React Around
redux
实现
// reducer.js 纯函数,计算出新的store
const initialState = {
count: 0
}
export function reducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'add':
return {
...state,
count: state.count + 1
}
case 'subtract':
return {
...state,
count: state.count - 1
}
default:
return initialState
}
}
type Actions = {
type: string
payload?: any
}
export const createStore = (
reducer: (state: any, action: Actions) => any,
heightener?: (any) => any
) => {
// heightener是一个高阶函数,用于增强createStore
//如果存在heightener,则执行增强后的createStore
if (heightener) {
return heightener(createStore)(reducer)
}
let currentState = {} // 公共状态
const observers = []
function getState() {
// getter
return currentState
}
function dispatch(action: Actions) {
// setter
currentState = reducer(currentState, action)
observers.forEach((fn) => fn())
}
function subscribe(fn) {
// 发布订阅
observers.push(fn)
}
dispatch({ type: '@@REDUX_INIT' }) //初始化store数据
return {
getState,
dispatch,
subscribe
}
}
const logger = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('logger1')
let result = next(action)
return result
}
const thunk = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('thunk')
const { dispatch, getState } = store
return typeof action === 'function'
? action(store.dispatch)
: next(action)
}
const logger2 = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log('log2')
let result = next(action)
return result
}
// 组合函数
function compose(...fns) {
if (fns.length === 0) return (arg) => arg
if (fns.length === 1) return fns[0]
return fns.reduce(
(res, cur) =>
(...args) =>
res(cur(...args))
)
}
const applyMiddleware =
(...middlewares) =>
(createStore) =>
(reducer) => {
const store = createStore(reducer)
let { getState, dispatch } = store
const params = {
getState,
dispatch: (action) => dispatch(action)
}
const middlewareArr = middlewares.map((middleware) =>
middleware(params)
)
dispatch = compose(...middlewareArr)(dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(logger, thunk, logger2))
export default function () {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<TestApp title="this is title props" />
</Provider>
)
}
// Provider.tsx
import React from 'react'
export const ReduxContext = React.createContext(null)
export function Provider(props) {
return (
<ReduxContext.Provider value={props.store}>
{props.children}
</ReduxContext.Provider>
)
}
// connect.tsx
import React, { useContext, useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react'
import { ReduxContext } from '@src/store/redux/Provider'
export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) {
return function (Component) {
return function Connect(props) {
const store = useContext(ReduxContext)
console.log(store)
const [state, setState] = useState(store.getState())
useEffect(() => {
console.log('useEffect running')
store.subscribe(() => {
// 根据mapStateToProps把state挂到this.props上
setState(mapStateToProps(store.getState()))
})
}, [])
return (
<Component
{...props}
{...state}
//{ ...mapStateToProps(store.getState()) }
// 根据mapDispatchToProps把dispatch(action)挂到this.props上
{...mapDispatchToProps(store.dispatch)}
/>
)
}
}
}
// 容器组件示例
const addCountAction = {
type: 'add'
}
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
count: state.count
}
}
function addCountActionAsync(dispatch) {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'add' })
}, 1000)
}
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => {
return {
addCount: () => {
dispatch(addCountAction)
},
addCountAsync: () => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(addCountActionAsync)
}, 1000)
}
}
}
function App(props) {
return (
<div>
<p>{props.title}</p>
<p>count: {props.count}</p>
<Divider />
<button onClick={() => props.addCount()}>add</button>
<Divider />
<button onClick={() => props.addCountAsync()}>addCountAsync</button>
</div>
)
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(App)react-redux 可以将 react 组件分为,展示组件和容器组件,容器组件的数据来源可以来自redux,修改视图可以使用 dispatch 向 redux 派发 action, 使用connect高阶组件完成connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(App),通过mapStateToProps函数,可以对全局状态进行过滤,而展示型组件不直接从global state获取数据,其数据来源于父组件。
本质上是利于了 React 的Context Api,可以跨组件通信,而connect就是获取context的值,通过 props 传给组件。而 react-redux 实现了发布订阅模式,在 dispatch 的时候,可以触发回调函数 的执行,所以只需要将更新 react 视图的方法添加到observers即可。
immutable.js
持久化数据结构和结构共享
Immutable Data是一种利用结构共享形成的持久化数据结构,一旦有部分被修改,那么将会返回一个全新的对象,并且原来相同的节点会直接共享。
每次修改一个 immutable 对象时都会创建一个新的不可变的对象,在新对象上操作并 不会影响到原对象的数据。
具体点来说,「immutable」 对象数据内部采用是多叉树的结构,凡是有节点被改变,那么它和与它相关的所有上级节点都更新。
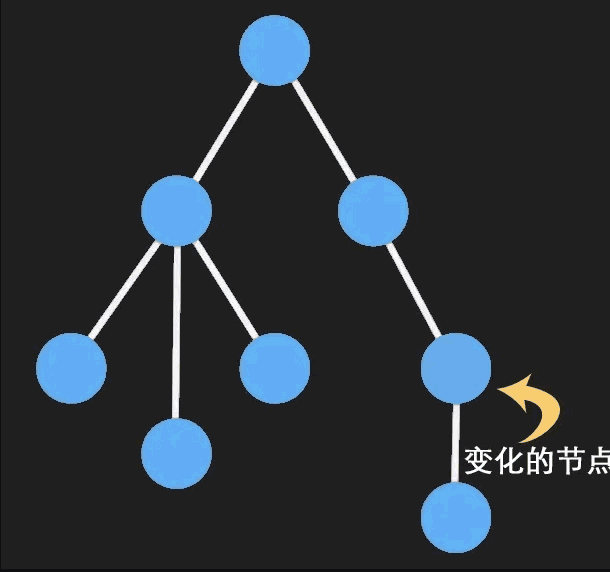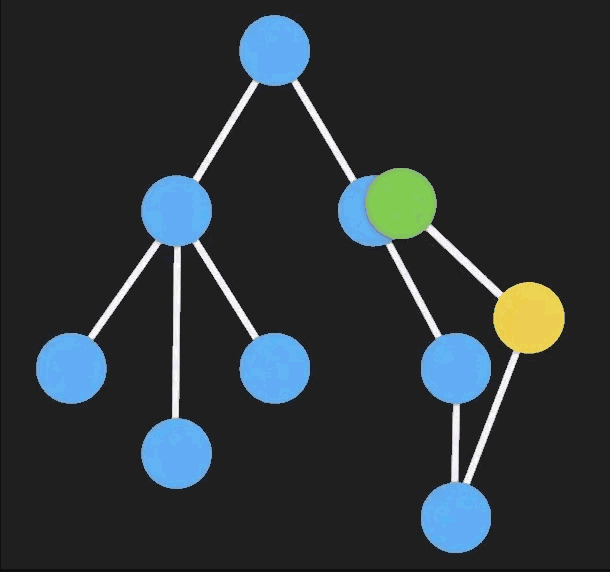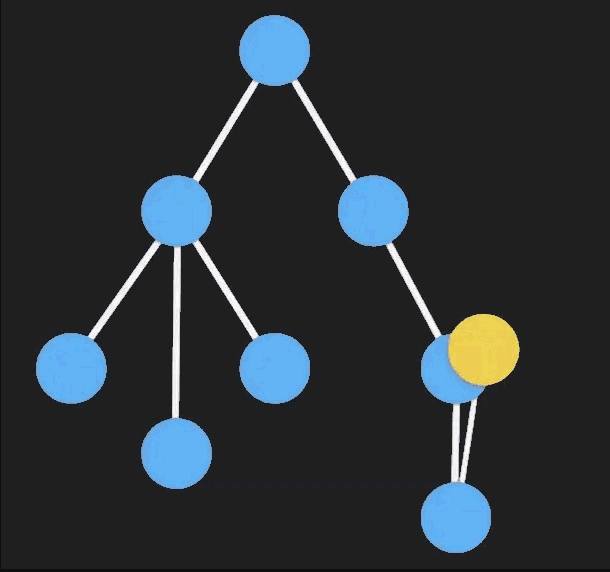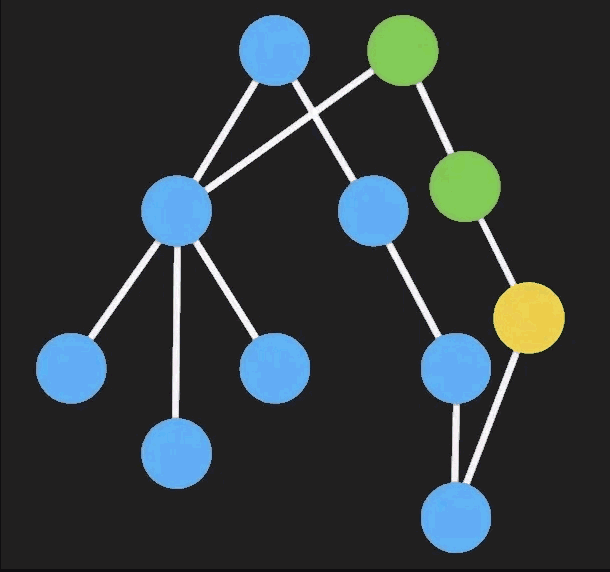
- Javascript 引用类型复用,不正确的操作导致复用前的数据也改变
- 使用深拷贝,有各种问题,比如性能,循环引用的处理,
key里面getter,setter以及原型链上的内容如何处理,React 使用时导致的不必要的重复渲染 - immutable: 创建一个被 deepClone 过的数据,新的数据进行有副作用 (side effect) 的操作都不会影响到之前的数据。其实就是创建全选的父引用,复用之前的引用类型,当对应的引用类型 的数据改变是,才创建新的复制。
即 2 个特点:
- 将所有的原生数据类型(Object, Array 等)都会转化成
immutable-js的内部对象(Map,List等),并且任何操作最终都会返回一个新的immutable的值。 - 在
immutable-js的数据结构中,深层次的对象 在没有修改的情况下仍然能够保证严格相等,即深层嵌套对象的结构共享
React Css 方案
- css modules
类似 Vue 的scoped,可以解决 CSS 变量名冲突
- css in js
写在 js 里,灵活,支持模板字符串,props 传参,很好的实现了作用域隔离。 但没有很难使用预处理器变量;另外代码冗余代码体积变大
1、样式写在 js 文件里,降低 js 对 css 文件的依赖。 2、样式可以使用变量,更加灵活。 3、使用方便,不需要配置 webpack、开箱即用。 4、SSR 类框架处理 CSS Modules 变量相当棘手,所以使用 styled-components 作方案
react 如何实现 keep-alive
什么是状态保存?
假设有下述场景:
移动端中,用户访问了一个列表页,上拉浏览列表页的过程中,随着滚动高度逐渐增加,数据也将采用触底分页加载的形式逐步增加,列表页浏览到某个位置,用户看到了感兴趣的项目,点击查看其详情,进入详情页,从详情页退回列表页时,需要停留在离开列表页时的浏览位置上
类似的数据或场景还有已填写但未提交的表单、管理系统中可切换和可关闭的功能标签等,这类数据随着用户交互逐渐变化或增长,这里理解为状态,在交互过程中,因为某些原因需要临时离开交互场景,则需要对状态进行保存
在 React 中,通常会使用路由去管理不同的页面,而在切换页面时,路由将会卸载掉未匹配的页面组件,所以上述列表页例子中,当用户从详情页退回列表页时,会回到列表页顶部,因为列表页组件被路由卸载后重建了,状态被丢失
解决方式
手动保存状态
手动保存状态,是比较常见的解决方式,可以配合 React 组件的 componentWillUnmount 生命周期通过 redux 之类的状态管理层对数据进行保存,通过 componentDidMount 周期进行数据恢复
在需要保存的状态较少时,这种方式可以比较快地实现所需功能,但在数据量大或者情况多变时,手动保存状态就会变成一件麻烦事。
通过路由实现自动状态保存(通常使用 react-router)
- 重写
<Route>组件,可参考react-live-route
重写可以实现想要的功能,但成本也比较高,需要注意对原始 <Route> 功能的保存,以及多个 react-router 版本的兼容
- 重写路由库,可参考react-keeper
重写路由库成本是一般开发者无法承受的,且完全替换掉路由方案是一个风险较大的事情,需要较为慎重地考虑
基于
<Route>组件现有行为做拓展,可参考react-router-cache-route
由于 React 会卸载掉处于固有组件层级内的组件,所以需要将 <KeepAlive> 中的组件,也就是其 children 属性抽取出来,渲染到一个不会被卸载的组件<Keeper>内,再使用 DOM 操作将 <Keeper> 内的真实内容移入对应 <KeepAlive>
点击查看代码
import React, {
createContext,
useState,
useEffect,
useRef,
useContext,
useMemo
} from 'react'
const Context = createContext(null)
interface KeepState {
id: {
id: string
children: React.ReactChildren
}
}
export function AliveScope(props) {
const [state, setState] = useState<KeepState | {}>({})
const ref = useMemo(() => {
return {}
}, [])
const keep = useMemo(() => {
return (id, children) =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
setState({
[id]: { id, children }
})
setTimeout(() => {
//需要等待setState渲染完拿到实例返回给子组件。
resolve(ref[id])
})
})
}, [ref])
return (
<Context.Provider value={keep}>
{props.children}
{Object.values(state).map(({ id, children }) => (
<div
key={id}
ref={(node) => {
ref[id] = node
}}
>
{children}
</div>
))}
</Context.Provider>
)
}
function KeepAlive(props) {
const keep = useContext(Context)
useEffect(() => {
const init = async ({ id, children }) => {
const realContent = await keep(id, children)
if (ref.current) {
ref.current.appendChild(realContent)
}
}
init(props)
}, [props, keep])
const ref = useRef(null)
return <div ref={ref} />
}
export default KeepAlive使用
点击查看代码
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import KeepAlive, { AliveScope } from './Keep-Alive'
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<div>
count: {count}
<button onClick={() => setCount((count) => count + 1)}>add</button>
</div>
)
}
function App() {
const [show, setShow] = useState(true)
return (
<AliveScope>
<div>
<button onClick={() => setShow((show) => !show)}>Toggle</button>
<p>无 KeepAlive</p>
{show && <Counter />}
<p>有 KeepAlive</p>
{show && (
<KeepAlive id="Test">
<Counter />
</KeepAlive>
)}
<hr />
{show && (
<KeepAlive id="Test2">
<Counter />
</KeepAlive>
)}
</div>
</AliveScope>
)
}
export default App