构建你自己的 React 框架
我们将从头开始,遵循真实的 React 源码架构,排除掉所有的优化和非必要的功能。一步一步地重新构建我们自己版本的 React。
这篇文章与你所阅读过其他相同主题的文章最大不同是基于 React 16.8 版本,因此我们可以使用钩子,并且删除所有与类相关的代码。
开始我们的教程之前,明确以下内容将是我们自己版本 React 的所有内容:
- createElement():创建节点对象
- render():渲染节点对象到 DOM
- Concurrent Mode:实现 JS 任务和 GUI 任务平衡
- Fibers:构建虚拟 DOM 对象
- Render and Commit Phases:收集变更,提交整体
- Reconciliation:处理变更收集
- Function Component:实现函数式组件
- Hooks:实现 useState 钩子
- 回顾
首先让我们回顾一些 React 相关的基础概念,如果你已经非常熟悉 React、JSX 和 DOM 元素的工作原理,你可以跳过此步骤。
const element = <h1 title="foo">Hello</h1>;
const container = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(element, container);最简单的 React 应用仅仅只需三行代码:第一行定义一个 React 节点元素,第二行从 DOM 中获取一个节点作为容器,最后一行调用 render 函数渲染 React 节点元素到容器中。
现在让我们删除所有 React 特殊语法(JSX)的代码,用原生 JavaScript 代码代替。
第一行代码定义一个节点元素使用到了 JSX 语法,它不是合法的 JavaScript 代码,让我们用原生语法替换它。
JSX 语法是通过 Babel 等构建工具在编译时转换为 JavaScript 的,它的转换过程十分简单:将标签替换为 createElement 的函数,依次传递参数标签名、标签属性和所有子节点,子节点转换过程递归进行。
这也是为什么用到 jsx 语法需要引入
import React from 'react'的原因。
const element = <h1 title="foo">Hello</h1>;
// 编译后
const element = React.createElement("h1", { title: "foo" }, "Hello");React.createElement 使用传递的参数创建一个对象,处理一些验证之外,没有其他额外功能。因此我们也可以将函数调用替换为其输出结果。
const element = React.createElement("h1", { title: "foo" }, "Hello");
// 替换后
const element = {
type: "h1",
props: {
title: "foo",
children: "Hello",
},
};所以一个 React 节点元素可以被简单描述为:一个具有两个属性 type 和 props 的对象(当然,它有更多的属性,但是我们只关心这两个)。
- createElement():创建节点对象
现在我们来自己实现创建节点对象的过程,就从替换 React.createElement 开始。
从 JSX 到 JS 的转换过程中,编译之后的代码调用的 createElement 函数,上一节中说明了一个节点会被描述为具有两个属性 type 和 props 的对象。所以函数唯一需要做的就是通过参数构造一个对象:
function createElement(type, props, ...children) {
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
children,
},
};
}children的类型可能会进一步嵌套,为了归一化处理,新增一个函数构造直接用于显示文本的节点
function createElement(type, props, ...children) {
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
// 思考:为什么不需要处理object类型的child?
children: children.map((child) =>
typeof child === "object" ? child : createTextElement(child)
),
},
};
}
function createTextElement(text) {
return {
type: "TEXT_ELEMENT",
props: {
nodeValue: text,
children: [],
},
};
}想要使用我们自己的函数处理 JSX,需要配置 tsconfig.json,如果有必要关闭一些检查。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"jsxFactory": "Didact.createElement"
}
}- render():渲染节点对象到 DOM
通过深度递归遍历 js 对象可以依次构造 dom 节点,最后挂载到根容器
function render(element, container) {
const dom =
element.type === "TEXT_ELEMENT"
? document.createTextNode("")
: document.createElement(element.type);
// 不为children的属性都复制到dom节点上
const isProperty = (key) => key !== "children";
Object.keys(element.props)
.filter(isProperty)
.forEach((name) => {
dom[name] = element.props[name];
});
// 递归构建dom树
element.props.children.forEach((child) => render(child, dom));
// 挂载到父节点
container.appendChild(dom);
}- Concurrent Mode:实现 JS 任务和 GUI 任务平衡
上一节的渲染方式有一个很大的问题:递归没法停止,一旦开始无法结束。如果元素树很大,它可能长时间阻塞主线程。如果浏览器需要做一些高优先级的事情,比如处理用户输入或者保持动画的平滑,它将不得不等待渲染完成。
所以我们将把工作分解成小单元,在我们完成每个单元后,如果有任何其他需要完成的事情,我们将让浏览器中断渲染。
我们使用 requestIdleCallback 来进行循环。你可以将 requestIdleCallback 看作是 setTimeout,但是我们不告诉它何时运行,浏览器将在主线程空闲时运行回调。
React 不使用 requestIdleCallback,它使用自己构建的 scheduler 库,但是概念上是相同的。
let nextUnitOfWork = null;
function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork && !shouldYield) {
// 执行单元任务
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
// 通过剩余时间判断是否需要立刻交还执行权
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1;
}
// 执行权交还给浏览器
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
function performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork) {
// TODO 处理单元任务
}- Fibers:构建虚拟 DOM 对象
在处理单元任务之前,我们需要明确如何切分任务。未优化之前一口气处理一整棵 dom 树,现在可以很自然地根据数据结构切分,我们将 dom 树每个节点的处理视为一个单元任务。对于每个节点的处理 React 构造了一个特殊的对象:Fiber,其实和我们之前了解的虚拟 dom 对象没什么不同。
下面我们开始讲解如何使用 Fiber 对象描述 dom 结构:
<div>
<h1>
<p />
<a />
</h1>
<h2 />
</div>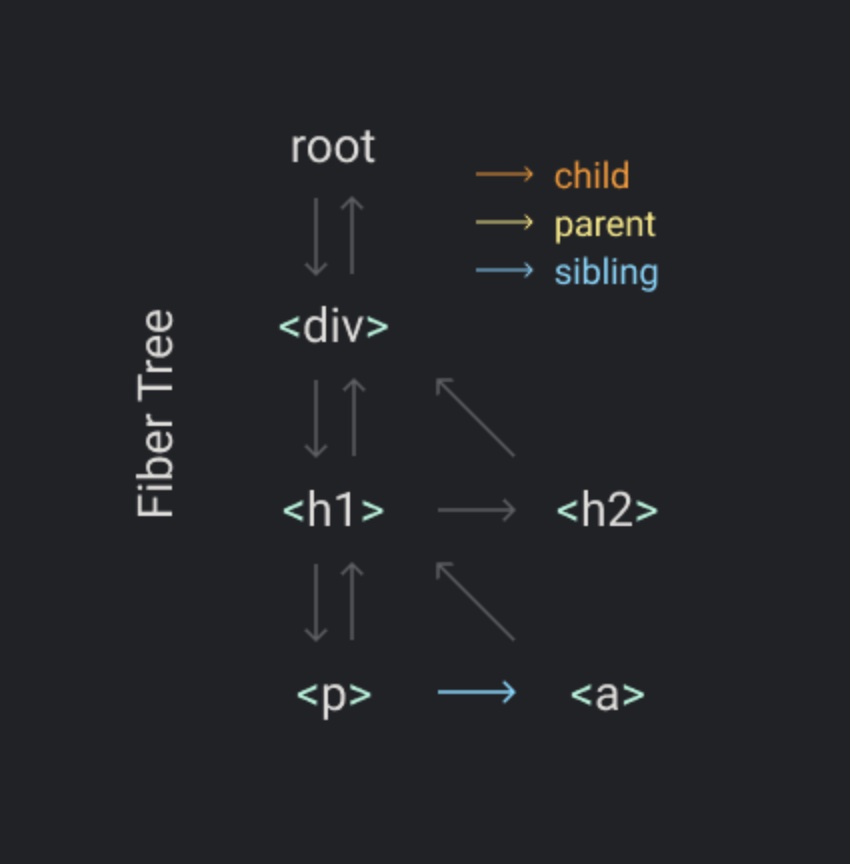
使用这样数据结构的目标之一是使查找下一个工作单元变得容易。 这就是为什么每个 Fiber 对象都链接到其第一个子节点,下一个兄弟节点和父节点。
在render函数中,我们会创建根 Fiber 然后设置其为第一个nextUnitOfWork,剩余任务将全部交给performUnitOfWork处理和 requestIdleCallback调度,对于每一个节点 Fiber,会做一下三件事情:
1. 添加节点元素到dom
2. 遍历节点的children属性创建Fiber对象
3. 设置一个Fiber对象作为下一个单元任务
当我们完成一个 Fiber 对象的工作后,如果它有 child,就把 child 构建为 Fiber 对象然后设置为下一个单元任务。
如果没有 child,就会使用此节点的 sibling 作为下一个目标
如果既没有 child 也没有 sibling,那么会回到父节点,如果父节点也没有 child 和 sibling,就会回到爷爷节点,依次类推。
回到代码,移除render函数的代码,将创建 dom 的逻辑拎出来
function createDom(fiber) {
const dom =
fiber.type == "TEXT_ELEMENT"
? document.createTextNode("")
: document.createElement(fiber.type)
const isProperty = key => key !== "children"
Object.keys(fiber.props)
.filter(isProperty)
.forEach(name => {
dom[name] = fiber.props[name]
})
return dom
}
function render(element, container) {}接着构造根 Fiber 对象作为第一个单元任务,然后准备处理任务
function render(element, container) {
nextUnitOfWork = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element],
},
};
}
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
// TODO 添加节点元素到dom
// TODO 遍历节点的children属性创建Fiber对象
// TODO 设置一个Fiber对象作为下一个单元任务
}最后依次实现 TODO 即可
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
// 添加节点元素到dom
// 如果没有dom属性,根据fiber新构建
if (!fiber.dom) {
fiber.dom = createDom(fiber);
}
// 如果存在父节点,将dom挂载
if (fiber.parent) {
fiber.parent.dom.appendChild(fiber.dom);
}
// 遍历节点的children属性创建Fiber对象
const elements = fiber.props.children;
let index = 0;
let prevSibling = null;
while (index < elements.length) {
const element = elements[index];
const newFiber = {
type: element.type,
props: element.props,
parent: fiber,
dom: null,
};
// 父fiber的child指向第一个子fiber
if (index === 0) {
fiber.child = newFiber;
} else {
// 如果存在兄弟节点,通过sibling关联
prevSibling.sibling = newFiber;
}
// 暂存上一个兄弟节点
prevSibling = newFiber;
index++;
}
// 设置一个Fiber对象作为下一个单元任务
// 优先使用父fiber的child
if (fiber.child) {
return fiber.child;
}
let nextFiber = fiber;
while (nextFiber) {
// 其次使用父fiber的sibling
if (nextFiber.sibling) {
return nextFiber.sibling;
}
// 如果没有回退到父节点的parent
nextFiber = nextFiber.parent;
}
}- Render and Commit Phases:收集变更,提交整体
运行一下看起来不错,但是仍然存在一个很大的问题:我们通过遍历 fiber 树的方式依次向 dom 上添加节点元素,运行过程依赖浏览器 API requestIdleCallback的调度,它不是同步的,一些优先级更高的任务可能会提前执行,从而阻塞或延迟我们的 dom 渲染,有可能会出现渲染不完整的 dom 情况。解决思路是把操作 dom 的逻辑和调度分离,从而同步完成 dom 的整体渲染。
首先移除操作 dom 的代码
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
// 移除dom操作
// if (fiber.parent) {
// fiber.parent.dom.appendChild(fiber.dom);
// }
}通过一个全局变量追踪正在处理的根 fiber
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element],
},
}
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot
}
let wipRoot = null在调度模块中,如果没有下一个单元任务且进行中的根节点存在,就提交整个 dom 树
function commitRoot() {
// 从根节点的child开始
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
// 完成后置空进行中根节点
wipRoot = null;
}
function commitWork(fiber) {
// child和sibling可能为undefined
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
const domParent = fiber.parent.dom;
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}
function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork && !shouldYield) {
// 执行单元任务
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
// 通过剩余时间判断是否需要立刻交还执行权
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1;
}
// 没有下一个单元任务且进行中的根节点存在
if (!nextUnitOfWork && wipRoot) {
commitRoot();
}
// 执行权交还给浏览器
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
}- Reconciliation:处理变更收集
目前为止,我们仅仅是添加节点,但是如何更新或删除节点呢?
将 render 函数接受的节点和最后一次构建的 fiber 树进行对比,以此来确定节点的添加、更新和删除。所以我们需要在每次提交渲染后保存刚构建的 fiber 树,并且为每个 fiber 对象添加一个额外属性用于链接旧的 fiber 对象(链接的对象总是 fiber 树同一个位置),通过这种方式复用对象。
额外创建一个 currentRoot 来保存刚渲染的 fiber 树根节点,并且把它和正在构建的 fiber 树根节点通过属性alternate链接
function commitRoot() {
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
currentRoot = wipRoot;
wipRoot = null;
}
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element],
},
alternate: currentRoot,
}
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot
}
let currentRoot = null然后让我们来重构performUnitOfWork的代码,新建一个reconcileChildren函数来调和变更,主要完成通过旧 fiber 构建新 fiber,提供标记以便提交阶段完成对应的 dom 操作。
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
if (!fiber.dom) {
fiber.dom = createDom(fiber)
}
const elements = fiber.props.children
reconcileChildren(fiber, elements)
if (fiber.child) {
return fiber.child
}
let nextFiber = fiber
while (nextFiber) {
if (nextFiber.sibling) {
return nextFiber.sibling
}
nextFiber = nextFiber.parent
}
}
function reconcileChildren(wipFiber, elements) {
// TODO 调和变更
}节点的变更先简单地分为三种情况:
1. 如果type相同,保留以前的dom,仅仅更新dom属性
2. 如果type不同,存在element,新建dom
3. 如果type不同,存在oldFiber,删除oldFiber的dom
function reconcileChildren(wipFiber, elements) {
let index = 0;
let oldFiber = wipFiber.alternate && wipFiber.alternate.child;
let prevSibling = null;
// TODO 思考:为什么不能用 oldFiber !== null
// oldFiber一直为undefined,会造成死循环
while (index < elements.length || oldFiber != null) {
const element = elements[index];
let newFiber = null;
const sameType = oldFiber && element && element.type == oldFiber.type;
// 更新
if (sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: oldFiber.type,
props: element.props,
dom: oldFiber.dom,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: oldFiber,
effectTag: "UPDATE",
};
}
// 重新创建
if (element && !sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: element.type,
props: element.props,
dom: null,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: null,
effectTag: "PLACEMENT",
};
}
// 删除
if (oldFiber && !sameType) {
oldFiber.effectTag = "DELETION";
deletions.push(oldFiber);
}
// 同时遍历旧fiber树
if (oldFiber) {
oldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
// 父fiber的child指向第一个子fiber
if (index === 0) {
wipFiber.child = newFiber;
} /* 当oldFiber != null时,需要判断element存在才设置sibling */ else if (
element
) {
// 如果存在兄弟节点,通过sibling关联
prevSibling.sibling = newFiber;
}
// 暂存上一个兄弟节点
prevSibling = newFiber;
index++;
}
}我们在newFiber上添加了effectTag来标记对应的 dom 操作,接下来会在 commit 阶段使用到。PLACEMENT对应新建 dom 节点;UPDATE对应更新节点属性;删除节点除了标记为DELETION,还需要特殊处理。因为无法通过newFiber节点访问到需要删除的节点,所以需要引入一个全局数组,暂存一下需要删除的节点,每次 render 之前置空:
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element],
},
alternate: currentRoot,
}
deletions = []
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot
}
let deletions = null修改 commit 节点代码,根据标记完成对应的 dom 操作
function commitRoot() {
// 优先进行删除操作
deletions.forEach(commitWork);
// 从根节点的child开始
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
// 保存刚构建的fiber树
currentRoot = wipRoot;
// 完成后置空进行中根节点
wipRoot = null;
}
function commitWork(fiber) {
// child和sibling可能为undefined
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
const domParent = fiber.parent.dom;
if (fiber.effectTag === "PLACEMENT" && fiber.dom != null) {
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "UPDATE" && fiber.dom != null) {
updateDom(fiber.dom, fiber.alternate.props, fiber.props);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "DELETION") {
domParent.removeChild(fiber.dom);
return;
}
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}抽离一个单独的方法updateDom更新 dom 属性
const isEvent = (key) => key.startsWith("on");
const isProperty = (key) => key !== "children" && !isEvent(key);
const isNew = (prev, next) => (key) => prev[key] !== next[key];
const isGone = (next) => (key) => !(key in next);
function updateDom(dom, prevProps, nextProps) {
// 移除旧事件
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter((key) => !(key in nextProps) || isNew(prevProps, nextProps)(key))
.forEach((name) => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.removeEventListener(eventType, prevProps[name]);
});
// 删除旧属性
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isGone(nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
dom[name] = "";
});
// 设置新属性
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
dom[name] = nextProps[name];
});
// 添加新事件
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.addEventListener(eventType, nextProps[name]);
});
}同样可以替换createDom中的 dom 操作,将prevProps设为空对象即可
function createDom(fiber) {
const dom =
fiber.type == "TEXT_ELEMENT"
? document.createTextNode("")
: document.createElement(fiber.type);
updateDom(dom, {}, fiber.props);
return dom;
}- Function Component:实现函数式组件
之前的章节全是围绕节点对象构建 Fiber 来渲染视图的,接下来就要为我们自己版本的 React 添加函数组件的支持。
const App = ({ name }) => {
return <div>Hi {name}</div>;
};
Didact.render(<App name="defpis" />, container);
// 编译后
const App = ({ name }) => {
return Didact.createElement("div", null, "Hi ", name);
};
const element = Didact.createElement(App, { name: "defpis" });函数组件和普通节点对象有两方面的不同
1. 函数组件的fiber没有dom属性
2. 函数组件的视图需要调用函数得到
因此在performUnitOfWork中分情况讨论
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
const isFunctionComponent = fiber.type instanceof Function;
if (isFunctionComponent) {
updateFunctionComponent(fiber);
} else {
updateHostComponent(fiber);
}
// ...
}
function updateFunctionComponent(fiber) {
// TODO 更新函数组件
}
function updateHostComponent(fiber) {
// 添加节点元素到dom
// 如果没有dom属性,根据fiber新构建
if (!fiber.dom) {
fiber.dom = createDom(fiber);
}
// 遍历节点的children属性创建Fiber对象
const elements = fiber.props.children;
// 调和fiber对象,设置状态:添加、更新和删除
reconcileChildren(fiber, elements);
}继续完善函数组件的更新逻辑,调用函数获取节点对象组成 children 即可
function updateFunctionComponent(fiber) {
const children = [fiber.type(fiber.props)];
reconcileChildren(fiber, children);
}但是reconcileChildren构建的 fiber 没有 dom 属性,所以 commit 阶段需要有所调整
function commitWork(fiber) {
// child和sibling可能为undefined
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
// 函数组件本身没有dom属性,需要向上寻找
let domParentFiber = fiber.parent;
while (!domParentFiber.dom) {
domParentFiber = domParentFiber.parent;
}
const domParent = domParentFiber.dom;
if (fiber.effectTag === "PLACEMENT" && fiber.dom != null) {
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "UPDATE" && fiber.dom != null) {
updateDom(fiber.dom, fiber.alternate.props, fiber.props);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "DELETION") {
commitDeletion(fiber, domParent);
return;
}
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}
function commitDeletion(fiber, domParent) {
// 找不到dom,继续向下寻找
if (fiber.dom) {
domParent.removeChild(fiber.dom);
} else {
commitDeletion(fiber.child, domParent);
}
}- Hooks:实现 useState 钩子
函数组件相较于类组件内部缺少存储状态的容器(class 的 this.state),因此需要引入 hook 实现视图和状态的关联。
还是从一个经典的例子计数器开始引出useState钩子
function Counter() {
const [state, setState] = Didact.useState(1);
return <button onClick={() => setState((c) => c + 1)}>Count: {state}</button>;
}
const element = <Counter />;
const container = document.getElementById("root");
Didact.render(element, container);引入全局变量来确定正在处理的 fiber 对象以及正在处理的 hook,每次更新函数组件前稍作处理
let wipFiber = null;
let hookIndex = null;
function updateFunctionComponent(fiber) {
wipFiber = fiber;
wipFiber.hooks = [];
hookIndex = 0;
const children = [fiber.type(fiber.props)];
reconcileChildren(fiber, children);
}在每次useState调用时通过旧的 fiber 对象很容易获取到之前的 hook 对象,把它的状态传递给新 fiber 的 hooks 数组,因此可以做到多次函数调用持久化状态。
function useState(initial) {
const oldHook =
wipFiber.alternate &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks[hookIndex];
const hook = {
state: oldHook ? oldHook.state : initial,
}
wipFiber.hooks.push(hook)
hookIndex++
return [hook.state]
}setState方法十分简单,在 hook 对象上维护一个队列,把回调函数都存放在里面,在下一次使用useState之前执行即可。为了保证setState会在之后生效,我们还需要将当前根 fiber 设置为下一次的单元任务。
function useState(initial) {
const oldHook =
wipFiber.alternate &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks[hookIndex];
const hook = {
state: oldHook ? oldHook.state : initial,
queue: [],
};
// 执行所有setState的回调函数
const actions = oldHook ? oldHook.queue : [];
actions.forEach((action) => {
hook.state = action(hook.state);
});
const setState = (action) => {
// 推入队列
hook.queue.push(action);
// 将下一次任务设为当前根fiber
wipRoot = {
dom: currentRoot.dom,
props: currentRoot.props,
alternate: currentRoot,
};
deletions = [];
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
};
wipFiber.hooks.push(hook);
hookIndex++;
return [hook.state, setState];
}运行代码,点击页面刷新,计数增加。
完整代码
import Didact from "./didact";
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = Didact.useState(0);
const [count2, setCount2] = Didact.useState(0);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setCount((c) => c + 1)}>Count: {count}</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount2((c) => c + 1)}>Count2: {count2}</button>
</div>
);
}
export default () => {
const container = document.getElementById("root");
Didact.render(<Counter />, container);
};const { requestIdleCallback } = window;
function createElement(type, props, ...children) {
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
children: children.map((child) =>
typeof child === "object" ? child : createTextElement(child)
),
},
};
}
function createTextElement(text: string) {
return {
type: "TEXT_ELEMENT",
props: {
nodeValue: text,
children: [],
},
};
}
function createDom(fiber) {
const dom =
fiber.type == "TEXT_ELEMENT"
? document.createTextNode("")
: document.createElement(fiber.type);
updateDom(dom, {}, fiber.props);
return dom;
}
const isEvent = (key) => key.startsWith("on");
const isProperty = (key) => key !== "children" && !isEvent(key);
const isNew = (prev, next) => (key) => prev[key] !== next[key];
const isGone = (next) => (key) => !(key in next);
function updateDom(dom, prevProps, nextProps) {
// 移除旧事件
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter((key) => !(key in nextProps) || isNew(prevProps, nextProps)(key))
.forEach((name) => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.removeEventListener(eventType, prevProps[name]);
});
// 删除旧属性
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isGone(nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
dom[name] = "";
});
// 设置新属性
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
dom[name] = nextProps[name];
});
// 添加新事件
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach((name) => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.addEventListener(eventType, nextProps[name]);
});
}
function commitRoot() {
// 优先进行删除操作
deletions.forEach(commitWork);
// 从根节点的child开始
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
// 保存刚构建的fiber树
currentRoot = wipRoot;
// 完成后置空进行中根节点
wipRoot = null;
}
function commitWork(fiber) {
// child和sibling可能为undefined
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
// 函数组件本身没有dom属性,需要向上寻找
let domParentFiber = fiber.parent;
while (!domParentFiber.dom) {
domParentFiber = domParentFiber.parent;
}
const domParent = domParentFiber.dom;
if (fiber.effectTag === "PLACEMENT" && fiber.dom != null) {
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "UPDATE" && fiber.dom != null) {
updateDom(fiber.dom, fiber.alternate.props, fiber.props);
}
if (fiber.effectTag === "DELETION") {
commitDeletion(fiber, domParent);
return;
}
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}
function commitDeletion(fiber, domParent) {
if (fiber.dom) {
domParent.removeChild(fiber.dom);
} else {
commitDeletion(fiber.child, domParent);
}
}
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element],
},
// 链接旧的fiber树
alternate: currentRoot,
};
// 需要删除的节点
deletions = [];
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
}
let nextUnitOfWork = null;
let currentRoot = null;
let wipRoot = null;
let deletions = null;
let wipFiber = null;
let hookIndex = null;
function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork && !shouldYield) {
// 执行单元任务
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
// 通过剩余时间判断是否需要立刻交还执行权
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1;
}
if (!nextUnitOfWork && wipRoot) {
commitRoot();
}
// 执行权交还给浏览器
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
const isFunctionComponent = fiber.type instanceof Function;
if (isFunctionComponent) {
updateFunctionComponent(fiber);
} else {
updateHostComponent(fiber);
}
// 设置一个Fiber对象作为下一个单元任务
// 优先使用父fiber的child
if (fiber.child) {
return fiber.child;
}
let nextFiber = fiber;
while (nextFiber) {
// 其次使用父fiber的sibling
if (nextFiber.sibling) {
return nextFiber.sibling;
}
// 如果没有回退到父节点的parent
nextFiber = nextFiber.parent;
}
}
function updateFunctionComponent(fiber) {
wipFiber = fiber;
wipFiber.hooks = [];
hookIndex = 0;
const children = [fiber.type(fiber.props)];
reconcileChildren(fiber, children);
}
function updateHostComponent(fiber) {
// 添加节点元素到dom
// 如果没有dom属性,根据fiber新构建
if (!fiber.dom) {
fiber.dom = createDom(fiber);
}
// 遍历节点的children属性创建Fiber对象
const elements = fiber.props.children;
// 调和fiber对象,设置状态:添加、更新和删除
reconcileChildren(fiber, elements);
}
/**
* 调和变更,生成最新的fiber树
* @param wipFiber 进行中的fiber节点对象
* @param elements 传入的jsx节点元素
*/
function reconcileChildren(wipFiber, elements) {
let index = 0;
let oldFiber = wipFiber.alternate && wipFiber.alternate.child;
let prevSibling = null;
// TODO 思考:为什么不能用 oldFiber !== null
// oldFiber一直为undefined,会造成死循环
while (index < elements.length || oldFiber != null) {
const element = elements[index];
let newFiber = null;
const sameType = oldFiber && element && element.type == oldFiber.type;
// 更新
if (sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: oldFiber.type,
props: element.props,
dom: oldFiber.dom,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: oldFiber,
effectTag: "UPDATE",
};
}
// 重新创建
if (element && !sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: element.type,
props: element.props,
dom: null,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: null,
effectTag: "PLACEMENT",
};
}
// 删除
if (oldFiber && !sameType) {
oldFiber.effectTag = "DELETION";
deletions.push(oldFiber);
}
// 同时遍历旧fiber树
if (oldFiber) {
oldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
// 父fiber的child指向第一个子fiber
if (index === 0) {
wipFiber.child = newFiber;
} /* 当oldFiber != null时,需要判断element存在才设置sibling */ else if (
element
) {
// 如果存在兄弟节点,通过sibling关联
prevSibling.sibling = newFiber;
}
// 暂存上一个兄弟节点
prevSibling = newFiber;
index++;
}
}
function useState(initial) {
const oldHook =
wipFiber.alternate &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks[hookIndex];
const hook = {
state: oldHook ? oldHook.state : initial,
queue: [],
};
const actions = oldHook ? oldHook.queue : [];
actions.forEach((action) => {
hook.state = action(hook.state);
});
const setState = (action) => {
hook.queue.push(action);
wipRoot = {
dom: currentRoot.dom,
props: currentRoot.props,
alternate: currentRoot,
};
deletions = [];
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
};
wipFiber.hooks.push(hook);
hookIndex++;
return [hook.state, setState];
}
const Didact = {
createElement,
render,
useState,
};
export default Didact;