优先级
- instanceof
- new
- call && apply & bind
- 手写promise
- 手写ajax
目录
- Object.create的实现
- instanceOf
- new实现
- call,apply,bind的实现
- es5实现继承
- 函数柯里化
- 组合函数的实现
- 深拷贝
- 手写EventHub(发布-订阅)
- 单例模式
- proxy实现响应式
- 数组map实现
- 数组reduce实现
- 数组splice实现
- 数组去重
- 取并集,交集,差集,子集
- 数组扁平化
- 数组操作
- JSONP的实现
- 基于promise封装ajax
- 异步循环打印
- 图片懒加载
- Promise
- async的实现
Object.create的实现
Object.create原本的行为:

Object.create这个 polyfill 涵盖了主要的应用场景,它创建一个已经选择了原型的新对象,但没有把第二个参数考虑在内。
请注意,尽管在 ES5 中 Object.create支持设置为[[Prototype]]为null,但因为那些ECMAScript5以前版本限制,此 polyfill 无法支持该特性。
if (typeof Object.create !== "function") {
Object.create = function (proto, propertiesObject) {
if (typeof proto !== 'object' && typeof proto !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('Object prototype may only be an Object: ' + proto);
} else if (proto === null) {
throw new Error("This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support 'null' as the first argument.");
}
if (typeof propertiesObject !== 'undefined') throw new Error("This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support a second argument.");
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F();
};
}
// 第二个参数示例
const obj = Object.create(null, {foo: {
writable:true,
configurable:true,
value: "hello"
}})instanceOf
instanceof 运算符用于检测构造函数的
prototype属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上。 实际上,实例对象上的__proto__就是指向构造函数的prototype
语法: result = variable instanceof constructor
思路:
步骤1:先取得当前类的原型,当前实例对象的原型链
步骤2:一直循环(执行原型链的查找机制)
- 取得当前实例对象原型链的原型链(
proto = proto.__proto__,沿着原型链一直向上查找) - 如果当前实例的原型链
__proto__上找到了当前类的原型prototype,则返回true - 如果一直找到
Object.prototype.__proto__=== null,Object的基类(null)上面都没找到,则返回false
function _instanceOf(instanceObject, classFunc) {
if (typeof instanceObject !== 'object' || instanceObject === null) return false
let protoType = classFunc.prototype
let proto = instanceObject.__proto__
// 或者
// let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(instanceObject)
while (true) {
if (proto === null) return false
if (proto === protoType) return true
proto = proto.__proto__
// 或者 proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto)
}
}new实现
要创建 Person 的实例,应使用 new 操作符。以这种方式调用构造函数会执行如下操作。(JS高级程序设计描述)
- (1) 在内存中创建一个新对象。
- (2) 这个新对象内部的
[[Prototype]]特性被赋值为构造函数的 prototype 属性。 - (3) 构造函数内部的 this 被赋值为这个新对象(即 this 指向新对象)。
- (4) 执行构造函数内部的代码(给新对象添加属性)。
- (5) 如果构造函数返回非空对象,则返回该对象;否则,返回刚创建的新对象
构造函数与普通函数唯一的区别就是调用方式不同。
function myNew() {
// 创建一个空对象,实例.__proto__ = 类.prototype
const object = {}
// 获取构造函数
const Constructor = [].shift.call(arguments)
// 某些函数未必有 `prototype` 属性,比如箭头函数
if (!Constructor.prototype) throw new Error('First argument is not a constructor.')
// 链接到原型
object.__proto__ = Constructor.prototype
// Object.setPrototypeOf(object, Constructor.prototype)
// 绑定this 执行构造函数
const result = Constructor.apply(object, arguments)
// 确保new出来是个对象
// 注意如果原构造函数有Object类型的返回值,包括Function, Array, Date, RegExg, Error
// 那么应该返回这个返回值
const isObject = typeof result === 'object' && result !== null
const isFunction = typeof result === 'function'
if(isObject || isFunction) {
return result
}
// 原构造函数没有Object类型的返回值,返回我们的新对象
return object
}
// test
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x
this.y = y
}
const point = myNew(Point, 1, 2)call,apply,bind的实现
模拟实现call
MDN: call() 方法使用一个指定的 this 值和单独给出的一个或多个参数来调用一个函数。
TIP
注意:该方法的语法和作用与 apply() 方法类似,只有一个区别,就是 call() 方法接受的是一个参数列表,而 apply() 方法接受的是一个包含多个参数的数组。
- 1.判断当前this是否为函数,防止Function.prototype.myCall() 直接调用
- 2.context 为可选参数,如果不传的话默认上下文为 window
- 3.为context 创建一个 Symbol(保证不会重名)属性,将当前函数赋值给这个属性
- 4.处理参数,传入第一个参数后的其余参数
- 5.调用函数后即删除该Symbol属性
Function.prototype.myCall = function(context, ...args) {
if (this === Function.prototype) {
return undefined // 用于防止 Function.prototype.myCall() 直接调用
}
// 首先判断调用对象
if(typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('error')
}
context = context || window
const fn = Symbol()
context[fn] = this
const result = context[fn](...args)
delete context[fn]
return result
}模拟实现apply
func.apply(thisArg, [argsArray])
apply实现类似call,参数为数组,从ECMAScript 5 开始可以使用类数组对象。
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context, args) {
if (this === Function.prototype) {
return undefined // 用于防止 Function.prototype.myCall() 直接调用
}
// 首先判断调用对象
if(typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('error')
}
context = context || window
const fn = Symbol()
context[fn] = this
// Array.isArray
if (!Array.isArray) {
Array.isArray = function(arg) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(arg) === '[object Array]'
}
}
const result = Array.isArray(args) ? context[fn](...args) : context[fn]()
delete context[fn]
return result
}模拟实现bind
语法: function.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
bind()方法创建一个新的函数,在bind()被调用时,这个新函数的 this 被指定为bind()的第一个参数,而其余参数将作为新函数的参数,供调用时使用。 绑定函数也可以使用new运算符构造,它会表现为目标函数已经被构建完毕了似的。提供的this会被忽略,但前置参数仍会提供给默认函数。
所以resultFunc 函数被当做构造函数使用的时候,应该忽略传入的 context 值,而使用resultFunc的this值。
同时当做构造函数使用时,还需要考虑原型链的处理,这里的处理类似于继承,func 函数的原型链应该指向原函数的原型链,但又不能直接赋值,否则会出现原型被共享的问题出现。
作为构造函数使用的绑定函数
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.x + ',' + this.y;
};
var p = new Point(1, 2);
p.toString(); // '1,2'
// var emptyObj = {};
// var YAxisPoint = Point.bind(emptyObj, 0/*x*/);
var YAxisPoint = Point.bind(null, 0/*x*/);
var axisPoint = new YAxisPoint(5);
axisPoint.toString(); // '0,5'
axisPoint instanceof Point; // true
axisPoint instanceof YAxisPoint; // true
new YAxisPoint(17, 42) instanceof Point; // true官方实现
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context) {
const slice = Array.prototype.slice
const args1 = slice.call(arguments, 1)
const func = this
if(typeof func !== 'function') {
throw new Error("Must accept function")
}
const NOOP = function () {}
NOOP.prototype = func.prototype
function resultFunc() {
const args2 = slice.call(arguments,0)
return func.apply(
(this instanceof NOOP) ? this : context, // 判断resultFunc是否是new 调用,如果是则传入this
// resultFunc.prototype.isPrototypeOf(this) ? this : context,
args1.concat(args2)
)
}
resultFunc.prototype = new NOOP() // 避免原型链污染
resultFunc.prototype.constructor = resultFunc
return resultFunc
}ES5 实现继承
寄生组合继承是ES5的最佳实现
所谓寄生组合式继承,即通过借用构造函数来继承属性,通过原型链的形式来继承方法。
只调用了一次父类构造函数,效率更高。避免在子类.prototype上面创建不必要的、多余的属性,与其同时,原型链还能保持不变。
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name
this.colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green']
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name)
this.age = age
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype)
Child.prototype.constructor = Child
Child.prototype.getAge = function () {
return this.age
}
let Tom = new Child('Tom', 17)
Tom.getAge()高阶的函数技术
函数柯里化
function curry(func) {
return function curried(...args) {
if (args.length >= func.length) {
return func.apply(this, args)
} else {
return function (...args2) {
return curried.apply(this, args.concat(args2))
}
}
}
}
// 用例
function sum(a, b, c) {
return a + b + c;
}
let curriedSum = curry(sum);
alert( curriedSum(1, 2, 3) ); // 6,仍然可以被正常调用
alert( curriedSum(1)(2,3) ); // 6,对第一个参数的柯里化
alert( curriedSum(1)(2)(3) ); // 6,全柯里化运用example
调用多次的操作是将数组的每一项都转化为百分比 1 --> 100%。
普通思维下封装
function getNewArray(array) {
return array.map(function(item) {
return item * 100 + '%'
})
}
getNewArray([1, 2, 3, 0.12]); // ['100%', '200%', '300%', '12%'];函数柯里化
function _map(arr, fn) {
return arr.map(fn)
}
const _getNewArray = curry(_map)
const getNewArray = _getNewArray(function(item) {
return item * 100 + '%'
})对数组进行一个过滤,找出数组中的所有Number类型的数据
function _filter(func, array) {
return array.filter(func);
}
const _find = curry(_filter);
const findNumber = _find(function(item) {
if (typeof item == 'number') {
return item;
}
})
findNumber([1, 2, 3, '2', '3', 4]); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 当继续封装另外的过滤操作时就会变得非常简单
// 找出数字为20的子项
const find20 = _find(function(item, i) {
if (item === 20) {
return i;
}
})
find20([1, 2, 3, 30, 20, 100]); // 4
// 找出数组中大于100的所有数据
const findGreater100 = _find(function(item) {
if (item > 100) {
return item;
}
})
findGreater100([1, 2, 101, 300, 2, 122]); // [101, 300, 122]组合函数的实现
function compose(...fns) {
if(fns.length === 0) return arg => arg
if(fns.length === 1) return fns[0]
return fns.reduceRight((res, cur) => (...args) => res((cur(...args))))
}function compose(...funcs) {
return function (x) {
return funcs.reduce(function (arg, fn) {
return fn(arg);
}, x);
};
}
// 例子
function lowerCase(input) {
return input && typeof input === "string" ? input.toLowerCase() : input;
}
function upperCase(input) {
return input && typeof input === "string" ? input.toUpperCase() : input;
}
function trim(input) {
return typeof input === "string" ? input.trim() : input;
}
function split(input, delimiter = ",") {
return typeof input === "string" ? input.split(delimiter) : input;
}
// compose函数的实现,请参考 “组合函数的实现” 部分。
const trimLowerCaseAndSplit = compose(trim, lowerCase, split);
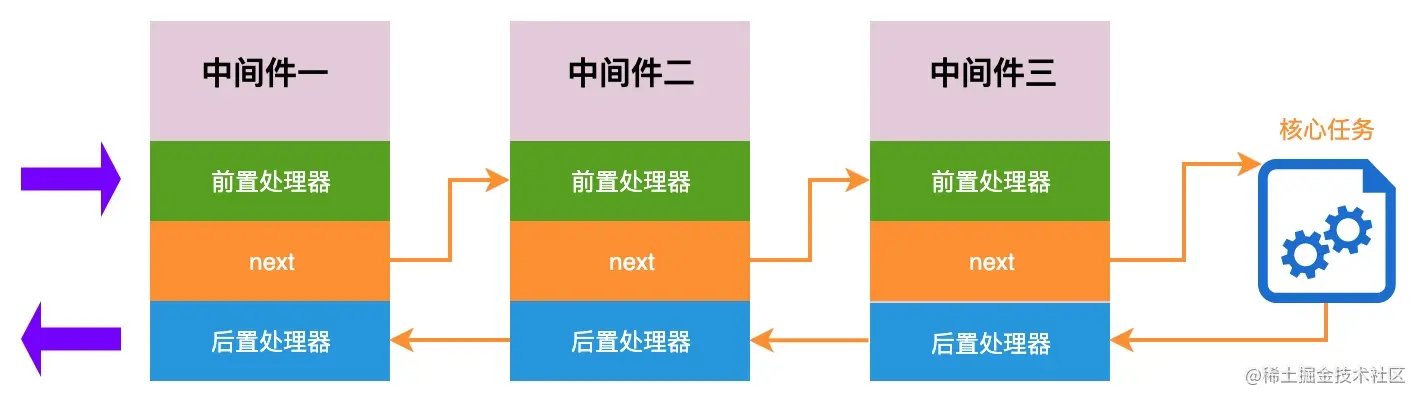
trimLowerCaseAndSplit(" a,B,C "); // ["a", "b", "c"]中间件和洋葱模型
compose 函数也是实现中间件和洋葱模型的关键
function compose(middleware) {
// 省略部分代码
return function (context, next) {
let index = -1;
return dispatch(0);
function dispatch(i) {
if (i <= index)
return Promise.reject(new Error("next() called multiple times"));
index = i;
let fn = middleware[i];
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next;
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve();
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1)));
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err);
}
}
};
}
深拷贝
// 数组浅拷贝可以用slice,concat, [...array],对象可以用Object.assign,{...obj}
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
const arrCopy = arr.slice()
arr.push(3)
// arrCopy 为[1,2,3]
var obj = {k: '1'}
var obj2 = {...obj}
// obj2 ==={k: "1"} true
obj.ff = '12'
// obj2 ==={k: "1"} true
// 面试手写版
function deepClone(obj, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if(obj === null || obj === undefined) return obj
if(obj instanceof Date) return new Date(obj)
if(obj instanceof RegExp) return new RegExp(obj)
if(typeof obj !== 'object') return obj
if(hash.get(obj)) return hash.get(obj)
let cloneObj = new obj.constructor()
hash.set(obj, cloneObj)
for(let key in obj) {
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
cloneObj[key] = deepClone(obj[key], hash)
}
}
return cloneObj
}
/*
递归,解决了嵌套引用,但会嵌套多层递归会爆栈
*/
function deepClone(target, hashMap = new WeakMap()){
if (target === null) return target // typeof null === 'object'
if (typeof target !== 'object') return target // undefined, string, number, function, symbol
// 是对象的话就要进行深拷贝
// 处理循环引用
if (hashMap.get(target)) {
return hashMap.get(target)
}
let cloneTarget = new target.constructor()
// 找到的是所属类原型上的constructor,而原型上的 constructor指向的是当前类本身
// 防止循环引用
hashMap.set(target, cloneTarget)
const stringType = Object.prototype.toString.call(target)
switch (stringType) {
case '[object Boolean]':
case '[object Number]':
case '[object String]':
case '[object Error]':
case '[object Date]':
case '[object RegExp]':
return new target.constructor(target)
case '[object Set]':
target.forEach(v => cloneTarget.add(deepClone(v, hashMap)))
break
case '[object Map]':
target.forEach((v, k) => cloneTarget.set(k, deepClone(v, hashMap)))
break
case '[object Array]':
target.forEach((v, index) => cloneTarget[index] = deepClone(v, hashMap))
break
case '[object Object]':
const keys = Object.keys(target)
keys.forEach(key => cloneTarget[key] = deepClone(target[key], hashMap))
break
}
return cloneTarget
}
function needDeepClone(target) {
const stringType = Object.prototype.toString.call(target)
return ['[object Set]', '[object Map]', '[object Array]', '[object Object]'].includes(stringType)
}
function copyBaseValue(target) {
if (target === null) return target // typeof null === 'object'
if (typeof target !== 'object') return target
return new target.constructor(target)
}
// 维护一个栈(数组),while循环 https://yanhaijing.com/javascript/2018/10/10/clone-deep/
function deepClone2(data) {
if (!needDeepClone(data)) return copyBaseValue(data)
const hashMap = new WeakMap()
const cloneData = new data.constructor()
const stack = [
{
source: data,
target: cloneData,
}
]
while (stack.length) {
// 深度优先遍历
const [source, target] = stack.pop()
if (!hashMap.has(source)) {
hashMap.set(source, target)
}
const stringType = Object.prototype.toString.call(source)
switch (stringType) {
case '[object Object]':
const keys = Object.keys(source)
keys.forEach(key => {
if(!needDeepClone(source[key])) {
target[key] = copyBaseValue(source[key])
} else {
if (hashMap.has(source[key])) target[key] = hashMap.get(source[key])
else {
const newTarget = new source[key].constructor()
stack.push({
source: source[key],
target: newTarget
})
target[key] = newTarget
}
}
})
break
case '[object Array]':
source.forEach(v => {
if (!needDeepClone(v)) {
target.push(copyBaseValue(v))
} else {
if (hashMap.has(v)) target.push(hashMap.get(v))
else {
const newTarget = new v.constructor()
stack.push({
source: v,
target: newTarget
})
target.push(newTarget)
}
}
})
break
case '[object Map]':
source.forEach((v, k) => {
if (!needDeepClone(v)) target.set(k, copyBaseValue(v))
else {
if (hashMap.has(v)) target.set(k, hashMap.get(v))
else {
const newTarget = new v.constructor()
stack.push({
source: v,
target: newTarget
})
target.set(k, newTarget)
}
}
})
break
case '[object Set]':
source.forEach(v => {
if (!needDeepClone(v)) target.add(copyBaseValue(v))
else {
if (hashMap.has(v)) target.add(hashMap.get(v))
else {
const newTarget = new v.constructor()
stack.push({
source: v,
target: newTarget
})
target.add(newTarget)
}
}
})
break
}
}
return cloneData
}手写EventHub(发布-订阅)
定义
发布-订阅模式其实是一种对象间一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发送改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都将得到状态改变的通知。
订阅者(Subscriber)把自己想订阅的事件注册(Subscribe)到调度中心(Event Channel),当发布者(Publisher)发布该事件(Publish Event)到调度中心,也就是该事件触发时,由调度中心统一调度(Fire Event)订阅者注册到调度中心的处理代码。
例如 Node.js EventEmitter 中的 on 和 emit 方法;Vue 中的 $on 和 $emit 方法。都使用了发布-订阅模式
优点: 对象之间解耦,异步编程中,可以更松耦合的代码编写;缺点:创建订阅者本身要消耗一定的时间和内存,虽然可以弱化对象之间的联系,多个发布者和订阅者嵌套一起的时候,程序难以跟踪维护
发布-订阅模式与观察者模式的区别
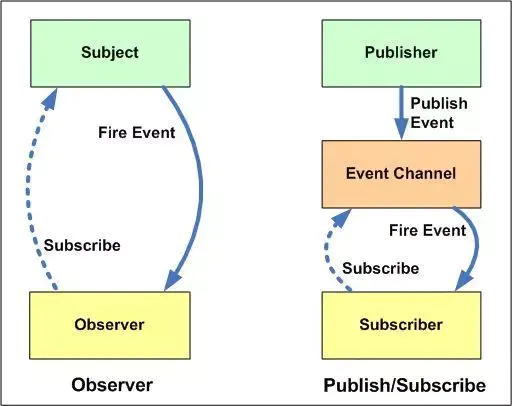
- 观察者模式: 观察者(Observer)直接订阅(Subscribe)主题(Subject),而当主题被激活的时候,会触发(Fire Event)观察者里的事件。
- 发布订阅模式: 订阅者(Subscriber)把自己想订阅的事件注册(Subscribe)到调度中心(Event Channel),当发布者(Publisher)发布该事件(Publish Event)到调度中心,也就是该事件触发时,由调度中心统一调度(Fire Event)订阅者注册到调度中心的处理代码。
发布订阅模式与观察者模式最大的区别在于发布订阅模式有一个第三方存在,成为代理或者事件总线。发布者与订阅者分别和这个代理交互,他们彼此不知道对方的存在也不需要,发布者发布消息通知代理,订阅者去代理那订阅。 观察者模式则可以直接交流,一方发生变化直接通知另一方。
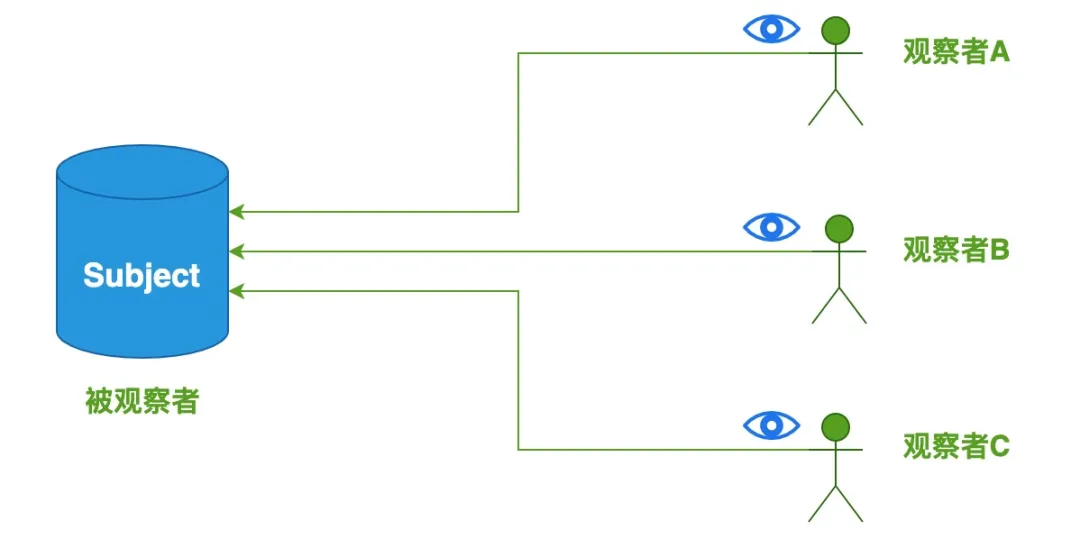
观察者模式
观察者模式,它定义了一种 一对多 的关系,让多个观察者对象同时监听某一个主题对象,这个主题对象的状态发生变化时就会通知所有的观察者对象,使得它们能够自动更新自己。在观察者模式中有两个主要角色:Subject(主题)和 Observer(观察者)。
class Observer {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
notify() {
console.log(`${this.name} has been notified.`);
}
}
class Subject {
constructor() {
this.observers = []
}
addObserver(observer) {
this.observers.push(observer)
}
notifyObservers () {
console.log("notify all the observers");
this.observers.forEach(observer => observer.notify())
}
}
// 1. 创建主题对象
const subject = new Subject()
// 2. 添加观察者
const observerA = new Observer('ObserverA')
const observerB = new Observer('ObserverB')
subject.addObserver(observerA)
subject.addObserver(observerB)
// 3. 通知所有观察者
subject.notifyObservers()
// notify all the observers
// ObserverA has been notified.
// ObserverC has been notified.Vue响应式原理就是基于此,实现了1.创建主题对象、2.添加观察者、3.通知观察者 这三个步骤实现自动化,这就是实现响应式的核心思路。
发布订阅
在软件架构中,发布/订阅是一种消息范式,消息的发送者(称为发布者)不会将消息直接发送给特定的接收者(称为订阅者)。而是将发布的消息分为不同的类别,然后分别发送给不同的订阅者。 同样的,订阅者可以表达对一个或多个类别的兴趣,只接收感兴趣的消息,无需了解哪些发布者存在。
在发布订阅模式中有三个主要角色:Publisher(发布者)、 Channels(通道)和 Subscriber(订阅者)。
核心思路是:
- 使用一个对象作为缓存
- on 负责把方法注册到缓存的 EventName 对应的数组
- emit 负责遍历触发 EventName 底下的方法数组
- off 找方法的索引,并删除
// 简单实现
class EventHub {
cache = {};
on(eventName, fn) {
this.cache[eventName] = this.cache[eventName] || [];
return this.cache[eventName].push(fn) -1; // push会返回数组length, 暂时用key作为键值
}
emit(eventName) {
this.cache[eventName].forEach((cb) => cb());
}
off(eventName, fn) {
const index = this.cache[eventName].findIndex(item => item === fn)
if (index === -1) return;
this.cache[eventName].splice(index, 1);
}
offIndex(eventName, index) {
this.cache[eventName].splice(index, 1);
}
}
// 更加完善
class EventEmitter {
constructor(_maxListeners = 10) {
this._maxListeners = _maxListeners
this._events = new Map()
}
// 向事件队列添加事件,相当于订阅
// prepend为true表示向事件队列头部添加事件
// node 中 emitter.on() 的别名。
addListener(type, listener, prepend = false) {
const events = this._events.get(type)
if(Array.isArray(events) && events === this._maxListeners) return false
if(!this._events.has(type)) this._events.set(type, [])
else if(prepend) events.unshift(listener)
else events.push(listener)
return true
}
// 移除某个事件
removeListener(type, listener) {
const events = this._events.get(type)
if(Array.isArray(events) && listener) {
this._events.set(type, events.filter(e => e !== listener && e.origin !== listener))
return true
} else return false
}
// 向事件队列添加事件,只执行一次
once(type, listener) {
const only = (...args) => {
this.removeListener(type, listener)
listener.apply(this, args)
}
only.origin = listener
this.addListener(type, only)
}
// 执行某类事件,相当于发布
emit(type, ...args) {
const events = this._events.get(type)
if(Array.isArray(events)) {
events.forEach(fn => fn.apply(this, args))
}
}
setMaxListeners(maxEventCount) {
this._maxListeners = maxEventCount
}
}
// old
function EventEmitter() {
this._maxListeners = 10
this._events = Object.create(null)
}
// 向事件队列添加事件
// prepend为true表示向事件队列头部添加事件
EventEmitter.prototype.addListener = function (type, listener, prepend) {
if (!this._events) {
this._events = Object.create(null)
}
if (this._events[type]) {
if (prepend) {
this._events[type].unshift(listener)
} else {
this._events[type].push(listener)
}
} else {
this._events[type] = [listener]
}
}
// 移除某个事件
EventEmitter.prototype.removeListener = function (type, listener) {
if (Array.isArray(this._events[type])) {
if (!listener) {
delete this._events[type]
} else {
this._events[type] = this._events[type].filter(e => e !== listener && e.origin !== listener)
}
}
}
// 向事件队列添加事件,只执行一次
EventEmitter.prototype.once = function (type, listener) {
const only = (...args) => {
listener.apply(this, args)
this.removeListener(type, listener)
}
only.origin = listener
this.addListener(type, only)
}
// 执行某类事件
EventEmitter.prototype.emit = function (type, ...args) {
if (Array.isArray(this._events[type])) {
this._events[type].forEach(fn => {
fn.apply(this, args)
})
}
}
// 设置最大事件监听个数
EventEmitter.prototype.setMaxListeners = function (count) {
this.maxListeners = count
}
// test
var emitter = new EventEmitter()
var onceListener = function (args) {
console.log('我只能被执行一次', args, this)
}
var listener = function (args) {
console.log('我是一个listener', args, this)
}
emitter.once('click', onceListener)
emitter.addListener('click', listener)
emitter.emit('click', '参数')
emitter.emit('click')
emitter.removeListener('click', listener)
emitter.emit('click')JavaScript自定义事件
DOM也提供了类似上面EventEmitter的API,基本使用:
//1、创建事件
var myEvent = new Event('myEvent')
//2、注册事件监听器
elem.addEventListener('myEvent', function (e) {
})
//3、触发事件
elem.dispatchEvent(myEvent)单例模式
// new OpenAI只会创建一次
export const getOpenaiClient: () => OpenAI = (function () {
let instance: OpenAI
return {
getInstance: function () {
if (!instance) {
instance = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseURL: process.env.OPENAI_BASE_URL,
})
}
return instance
},
}
})().getInstanceclass Singleton {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
static instance = null // 类的静态属性可遍历enumerable为true
static getInstance (name) { // 类的静态方法不遍历enumerable为false
if(!this.instance) this.instance = new Singleton(name)
return this.instance
}
}
var a = Singleton.getInstance('tom')
var b = Singleton.getInstance('Tom')
console.log(a === b)class Singleton {
private static singleton: Singleton;
private constructor() {
}
public static getInstance(): Singleton {
if (!Singleton.singleton) {
Singleton.singleton = new Singleton();
}
return Singleton.singleton;
}
}
let instance1 = Singleton.getInstance();
let instance2 = Singleton.getInstance();
console.log(instance1 === instance2); // true使用闭包实现
function Singleton(name) {
this.name = name
}
Singleton.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
Singleton.getInstance = (function () {
let instance
return function (name) {
if (!instance) {
instance = new Singleton(name)
}
return instance
}
})()
var a = Singleton.getInstance('tom')
var b = Singleton.getInstance('Tom')
console.log(a === b)proxy实现响应式
简单的example, 注意是变动logedObj才会触发Proxy的handler
const obj = {}
const logedObj = new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, name) {
console.log('get', target, name);
return Reflect.get(target, name);
},
set: function(target, name, value, receiver) {
const success = Reflect.set(target, name, value, receiver);
if (success) {
console.log('property ' + name + ' on ' + target + ' set to ' + value);
}
return success;
},
deleteProperty(target, name) {
console.log('delete' + name);
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, name);
},
has(target, name) {
console.log('has' + name);
return Reflect.has(target, name);
}
})<p id="paragraph"></p>
<input type="text" id="input">
<script>
const paragraph = document.getElementById('paragraph');
const input = document.getElementById('input');
// 需要代理的数据对象
const data = {
text: 'hello world'
};
const handler = {
get (target, key, receiver) {
return Reflect.get(target, p, receiver);
},
// 监控data中text属性的变化
set (target, prop, value, receiver) {
if (prop === 'text') {
// 更新值
target[prop] = value;
// 更新视图
paragraph.innerHTML = value;
input.value = value;
return true
}
return Reflect.set(target, key, value,receiver)
}
}
// 构造proxy对象
const myText = new Proxy(data, handler);
// 添加input监听事件
input.addEventListener('input', function (e) {
myText.text = e.target.value
}, false);
// 初始化值
myText.text = data.text;
</script>数组map实现
依照 ecma262 草案,实现的map的规范如下:

Array.prototype.map = function(callbackFn, thisArg) {
// 处理数组类型异常
if (this === null || this === undefined) {
throw new TypeError("Cannot read property 'map' of null or undefined");
}
// 处理回调类型异常
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(callbackfn) != "[object Function]") {
throw new TypeError(callbackfn + ' is not a function')
}
// 草案中提到要先转换为对象
let O = Object(this);
let T = thisArg;
let len = O.length >>> 0;
let A = new Array(len);
for(let k = 0; k < len; k++) {
// 还记得原型链那一节提到的 in 吗?in 表示在原型链查找
// 如果用 hasOwnProperty 是有问题的,它只能找私有属性
if (k in O) {
let kValue = O[k];
// 依次传入this, 当前项,当前索引,整个数组
let mappedValue = callbackfn.call(T, KValue, k, O);
A[k] = mappedValue;
}
}
return A;
}length >>> 0, 字面意思是指"右移 0 位",但实际上是把前面的空位用0填充,这里的作用是保证len为数字且为整数。
V8源码
function ArrayMap(f, receiver) {
CHECK_OBJECT_COERCIBLE(this, "Array.prototype.map");
// Pull out the length so that modifications to the length in the
// loop will not affect the looping and side effects are visible.
var array = TO_OBJECT(this);
var length = TO_LENGTH(array.length);
if (!IS_CALLABLE(f)) throw %make_type_error(kCalledNonCallable, f);
var result = ArraySpeciesCreate(array, length);
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (i in array) {
var element = array[i];
%CreateDataProperty(result, i, %_Call(f, receiver, element, i, array));
}
}
return result;
}数组reduce实现
arr.reduce(callback(accumulator, currentValue,currentIndex, array)[, initialValue])
如果没有提供initialValue,reduce 会从索引1的地方开始执行 callback 方法,跳过第一个索引。如果提供initialValue,从索引0开始。
如果数组为空且没有提供initialValue,会抛出TypeError 。如果数组仅有一个元素(无论位置如何)并且没有提供initialValue, 或者有提供initialValue但是数组为空,那么此唯一值将被返回并且callback不会被执行。
// 实现reduce
// prev, next, currentIndex, array
Array.prototype.myReduce = function (cb, prev) {
let i = 0
if (!prev) {
prev = prev || this[0]
i++
}
for (; i < this.length; i++) {
prev = cb(prev, this[i], i, this)
}
return prev
}
// 测试
const sum = [1, 2, 3].myReduce((prev, next) => {
return prev + next
})
console.log(sum) // 6
function unique(arr) {
return arr.myReduce((prev, cur) => prev.includes(cur) ? prev : [...prev, cur], [])
}
const arr2 = [1, 1, 'true', 'true', true, true, 15, 15, false, false, undefined, undefined, null, null, NaN, NaN, 'NaN', 0, 0, 'a', 'a', {}, {}]
console.log(unique(arr2))
Array.prototype.reduce = function(callbackfn, initialValue) {
// 异常处理,和 map 一样
// 处理数组类型异常
if (this === null || this === undefined) {
throw new TypeError("Cannot read property 'reduce' of null or undefined");
}
// 处理回调类型异常
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(callbackfn) != "[object Function]") {
throw new TypeError(callbackfn + ' is not a function')
}
let O = Object(this);
let len = O.length >>> 0;
let k = 0;
let accumulator = initialValue;
if (accumulator === undefined) {
for(; k < len ; k++) {
// 查找原型链
if (k in O) {
accumulator = O[k];
k++;
break;
}
}
// 循环结束还没退出,就表示数组全为空
throw new Error('Each element of the array is empty');
}
for(;k < len; k++) {
if (k in O) {
// 注意,核心!
accumulator = callbackfn.call(undefined, accumulator, O[k], O);
}
}
return accumulator;
}V8源码
function ArrayReduce(callback, current) {
CHECK_OBJECT_COERCIBLE(this, "Array.prototype.reduce");
// Pull out the length so that modifications to the length in the
// loop will not affect the looping and side effects are visible.
var array = TO_OBJECT(this);
var length = TO_LENGTH(array.length);
return InnerArrayReduce(callback, current, array, length,
arguments.length);
}
function InnerArrayReduce(callback, current, array, length, argumentsLength) {
if (!IS_CALLABLE(callback)) {
throw %make_type_error(kCalledNonCallable, callback);
}
var i = 0;
find_initial: if (argumentsLength < 2) {
for (; i < length; i++) {
if (i in array) {
current = array[i++];
break find_initial;
}
}
throw %make_type_error(kReduceNoInitial);
}
for (; i < length; i++) {
if (i in array) {
var element = array[i];
current = callback(current, element, i, array);
}
}
return current;
}数组去重
- 1、使用set
function unique(array) {
return Array.from(new Set(array))
}- 2、利用for嵌套for,然后splice去重(ES5中最常用)
function unique(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[i] === array[j]) {
array.splice(j, 1)
j--
}
}
}
return array
}- 3、使用indexOf, push
function unique(array) {
const arr = []
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (arr.indexOf(array[i]) === -1) {
arr.push(array[i])
}
}
return arr
}取并集,交集,差集,子集
// 取并集
const arrayA = [1, 2, 3], arrayB = [2, 4, 3, 5]
function unionArray(arrayA, arrayB, compareFun = (a, b) => a === b) {
const result = [...arrayA]
arrayB.forEach(b => {
if (!result.find(a => compareFun(a, b))) result.push(b)
})
return result
}
// 简化写法
console.log([...new Set([...arrayA, ...arrayB])])
// 取交集
function intersectionArray(arrayA, arrayB, compareFun = (a, b) => a === b) {
return arrayA.filter(a => arrayB.find(b => compareFun(a, b)) !== undefined)
}
console.log(intersectionArray(arrayA, arrayB))
// 简化写法
const intersectionResult = [...new Set(arrayA.filter(v => new Set(arrayB).has(v)))]
console.log(intersectionResult)
// 取差集
function differenceArray(arrayA, arrayB, compareFun = (a, b) => a === b) {
return arrayA.filter(a => arrayB.find(b => compareFun(a, b))!== undefined)
}
console.log(differenceArray(arrayA, arrayB))
const differenceResult = [...new Set(arrayA.filter(v => !new Set(arrayB).has(v)))]
console.log(differenceResult)数组扁平化
// es5
let arr = [
[1, 2, 2],
[3, 4, 5, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10
]
function myFlatArray(array) {
const result = []
let cycleArray = (arr) => {
arr.forEach(v => {
if (Array.isArray(v)) {
cycleArray(v)
} else {
result.push(v)
}
})
}
cycleArray(array)
return result
}
function flatten(array) {
return array.reduce(
(target, current) =>
Array.isArray(current) ?
target.concat(flatten(current)) :
target.concat(current)
, [])
}
// reduce + concat + isArray + recursivity
// to enable deep level flatten use recursion with reduce and concat
function flatDeep(arr, d = 1) {
return d > 0 ? arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc.concat(Array.isArray(val) ? flatDeep(val, d - 1) : val), [])
: arr.slice();
};
flatDeep(arr, Infinity);
// Use Generator function
function* flatten2(array, depth) {
if(depth === undefined) {
depth = 1;
}
for(const item of array) {
if(Array.isArray(item) && depth > 0) {
yield* flatten2(item, depth - 1);
} else {
yield item;
}
}
}
const arr2 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]];
const flattened = [...flatten2(arr2, Infinity)];
let ary = [1, [2, [3, [4, 5]]], 6];// -> [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
let str = JSON.stringify(ary);
// 调用ES6中的flat方法
ary = arr.flat(Infinity);
// replace + split
ary = str.replace(/(\[|\])/g, '').split(',')使用堆栈stack
// 无递归数组扁平化,使用堆栈
// 注意:深度的控制比较低效,因为需要检查每一个值的深度
// 也可能在 shift / unshift 上进行 w/o 反转,但是末端的数组 OPs 更快
var arr1 = [1,2,3,[1,2,3,4, [2,3,4]]];
function flatten(input) {
const stack = [...input];
const res = [];
while (stack.length) {
// 使用 pop 从 stack 中取出并移除值
const next = stack.pop();
if (Array.isArray(next)) {
// 使用 push 送回内层数组中的元素,不会改动原始输入
stack.push(...next);
} else {
res.push(next);
}
}
// 反转恢复原数组的顺序
return res.reverse();
}
flatten(arr1);// [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4]数组操作
const array = [3, 2, 1, 4, 5]
// 最值
// reduce
array.reduce((c, n) => Math.max(c, n))
// Math.math
Math.max.apply(null, array)
Math.max(...array)
Array.prototype.reduceToMap = function (handler) {
return this.reduce((target, current, index) => {
target.push(handler.call(this, current, index))
return target
}, [])
}
Array.prototype.reduceToFilter = function (handler) {
return this.reduce((target, current, index) => {
if (handler.call(this, current, index)) {
target.push(current)
}
return target
}, [])
}
// 数组乱序
// 从最后一个元素开始,从数组中随机选出一个位置,交换,直到第一个元素。
function disorder(array) {
const length = array.length
let current = length - 1
let random
while (current > -1) {
random = Math.floor(length * Math.random());
[array[current], array[random]] = [array[random], array[current]]
current--
}
return array
}JSONP的实现
需要服务端配合,返回能执行回调函数的js
利用<script>标签没有跨域限制的“漏洞”来达到与第三方通讯的目的。 当需要通讯时,本站脚本创建一个<script>元素,地址指向第三方的API网址, 形如:<script src="http://www.example.net/api?param1=1¶m2=2"></script> 并提供一个回调函数来接收数据(函数名可约定,或通过地址参数传递)。
第三方产生的响应为json数据的包装(故称之为jsonp,即json padding), 形如:callback({"name":"hax","gender":"Male"})这样浏览器会调用callback函数,并传递解析后json对象作为参数。本站脚本可在callback函数里处理所传入的数据。
- 1.将传入的data数据转化为url字符串形式
- 2.处理url中的回调函数
- 3.创建一个script标签并插入到页面中
- 4.挂载回调函数
(function (window, document) {
'use strict'
var jsonp = function (url, data, callback) {
// 1.将传入的data数据转化为url字符串形式
// {id:1,name:'jack'} => id=1&name=jack
var dataStr = url.indexOf('?') === -1 ? '?' : '&'
for (var key in data) {
dataStr += key + '=' + data[key] + '&'
}
// 2 处理url中的回调函数
// cbFuncName回调函数的名字 :my_json_cb_名字的前缀 + 随机数(把小数点去掉)
var cbFuncName = 'my_json_cb_' + Math.random().toString().replace('.', '')
dataStr += 'callback=' + cbFuncName
// 3.创建一个script标签并插入到页面中
var scriptEle = document.createElement('script')
scriptEle.src = url + dataStr
// 4.挂载回调函数
window[cbFuncName] = function (data) {
callback(data)
// 处理完回调函数的数据之后,删除jsonp的script标签
document.body.removeChild(scriptEle)
}
document.body.appendChild(scriptEle)
}
window.$jsonp = jsonp
})(window, document)基于Promise封装Ajax
const getJSON = function(url) {
const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
const handler = function() {
if (this.readyState !== 4) {
return;
}
if (this.status === 200) {
resolve(this.response);
} else {
reject(new Error(this.statusText));
}
};
const client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("GET", url);
client.onreadystatechange = handler;
client.responseType = "json";
client.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json");
client.send();
});
return promise;
};
getJSON("/posts.json").then(function(json) {
console.log('Contents: ' + json);
}, function(error) {
console.error('出错了', error);
});
function ajax(method = 'get', url, params) {
return new Promise(((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
const paramString = getStringParam(params)
if (method === 'get' && paramString) {
url.indexOf('?') ? url += paramString : url += `?${paramString}`
}
xhr.open(method, url)
xhr.onload = function () {
const result = {
status: xhr.status,
statusText: xhr.statusText,
headers: xhr.getAllResponseHeaders(),
data: xhr.response || xhr.responseText
}
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
resolve(result)
} else {
reject(result)
}
}
// 设置请求头
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
// 跨域携带cookie
xhr.withCredentials = true
// 错误处理
xhr.onerror = function () {
reject(new TypeError('请求出错'))
}
xhr.timeout = function () {
reject(new TypeError('请求超时'))
}
xhr.onabort = function () {
reject(new TypeError('请求被终止'))
}
if (method === 'post') {
xhr.send(paramString)
} else {
xhr.send()
}
}))
}异步循环打印
const sleep = function (time, i) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve(i)
}, time)
})
}
const start = async function () {
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
let result = await sleep(1000, i)
console.log(result)
}
}
start()图片懒加载
监听图片高度
图片,用一个其他属性存储真正的图片地址:
<img src="loading.gif" data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2015/09/09/16/05/forest-931706_1280.jpg" alt="">
<img src="loading.gif" data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2014/08/01/00/08/pier-407252_1280.jpg" alt="">
<img src="loading.gif" data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2014/12/15/17/16/pier-569314_1280.jpg" alt="">
<img src="loading.gif" data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2010/12/13/10/09/abstract-2384_1280.jpg" alt="">
<img src="loading.gif" data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2015/10/24/11/09/drop-of-water-1004250_1280.jpg">通过图片offsetTop(元素距离页面顶部的高度)和window的innerHeight(页面可视高度),scrollTop(滚动高度)判断图片是否位于可视区域。
或者使用API Element.getBoundingClientRect()
var img = document.getElementsByTagName('img')
var n = 0 //存储图片加载到的位置,避免每次都从第一张图片开始遍历
lazyload() //页面载入完毕加载可是区域内的图片
// 节流函数,保证每200ms触发一次
function throttle(event, time) {
let timer = null
return function (...args) {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
event.apply(this, args)
}, time)
}
}
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', throttle(lazyload, 200))
function lazyload() { //监听页面滚动事件
var seeHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight //可见区域高度
var scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop //滚动条距离顶部高度 document.body.scrollTop兼容IE
for (var i = n; i < img.length; i++) {
console.log(img[i].offsetTop, seeHeight, scrollTop)
if (img[i].offsetTop < seeHeight + scrollTop) {
if (img[i].getAttribute('src') === 'loading.gif') {
img[i].src = img[i].getAttribute('data-src')
}
n = i + 1
}
}
}IntersectionObserver
IntersectionObserver接口 (从属于Intersection Observer API) 提供了一种异步观察目标元素与其祖先元素或顶级文档视窗(viewport)交叉状态的方法。祖先元素与视窗(viewport)被称为根(root)。
Intersection Observer可以不用监听scroll事件,做到元素一可见便调用回调,在回调里面我们来判断元素是否可见。
if (IntersectionObserver) {
let lazyImageObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach((entry, index) => {
let lazyImage = entry.target
// 如果元素可见
if (entry.intersectionRatio > 0) {
if (lazyImage.getAttribute('src') == 'loading.gif') {
lazyImage.src = lazyImage.getAttribute('data-src')
}
lazyImageObserver.unobserve(lazyImage)
}
})
})
for (let i = 0; i < img.length; i++) {
lazyImageObserver.observe(img[i])
}
}promise
promise 实现进度通知
class TrackAblePromise extends Promise {
constructor(executor){
const notifyHandlers = []
super((resolve, reject) => {
return executor(resolve, reject, (status) => {
notifyHandlers.map((handler) => handler(status))
})
})
this.notifyHandlers = notifyHandlers
}
notify (notifyHandler) {
this.notifyHandlers.push(notifyHandler)
return this
}
}
let p = new TrackAblePromise((resolve, reject, notify) => {
function countDown(x){
if (x > 0) {
notify(`${ 20 * x} % remaining`)
setTimeout(() => countDown(x - 1), 1000)
} else {
resolve()
}
}
countDown(5)
})
p.notify((x) => setTimeout(console.log, 0 , 'progress:', x))
p.then(() => console.log('completed'))手写promise
简单的promise
// 定义Promise的三种状态常量
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'
class MyPromise {
constructor (handle) {
if (typeof handle !== 'function') {
throw new Error('MyPromise must accept a function as a parameter')
}
// 添加状态
this._status = PENDING
// 添加状态
this._value = undefined
// 执行handle
try {
handle(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this))
} catch (err) {
this._reject(err)
}
}
// 添加resolve时执行的函数
_resolve (val) {
if (this._status !== PENDING) return
this._status = FULFILLED
this._value = val
}
// 添加reject时执行的函数
_reject (err) {
if (this._status !== PENDING) return
this._status = REJECTED
this._value = err
}
}面试版
- 没有实现then的透传
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'
class Promise {
constructor(executor){
if (typeof executor !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Promise must accept a function as a parameter')
}
this.status = PENDING
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
// 存放成功的回调
this.onResolvedCallbacks = []
// 存放失败的回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks = []
let resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = FULFILLED
this.value = value
// 依次将对应的函数执行
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())
}
}
let reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
// 依次将对应的函数执行
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
onRejected(this.reason)
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
// 如果promise的状态是 pending,需要将 onFulfilled 和 onRejected 函数存放起来,等待状态确定后,再依次将对应的函数执行
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
})
// 如果promise的状态是 pending,需要将 onFulfilled 和 onRejected 函数存放起来,等待状态确定后,再依次将对应的函数执行
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
onRejected(this.reason)
})
}
}
}function Promise(fn) {
this.cbs = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.data = value;
this.cbs.forEach((cb) => cb(value));
});
}
fn(resolve);
}
Promise.prototype.then = function (onResolved) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
this.cbs.push(() => {
const res = onResolved(this.data);
if (res instanceof Promise) {
res.then(resolve);
} else {
resolve(res);
}
});
});
};- promise.all
Promise.all = function(promiseArrays){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (!Array.isArray(promiseArrays)) {
const type = typeof promiseArrays
return reject(new TypeError(`TypeError: ${type} ${promiseArrays} is not iterable`))
}
const length = promiseArrays.length
let resultArr = []
let counter = 0
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Promise.resolve(promiseArrays[i])
.then(res => {
resultArr[i] = res
counter++
if(counter === length) resolve(resultArr)
})
.catch(err => {
reject(err)
})
}
})
}这个思路比较清晰,但没有通过官方872个测试用例
点击查看代码
// 定义Promise的三种状态常量
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'
class MyPromise {
constructor(handle){
if (typeof handle !== 'function') {
throw new Error('MyPromise must accept a function as a parameter')
}
// 添加状态
this._status = PENDING
this._value = undefined
// 添加成功回调函数队列
this._fulfilledQueues = []
// 添加失败回调函数队列
this._rejectedQueues = []
try {
handle(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this))
} catch (err) {
this._reject(err)
}
}
// 添加resolve时执行的函数
_resolve(val){
const run = () => {
if (this._status !== PENDING) return
// 依次执行成功队列中的函数,并清空队列
const runFulfilled = (value) => {
let cb
while (cb = this._fulfilledQueues.shift()) {
cb(value)
}
}
// 依次执行失败队列中的函数,并清空队列
const runRejected = (error) => {
let cb
while (cb = this._rejectedQueues.shift()) {
cb(error)
}
}
/* 如果resolve的参数为Promise对象,则必须等待该Promise对象状态改变后,
当前Promise的状态才会改变,且状态取决于参数Promise对象的状态
*/
if (val instanceof MyPromise) {
val.then(value => {
this._value = value
this._status = FULFILLED
runFulfilled(value)
}, err => {
this._value = err
this._status = REJECTED
runRejected(err)
})
} else {
this._value = val
this._status = FULFILLED
runFulfilled(val)
}
}
// 为了支持同步的Promise,这里采用异步调用
// js执行顺序是同步任务-微任务-宏任务,链式调用的时候是同步的,这样可以保证同步任务是优先执行完的
setTimeout(run, 0)
}
// 添加reject时执行的函数
_reject(err){
if (this._status !== PENDING) return
// 依次执行失败队列中的函数,并清空队列
const run = () => {
this._status = REJECTED
this._value = err
let cb
while (cb = this._rejectedQueues.shift()) {
cb(err)
}
}
// 为了支持同步的Promise,这里采用异步调用
setTimeout(run, 0)
}
// 添加then方法
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
const { _value, _status } = this
// 返回一个新的Promise对象
return new MyPromise((onFulfilledNext, onRejectedNext) => {
// 封装一个成功时执行的函数
let fulfilled = value => {
try {
if (!(typeof onFulfilled === 'function')) {
onFulfilledNext(value)
} else {
let res = onFulfilled(value)
if (res instanceof MyPromise) {
// 如果当前回调函数返回MyPromise对象,必须等待其状态改变后在执行下一个回调
res.then(onFulfilledNext, onRejectedNext)
} else {
//否则会将返回结果直接作为参数,传入下一个then的回调函数,并立即执行下一个then的回调函数
onFulfilledNext(res)
}
}
} catch (err) {
// 如果函数执行出错,新的Promise对象的状态为失败
onRejectedNext(err)
}
}
// 封装一个失败时执行的函数
let rejected = error => {
try {
if (!(typeof onRejected === 'function')) {
onRejectedNext(error)
} else {
let res = onRejected(error)
if (res instanceof MyPromise) {
// 如果当前回调函数返回MyPromise对象,必须等待其状态改变后在执行下一个回调
res.then(onFulfilledNext, onRejectedNext)
} else {
//否则会将返回结果直接作为参数,传入下一个then的回调函数,并立即执行下一个then的回调函数
onFulfilledNext(res)
}
}
} catch (err) {
// 如果函数执行出错,新的Promise对象的状态为失败
onRejectedNext(err)
}
}
switch (_status) {
// 当状态为pending时,将then方法回调函数加入执行队列等待执行
case PENDING:
this._fulfilledQueues.push(fulfilled)
this._rejectedQueues.push(rejected)
break
// 当状态已经改变时,立即执行对应的回调函数
case FULFILLED:
fulfilled(_value)
break
case REJECTED:
rejected(_value)
break
}
})
}
// 添加catch方法
catch(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected)
}
// 添加静态resolve方法
static resolve(value){
// 如果参数是MyPromise实例,直接返回这个实例
if (value instanceof MyPromise) return value
return new MyPromise(resolve => resolve(value))
}
// 添加静态reject方法
static reject(value){
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => reject(value))
}
// 添加静态all方法
static all(list){
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
/**
* 返回值的集合
*/
let values = []
let count = 0
for (let [i, p] of list.entries()) {
// 数组参数如果不是MyPromise实例,先调用MyPromise.resolve
this.resolve(p).then(res => {
values[i] = res
count++
// 所有状态都变成fulfilled时返回的MyPromise状态就变成fulfilled
if (count === list.length) resolve(values)
}, err => {
// 有一个被rejected时返回的MyPromise状态就变成rejected
reject(err)
})
}
})
}
// 添加静态race方法
static race(list){
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
for (let p of list) {
// 只要有一个实例率先改变状态,新的MyPromise的状态就跟着改变
this.resolve(p).then(res => {
resolve(res)
}, err => {
reject(err)
})
}
})
}
finally(cb){
return this.then(
value => MyPromise.resolve(cb()).then(() => value),
reason => MyPromise.resolve(cb()).then(() => {
throw reason
})
)
}
}点击查看代码
const isFunction = obj => typeof obj === 'function'
const isObject = obj => !!(obj && typeof obj === 'object')
const isThenable = obj => (isFunction(obj) || isObject(obj)) && 'then' in obj
const isPromise = promise => promise instanceof Promise
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
function Promise(f) {
this.result = null
this.state = PENDING
this.callbacks = []
let onFulfilled = value => transition(this, FULFILLED, value)
let onRejected = reason => transition(this, REJECTED, reason)
let ignore = false
let resolve = value => {
if (ignore) return
ignore = true
resolvePromise(this, value, onFulfilled, onRejected)
}
let reject = reason => {
if (ignore) return
ignore = true
onRejected(reason)
}
try {
f(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
Promise.prototype.then = function(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let callback = { onFulfilled, onRejected, resolve, reject }
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.callbacks.push(callback)
} else {
setTimeout(() => handleCallback(callback, this.state, this.result), 0)
}
})
}
Promise.prototype.catch = function(onRejected){
return this.then(null, onRejected)
}
Promise.resolve = value => new Promise(resolve => resolve(value))
Promise.reject = reason => new Promise((_, reject) => reject(reason))
const handleCallback = (callback, state, result) => {
let { onFulfilled, onRejected, resolve, reject } = callback
try {
if (state === FULFILLED) {
isFunction(onFulfilled) ? resolve(onFulfilled(result)) : resolve(result)
} else if (state === REJECTED) {
isFunction(onRejected) ? resolve(onRejected(result)) : reject(result)
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
const handleCallbacks = (callbacks, state, result) => {
while (callbacks.length) handleCallback(callbacks.shift(), state, result)
}
const transition = (promise, state, result) => {
if (promise.state !== PENDING) return
promise.state = state
promise.result = result
setTimeout(() => handleCallbacks(promise.callbacks, state, result), 0)
}
const resolvePromise = (promise, result, resolve, reject) => {
if (result === promise) {
let reason = new TypeError('Can not fufill promise with itself')
return reject(reason)
}
if (isPromise(result)) {
return result.then(resolve, reject)
}
if (isThenable(result)) {
try {
let then = result.then
if (isFunction(then)) {
return new Promise(then.bind(result)).then(resolve, reject)
}
} catch (error) {
return reject(error)
}
}
resolve(result)
}
module.exports = Promise
// promise 测试工具
// npm install promises-aplus-tests -D
Promise.defer = Promise.deferred = function () {
let deferred = {}
deferred.promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
deferred.resolve = resolve
deferred.reject = reject
})
return deferred
}async的实现
结合promise和generator,实现async函数
function getJSON(data) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(data)
}, 3000)
})
}
asyncRT(function* () {
try {
console.log('start')
console.time()
const result1 = yield getJSON('data/first.json')
const result2 = yield getJSON(result1.repeat(2))
const result3 = yield getJSON(result2.repeat(2))
console.log(result3)
console.timeEnd()
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
}
})
function asyncRT(generator) {
return new Promise(((resolve, reject) => {
// 创建一个迭代器
const gen = fn()
// generator执行顺序控制器
function next(...args){
const { done, value } = gen.next(...args)
if (done) return resolve(value)
// 如果是Promise则在then里执行next
/**
if (value instanceof Promise) {
value.then(res => next(res))
.catch(err => gen.throw(err))
} else next(value)
**/
// 使用Promise.resolve包裹不用判断
Promise.resolve(value)
.then(res => {
next(res)
})
.catch(e => gen.throw(e))
}
try {
next()
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
}))
}async 函数的实现原理,就是将 Generator 函数和自动执行器,包装在一个函数里。
async function fn(args) {
// ...
}
// 等同于
function fn(args) {
return spawn(function* () {
// ...
});
}所有的async函数都可以写成上面的第二种形式,其中的spawn函数就是自动执行器。
function spawn(genF) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
const gen = genF();
function step(nextF) {
let next;
try {
next = nextF();
} catch(e) {
return reject(e);
}
if(next.done) {
return resolve(next.value);
}
Promise.resolve(next.value).then(function(v) {
step(function() { return gen.next(v); });
}, function(e) {
step(function() { return gen.throw(e); });
});
}
step(function() { return gen.next(undefined); });
});
}
function timeout(ms) {
return new Promise((resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve,ms)
}))
}
async function asyncPrint(value, ms) {
await timeout(ms);
console.log(value);
}
function fn(value, ms) {
return spawn(function* () {
yield timeout(ms)
console.log(value);
});
}
// asyncPrint('hello world', 2000);
fn('hello world', 2000);version2
function myCo(gen) {
return new Promise(((resolve, reject) => {
function next(data) {
try {
var { value, done } = gen.next(data)
} catch (e) {
return reject(e)
}
if (!done) {
//done为true,表示迭代完成
//value 不一定是 Promise,可能是一个普通值。使用 Promise.resolve 进行包装。
Promise.resolve(value).then(val => {
next(val)
}, reject)
} else {
resolve(value)
}
}
next() //第一次调用next函数时,传递的参数无效
}))
}
function* test() {
yield new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 100)
})
yield new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// throw Error(1);
resolve(10)
})
yield 10
return 1000
}
myCo(test()).then(data => {
console.log(data) //输出1000
}).catch((err) => {
console.log('err: ', err)
})