node) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.right
}
}
return root
};
const convertBST = (root) => {
let sum = 0;
let stack = [];
let cur = root;
while (cur) { // 右子节点先不断压栈
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
while (stack.length) { // 一直到清空递归栈
cur = stack.pop(); // 位于栈顶的节点出栈
sum += cur.val; // 做事情
cur.val = sum; // 做事情
cur = cur.left; // 找左子节点
while (cur) { // 存在,让左子节点压栈
stack.push(cur); //
cur = cur.right; // 让当前左子节点的右子节点不断压栈
}
}
return root;
};恢复二叉搜索树
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/recover-binary-search-tree/solution/tu-jie-hui-fu-yi-ge-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-hyj8/
var recoverTree = function(root) {
let prev = new TreeNode(-Infinity)
let err1 = null, err2 = null
function trverseTree(node) {
if(node === null) return
trverseTree(node.left)
if(err1 === null && prev.val > node.val) {
err1 = prev
}
if(err1 !== null && prev.val > node.val) {
err2 = node
}
prev = node
trverseTree(node.right)
}
trverseTree(root)
let temp = err1.val
err1.val = err2.val
err2.val = temp
};判断BST的合法性
function isValidBST(root) {
/* 限定以 root 为根的子树节点必须满足 max.val > root.val > min.val */
function isValidBST(root, min, max) {
// base case
if (root === null) return true
// 若 root.val 不符合 max 和 min 的限制,说明不是合法 BST
if (min !== null && root.val <= min.val) return false
if (max !== null && root.val >= max.val) return false
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root) && isValidBST(root.right, root, max)
}
return isValidBST(root, null, null)
}中序遍历
var isValidBST = function(root) {
let stack = [];
let inorder = -Infinity;
while (stack.length || root !== null) {
while (root !== null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
// 如果中序遍历得到的节点的值小于等于前一个 inorder,说明不是二叉搜索树
if (root.val <= inorder) {
return false;
}
inorder = root.val;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
};在BST中搜索一个数
function isInBST(root, target) {
if (root === null) return true
if (root.val === target) return true
if (root.val > target) return isInBST(root.left, target)
if (root.val < target) return isInBST(root.right, target)
}不同的二叉搜索树
动态规划
假设n个节点存在二叉排序树的个数是G(n),令f(i)为以i为根的二叉搜索树的个数
即有:G(n) = f(1) + f(2) + f(3) + f(4) + ... + f(n)
n为根节点,当i为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为[1,2,3,...,i-1],右子树节点个数为[i+1,i+2,...n],所以当i为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为i-1个,右子树节点为n-i,即f(i) = G(i-1)*G(n-i),
上面两式可得:G(n) = G(0)*G(n-1)+G(1)*(n-2)+...+G(n-1)*G(0)
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var numTrees = function(n) {
const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}